This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs located in or on the surface of the ovary. Every woman has two ovaries and is at risk for ovarian cysts at some point in her life. However, compared with functional ovarian cysts, organic ovarian cysts are not changeable with the menstrual cycle and usually carry more risks.
1. What is an ovarian cyst?
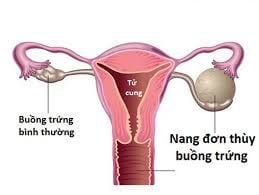
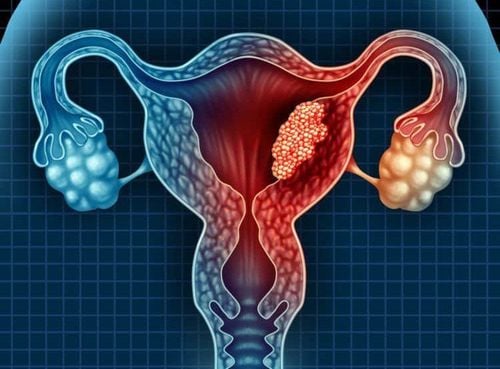
The ovaries are important organs of the female reproductive system, located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries have two main functions:Produce ovulation every 28 days as a pivotal part of the menstrual cycle Synthesize and release into the bloodstream the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, which play a role Regulate the menstrual cycle as well as during pregnancy Ovarian cysts are a common disease of the ovaries, which can affect one or both ovaries at the same time. Usually, ovarian cysts cause no symptoms. Accordingly, a woman may never be aware of the presence of ovarian cysts until they cause symptoms such as bloating, lower abdominal pain, abnormal bleeding, or an acute event such as a cyst. rupture or cause torsion or necrosis of the ovary.
2. What is a physical ovarian cyst?
All cases of ovarian cysts are divided into two broad groups:Functional ovarian cysts: which form as a normal part of the menstrual cycle, such as cystic or luteal cysts. These types of ovarian cysts will clear up on their own after one or several menstrual cycles without any specific intervention.
Physical ovarian cysts: are cysts that exist that have nothing to do with the menstrual cycle, including:
Dermoid cysts: also known as teratomas, the interior may contain tissue, such as hair, skin or teeth, as they form from embryonic cells. This type of cyst rarely turns cancerous.
Mucinous cyst: this type of lesion usually develops on the surface of the ovary and can be filled with mucus, is often large in size and has a very high risk of malignancy; Sometimes there can be metastasis from other primary foci, especially when it occurs on both ovaries.
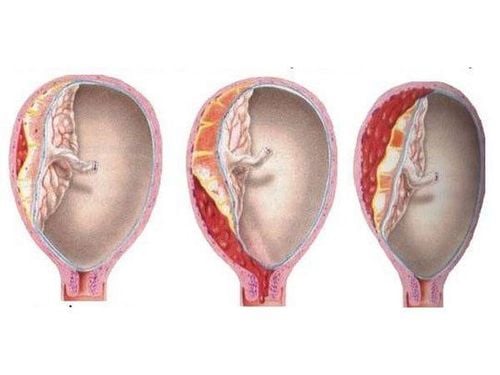
Endometriosis : develops due to a condition where endometrial cells are located outside the uterus. These cells are still under the influence of hormones according to the menstrual cycle, still have the phenomenon of proliferation and peeling but cannot escape; As a result, the tumor size will increase over time if it does not dissolve on its own.
In addition, organic ovarian cysts include less common forms such as hemorrhagic functional ovarian cysts, ovarian gland cysts,...
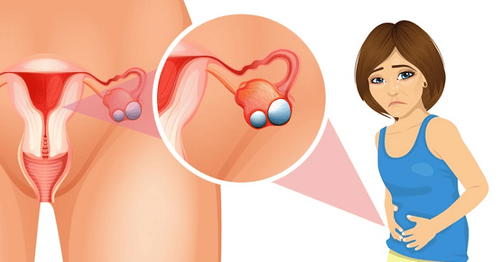
Abdominal pain : pain smoldering in the abdomen or pelvis, especially during intercourse. Feeling of fullness, heaviness in the abdomen, pressure or bloating. Abnormal vaginal bleeding: occurs during or shortly after the start or end of a menstrual period, bleeding during intercourse. Irregular menstruation . Disturbances in urination habits such as change in frequency or urge to urinate, inability to empty the bladder completely, or difficulty having a bowel movement due to the pressure of a cyst in the adjacent pelvis. The above symptoms usually occur for a long time until the woman goes to the doctor or sometimes the patient is hospitalized in the acute setting due to complications of ovarian cysts:
Cyst rupture: Cyst cyst A ruptured ovary often causes sudden, intense abdominal pain. If a large ovarian cyst ruptures, it can cause bleeding inside the abdominal cavity and in some cases can cause shock and collapse due to blood loss. Ovarian torsion, necrosis: Large ovarian cysts increase the risk of ovarian torsion, which can interfere with blood flow and lead to ovarian necrosis.
