This is an automatically translated article.
Glioblastoma is a rather dangerous disease related to a woman's pregnancy, it is invasive and has the ability to secrete hCG (a hormone secreted by the placenta).1. Concepts
Trophoblast is a concept that refers to the abnormal development of trophoblasts arising from the placenta during pregnancy. Troblastoma is classified into two main types: oocyte (with a tendency to malignancy) and glioblastoma.
Gostroblastoma is a malignant disease with invasive features and the ability to secrete hCG (a hormone secreted by the placenta). Types of glioblastoma include:
Existing glioblastoma: This is considered stage I of glioblastoma when the disease occurs in the uterus. Invasive ectopic pregnancy: The trophoblast invades the uterus, causing the ovum to perforate and bleed. Invasive ovum also has cancerous properties and can metastasize to distant sites. Placental trophoblastic neoplasms: The trophoblastic mediators attack starting in the placental (vegetable) area that attaches to the inside of the uterus. Glioblastoma: When glioblastoma has spread to the vagina or lungs, followed by other severe symptoms, it is considered cancer.
2. Causes and symptoms
Origin of trophoblastic neoplasms can be related to miscarriage or abortion and especially ovum. Up to 70% of trophoblastic neoplasms appear on pathology after about 4 months of total egg curettage. But until now, medical experts have not yet determined what the cause of glioblastoma is.
Factors such as: taking oral contraceptives; smoking habits; exposure to certain chemicals or viruses; The number of births, the age of the fetus, or the mother's blood type had no effect on the risk of disease.
Common signs of trophoblastic neoplasia are:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding not due to menstruation Large, soft, elastic uterus Gynecological examination shows enlarged thyroid cyst causing compression If the patient is pregnant with oocytes, when having glioblastoma, the oocyte is difficult to recover and does not show signs of stopping proliferation after 4 weeks. Beta hCG and through specialist examination.
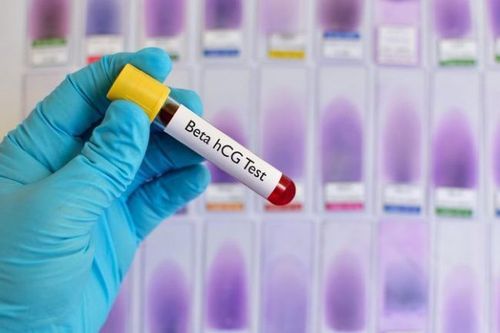
Nồng độ Beta hCG là chỉ số quan trọng để chẩn đoán bệnh u nguyên bào nuôi
3. Subjects susceptible to glioblastoma
Subjects susceptible to trophoblastic neoplasms are pregnant women or of reproductive age who have been pregnant. Glioblastoma is more common in women with low living standards and difficult economic conditions than in developed countries. The older a woman is, the higher the risk of this disease.
The method of diagnosis and treatment of glioblastoma is quite complicated, requiring high expertise from a team of experienced medical staff. Women who detect the disease at an early stage have a better chance of being cured and cured. In other cases, it is necessary to be closely monitored and follow the doctor's treatment regimen.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.