This is an automatically translated article.
A kidney biopsy is taking a small sample of tissue from the kidney for testing. A kidney biopsy is done to diagnose and monitor certain kidney problems. For example, nephritis, or kidney cancer... classify and monitor some cases of kidney disease.1. What is a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy is a technique in which a doctor takes a sample of kidney tissue to examine under a microscope to identify signs of damage or disease.
Your doctor may order a kidney biopsy to diagnose a suspected kidney problem, to determine the severity of your kidney disease, or to monitor the outcome of your treatment. A kidney biopsy is also performed if, after kidney transplantation, the patient's kidney function is not satisfactory.
In most cases, the doctor performs a kidney biopsy using the percutaneous renal biopsy technique (the instrument used for the biopsy is a thin needle), and usually the technique is performed under the guidance of imaging. .
2. Why is a kidney biopsy necessary?
A kidney biopsy may be done for a number of reasons:
Need to diagnose a kidney problem that other methods do not give definitive results. Support the treatment plan based on the patient's kidney condition. Determine the rate of progression of kidney disease. Determine the extent of damage caused by kidney disease or other disease. Monitor and evaluate treatment results. Monitor the condition after kidney transplant, or find the cause of unsatisfactory transplant kidney function. The doctor may also order a kidney biopsy based on the results of a blood or urine test in the following cases:
Blood in the urine originates from the kidney. Protein in the urine is above the threshold, is elevated, or is associated with other signs of kidney disease. There is a problem with kidney function, leading to increased levels of substances that need to be eliminated in the blood. Not all cases of these symptoms require a kidney biopsy. Whether or not a kidney biopsy is indicated, the doctor will depend on the signs, symptoms, test results, and general condition of the patient.
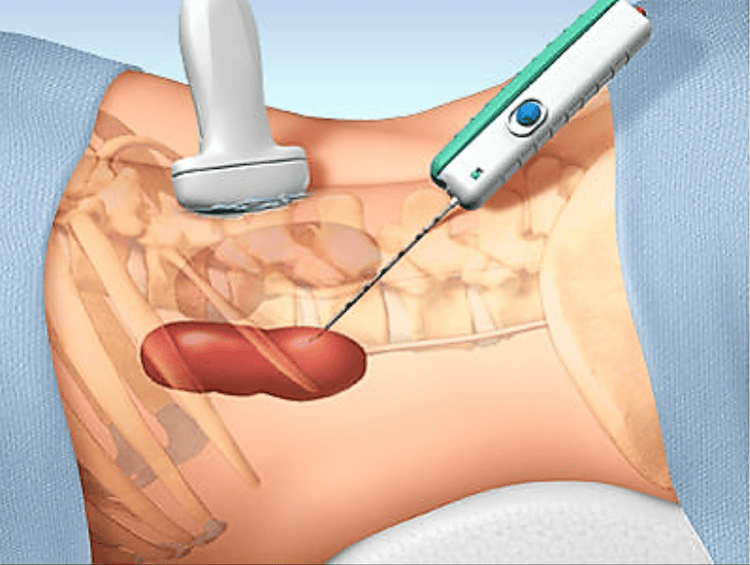
Tại sao cần thực hiện sinh thiết thận?
3. Possible risks of kidney biopsy
Usually a percutaneous kidney biopsy is a safe technique, but there can be risks, including:
Bleeding: The most common complication in a kidney biopsy is blood in the urine. The bleeding will usually stop after a few days. Rarely, bleeding is so severe that a blood transfusion is needed (only a very small percentage of all kidney biopsies). And very rarely, surgery is needed to stop the bleeding. Pain: Pain at the site of the puncture of the biopsy needle is common, but usually lasts only a few hours. Arteriovenous Catheterization: If the biopsy needle accidentally injures the wall of a nearby artery and vein, an abnormal bridge can form between the two vessels. This type of AVM is usually asymptomatic and will close on its own. Other complications: Hematoma in the kidney infected with bacteria. This complication can be resolved with the use of antibiotics and surgical drainage. Another uncommon complication is massive thrombosis-associated hypertension.
4. Kidney biopsy techniques
Percutaneous kidney biopsy is the most commonly used kidney biopsy technique, but it is not a technique that can be applied to all cases. If the patient has a history of coagulopathy, a history of bleeding, or a patient with only one kidney, the doctor will consider endoscopic biopsy.
Endoscopy biopsy is a biopsy technique in which the endoscopic doctor will observe the general shape of the kidney, as well as take a biopsy sample with an endoscope.
5. Prepare before conducting a kidney biopsy
Patients can consult their doctor about all their questions and concerns. The patient also needs to write a written consent to have a kidney biopsy done. Patients need to inform the doctor about all the drugs and supplements the patient is using, the doctor will have specific instructions for the patient. Before undergoing a kidney biopsy, the patient should have blood and urine tests done to make sure there is no infection or other abnormality that would put the biopsy at risk.
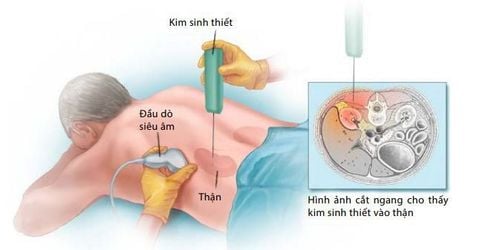
Sinh thiết thận cần được tiến hành tại các bệnh viện uy tín, có đầy đủ trang thiết bị hiện đại
6. After a kidney biopsy
After the kidney biopsy, the patient will:
Be monitored for blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate. Get a complete blood count and urine test to check for bleeding and other complications. Lie quietly for a few hours. Get specific instructions on care after a kidney biopsy. You will feel pain at the biopsy site for several hours and will be given pain medication. Most patients can go home the same day, but patients should stay in bed for 12 to 24 hours after the biopsy as recommended by their doctor.
Contact your doctor immediately if any of the following signs appear:
Urine is bright red, or has blood clots that persist for more than 24 hours after the biopsy. Unable to urinate. Pain at the biopsy site is getting worse. Fever above 380C. Very tired or want to pass out.
7. Kidney biopsy results
The tissue sample obtained from the biopsy will be sent for pathology. Results are usually returned in 7 days, but if there is an emergency, all or part of the results will be returned within 24 hours. When receiving the results, the doctor will discuss with the patient the current kidney condition, the cause of the abnormality, what to do about this case and agree with the patient on the optimal treatment plan.
It is best to choose large and reputable medical facilities not only in the general hospital system but also to stand out and take the lead in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment.
For detailed advice on kidney biopsy techniques at Vinmec, you can go directly to the Vinmec medical system nationwide or contact to book an online examination HERE.
Articles refer to sources: mayoclinic.org and stanfordhealthcare.org
SEE ALSO:
Some things to know about kidney transplant Vinmec launches post-transplant examination and follow-up service SUCCESSFULLY PATIENT HAS BEEN A 3rd Kidney Transplant AT VIETNAM