4. How is a physical ovarian cyst diagnosed?
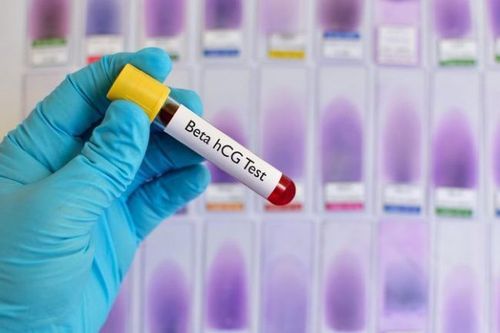
Most women with organic ovarian cysts can be diagnosed with a pelvic exam and the necessary tests to determine the nature of the cyst and guide treatment:Pregnancy test: Results A positive test result may suggest that the patient has a corpus luteum cyst rather than a physical ovarian cyst Pelvic ultrasound : A device with a transducer that emits and receives high-frequency sound waves through the vagina to produces a clear image of the uterus and ovaries on the screen. Thereby, the doctor analyzes the images to classify the cyst, based on the size and density inside the tumor. For organic ovarian cysts, the density is usually dense with thick echogenicity, uniformity, or heterogeneity; In contrast to a functional ovarian cyst, on ultrasound is an empty, homogenous mass. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): These are more advanced imaging modalities than ultrasound, with greater sensitivity and specificity in their ability to confirm organic ovarian cysts. or differential diagnosis with lesions from adjacent organs, especially in patients with a previous history. Laparoscopy: Using a laparoscope, inserted into the patient's abdomen through a small incision in the abdominal wall, the doctor can see lesions if any on the surface of the ovary, take a biopsy sample as well as remove the cyst if possible in one stroke. CA 125 blood test: Blood levels of a protein called cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) are often elevated in women with ovarian cancer in cases of organic ovarian cysts.
5. How are organic ovarian cysts treated?
The treatment of organic ovarian cyst depends on many different factors such as age, need for pregnancy, size of the organic ovarian cyst, and most importantly, the nature of the lesion through anatomy. . However, in most cases, surgery for ovarian cysts is usually the first choice. The entrance of surgery can be through endoscopic vaginal, endoscopic fall on the abdominal wall and open surgery if the size of the cyst is large and complicated. In some patients, especially women of childbearing age and planning a pregnancy, surgical manipulations should be performed more carefully than usual, both to preserve ovarian integrity and to maintain the integrity of the ovaries. Limit trauma, easily cause the risk of adhesions when healing scars, increase the possibility of infertility. In contrast, if the subject is a postmenopausal woman, especially for malignant lesions, the surgeon can remove both the uterus and appendages to radicalize.Treatment details for each type of organic ovarian cyst are as follows:
For dermoid cysts: radical surgical excision is the treatment of choice in most cases despite this type of lesion. No risk of cancer. For mucinous cysts: Surgery is always recommended in most cases of mucinous ovarian cysts because of the high risk of malignancy. Even better, laparotomy is needed to perform a total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and regional lymph node dissection for radical ablation in postmenopausal women who no longer wish to have more children. For endometrioma: there is also an indication for early surgical removal because delay will risk massive adnexal bleeding. Pay attention to remove endometriosis tissue to avoid the possibility of recurrence. For ovarian cancer: surgery is absolutely indicated in the early stages, removal of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes to radicalize as well as supplement chemotherapy - radiation therapy afterwards. However, when the disease is at a late stage, has distant metastases, and the patient's condition is poor, palliative care measures will be preferred. In summary, organic ovarian cysts include many different types of lesions with different pathophysiological nature. Either way, ovarian cysts - especially those that have ruptured - can cause serious symptoms. Therefore, the treatment attitude should be positive right from the time the disease is detected, but it is still best to have regular gynecological examinations for women to actively prevent diseases and protect health. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a basic gynecological examination and screening package, helping customers to detect early diseases of inflammatory diseases for easy and inexpensive treatment. Screening for early detection of gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) for female customers even if there are no symptoms or may have the following symptoms:
Female customers have several factors Risks such as poor personal hygiene, unsafe sex, abortion, ... Female customers have other symptoms such as: abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the intimate area, vaginal bleeding abnormal. Irregular bleeding in the vaginal area Menstrual problems: irregular periods, irregular periods Abnormal vaginal discharge (with a bad smell, a different color) Pain, itching in the vagina If needed consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: nhs.uk, mayoclinic.org