This is an automatically translated article.
Insulin is a very familiar substance, especially for people with diabetes or those who have a family member with diabetes. So what are the roles, side effects, and notes when using insulin according to the instructions of the Ministry of Health? Please refer to the following article.
1. What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the islet cells in the pancreas. They have the effect of metabolizing carbohydrates in the body. Insulin also works to convert fatty tissue and liver into ATP energy to supply the body's activities.
Insulin is synthesized in the beta cells of the pancreas by the action of the protein synthesis machinery in the cell. Insulin is also the only agent in the body that can lower blood glucose levels.
2. Role of Insulin
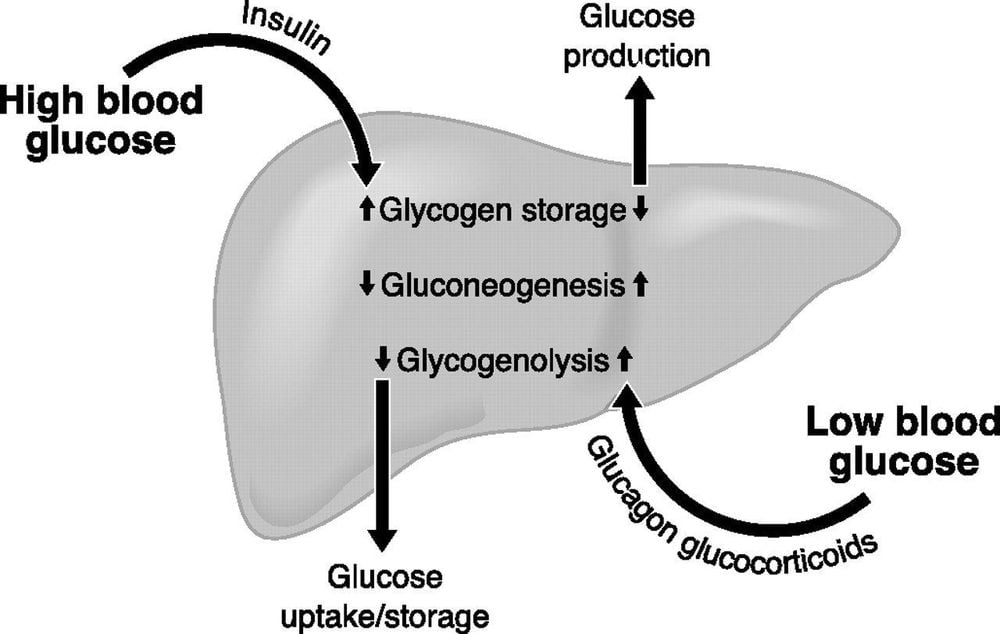
After we eat a meal, a fairly large amount of starch will enter the body, then they will increase the stimulation of beta cells in the pancreas to be able to secrete insulin. Then, insulin will affect the processes of keeping and storing glucose in the body and especially the liver and adipose tissue.
When your blood glucose level is high, glucose will be stored as glycogen and stored in the liver and when you are hungry, blood glucose levels drop, glycogen will be converted back into glucose to continue entering blood, ensure blood sugar level.
Role of Insulin:
Insulin inhibits the enzyme phosphorylase, which slows down the conversion of glycogen into glucose. Insulin enhances glucose absorption. Insulin enhances the activity of enzymes for glycogen synthesis. Insulin has a big effect on blood sugar levels. Diabetes is caused by high blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone that inhibits the conversion of glycogen into glucose and enters the blood, if there is a shortage of insulin, glycogen will not stop metabolizing and put an excess of glucose into the blood, causing diabetes.
Insulin trong cơ thể
3. Types of insulin and notes when using it
According to the guidance of the Ministry of Health, for people with diabetes, insulin is an important drug in the treatment of this disease. There are four main types of insulin: rapid and short acting insulin, intermediate acting insulin, intermediate acting insulin, slow acting insulin, long acting insulin and finally mixed and mixed insulin.
Rapid and short acting insulins are usually injected directly under the skin, the drug will dissociate rapidly into monomers and be absorbed. After about 1 hour, the drug will reach the peak of absorption. Due to the rapid action of this type of insulin, the patient needs to be very careful about the amount of carbohydrates in the meal.
For intermediate-acting insulin, the drug will have a longer-lasting effect thanks to the combination of 2 parts of insulin zinc soluble with protamine zinc Insulin. This drug, after being injected under the skin, begins to work after 2-4 hours, peaks after 6-7 hours and lasts about 10-20 hours. This drug needs to be injected twice a day to be effective.
Slow-acting and long-acting insulins are usually taken at night. This category also has a variety of medications that vary from patient to patient.
Mixed insulin is insulin that has 2 types of rapid-acting and long-acting insulin premixed in the same or the same injection. Therefore, the drug will have two peaks of action, one is the effect of rapid insulin on the amount of carbohydrates in the meal and the effect of long insulin to create basal insulin levels.
Không nên tự ý tiêm insulin
Some other important notes
Insulin is the most powerful blood sugar-lowering drug. There is no insulin dose limit. Insulin is given only under the skin, usually in the abdomen, upper arms, and thighs. Insulin is often used in combination with pills. Insulin is used for intravenous infusion in emergency cases of ketoacidosis, during surgery, or hyperosmolarity. Insulin-only therapy can be used for severe insulin deficiency. Premixed insulin can be administered twice a day, before breakfast and in the evening. Premixed analog insulin can be injected 3 times a day. For each patient with different medical conditions, the insulin dose can be adjusted every 3-4 times/day.
4. Insulin Side Effects
Insulin has typical side effects such as hypoglycemia, somogyi phenomenon, insulin allergy, adipose tissue dystrophy, weight gain. In particular, hypoglycemia is the most common side effect when using insulin injected directly into the body. When the amount of insulin is too much, it will also inhibit the metabolism of glycogen, causing the amount of glucose in the blood to drop sharply.
Somogyi phenomenon is the phenomenon of insulin overdose, leading to hypoglycemia and excessive release of counterregulatory hormones causing reactive hyperglycemia.
Other side effects such as insulin allergy are quite rare at the moment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.