This is an automatically translated article.
Renal cell carcinoma is one of the most common types of urinary tract cancer, often seen in people over the age of 50. This is a dangerous cancer that can cause serious complications for the patient, even lead to death if not treated promptly.
1. What is renal cell carcinoma?
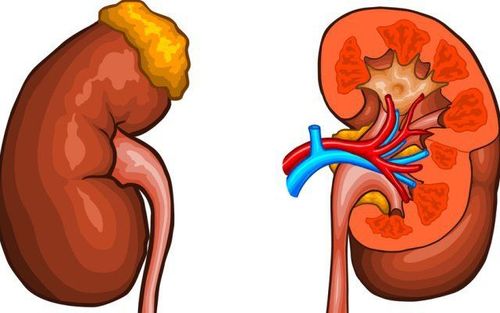
In the human body, the kidney is an extremely important organ, with the main role in filtering blood and creating urine, helping the body eliminate waste products outside. The kidneys usually have two organs located just behind the abdominal organs, one on each side of the spine.
Renal cell carcinoma (also called renal cell cancer) occurs when a tumor develops in the kidney. Tumors can be found on the same side of the kidney or even on both sides. Most people with renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between the ages of 50 and 70.
With renal cell carcinoma, the tumor gradually grows and proliferates, causes pressure on other tissues in the kidney and disrupts the main functions of the kidneys, making it difficult for the body to eliminate waste products. Cancer is often detected at a late stage, so definitive treatment for this disease is extremely difficult and has a very high mortality rate.
Main stages of renal cell carcinoma
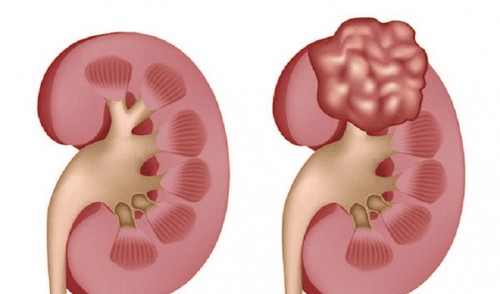
Hình ảnh ung thư biểu mô tế bào thận
Renal cell carcinoma usually has 4 main stages:
*Stage I: The tumor begins to form inside the kidney. At this time, the tumor is very small in size and difficult to detect through conventional diagnosis (such as ultrasound). This is the localized stage of the cancer, meaning the cancer has not spread to other areas. *Stage II: The cancerous tumor is gradually growing and is larger than 7cm. Cancer has not yet spread to other organs of the body. * Stage III: The tumor has spread to regional lymph nodes, or has gone deep into the main vein and surrounding tissues. However, it has not yet spread to organs outside the kidney. * Stage IV: This is the final stage of renal cell carcinoma and also the most advanced stage of the disease. At this point, the tumor has invaded the adrenal gland, lymph nodes, or metastasized to any other part of the body (eg, bones, lungs, or brain).
2. Causes of renal cell carcinoma
Currently, medicine has not made an exact conclusion about the cause of renal cell carcinoma. Research results show that most kidney cancers are caused by problems with genes in the kidneys. A mutation in the DNA of kidney cells causes them to grow and divide rapidly. The abnormal cells that accumulate to form a tumor can extend beyond the kidney, or break off and spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
Although there is no exact cause of the disease, researchers have identified high-risk factors for renal cell carcinoma. Specifically:
Elderly: The risk of renal cell carcinoma increases with increasing age. Smoking: In cigarettes containing nicotine - an extremely dangerous substance that can disrupt or destroy the body's cell regeneration process, leading to a high risk of cancer. including renal cell carcinoma.

Hút thuốc lá có thể gây ung thư biểu mô tế bào thận
3. Signs and symptoms of renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma rarely shows signs or symptoms in its early stages. Besides, at present, conventional tests used in screening for kidney cancer are also difficult to detect cancer in cases where there are no specific symptoms, which can lead to confusion with kidney cancer. other urinary tract diseases. Until the later stage (advanced stage of the disease), the patient begins to show obvious symptoms, including:
Blood in urine: Blood in the urine appears. Blood is usually pink, red, or cola-colored. In some cases where it is difficult to detect the amount of red blood cells in the urine, you can find out through a urinalysis at the hospital. Hip and back pain: Renal cell carcinoma often causes dull and long-lasting pain in the hip or back area. The pain usually occurs in the flanks and spreads to the back.
Đau vùng hông và lưng là triệu chứng của ung thư biểu mô tế bào thận
Unexplained weight loss Fever Body weakness, fatigue Lightheadedness, dizziness Loss of appetite Severe anemia Night sweats High blood calcium levels High blood pressure

Người có huyết áp cao cần thận trọng
4. Methods of prevention of renal cell carcinoma
Proactively implementing health-promoting approaches can effectively prevent the risks of renal cell carcinoma. These measures include:
Quit smoking Limit the use of stimulants such as alcohol Maintain a reasonable weight Control high blood pressure with regular exercise Drink plenty of water Exercise a nutritious, healthy diet. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is applying cancer screening packages to detect the disease at an early stage, shorten the treatment time, reduce the economic burden and maximize the possibility of recovery for customers. .
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide to visit or book an appointment online HERE for support.
Reference sources: mayoclinic.org, webmd.com
SEE MORE
Kidney cancer: What you need to know Advances in the treatment of kidney cancer Laparoscopic surgery with Robotic support for kidney cancer treatment