This is an automatically translated article.
Estrogen is a hormone that plays an important role in maintaining a woman's beauty. The decline in this hormone can cause health, beauty and physiological problems.1. What is estrogen?
Hormones are chemical markers that tell how specific tissues are functioning.During puberty, the ovaries begin to secrete a limited amount of the hormone estrogen for each menstrual cycle. Estrogen levels rise suddenly in the middle of the cycle, which triggers the release of an egg. Levels of this hormone then drop rapidly after ovulation.
Estrogen normally travels through the blood vessels, coming into contact with cells in many types of tissues in the body and giving a message or instruction.
This is one of the most important hormones for women, next to progesterone. Progesterone helps maintain the pregnancy and implant the egg in the uterus.
Estrogen classification :
Estrone (E1) : This is a weak form of estrogen and is the only one found in women after menopause. Small amounts of estrone are found in most body tissues, mainly fat and muscle. The body can convert estrone to estradiol and estradiol to estrone. Estradiol (E2): This is the most potent type of estrogen. Estradiol is a steroid produced by the ovaries. It is believed to be one of the causes of a variety of gynecological problems, such as endometriosis, fibroids, and cancers that occur in women, especially endometrial cancer. Estriol (E3): This is the weakest type of estrogen and a waste product produced after the body uses estradiol. Pregnancy is the only time at which a significant amount of estriol is made. Estriol cannot be converted to estradiol or estrone. Estrogen also exists in men, but estrogen levels are much lower than in women.
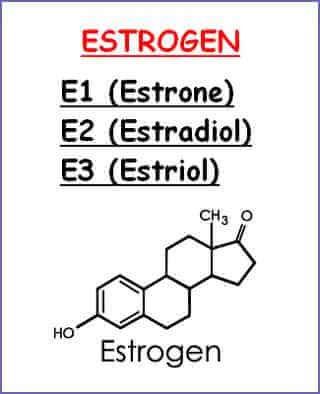
Có 3 loại estrogen
2. What role does estrogen play?
In women, estrogen affects the following parts of the body:Ovaries: Estrogen helps stimulate the growth of follicles. Vagina: It also stimulates the growth of the vagina to the size of an adult's vagina, thickens the vaginal wall and increases vaginal acidity reducing bacterial infections. It also helps lubricate the vagina. Fallopian tubes: Estrogen is responsible for the growth of thick, muscular walls in the fallopian tubes and for contractions of the muscles that help move eggs and sperm cells. Uterus: Estrogen strengthens and maintains the mucus lining of the uterus. It increases the size of the endometrium as well as enhances blood flow, protein content and enzyme activity. Estrogen also stimulates the muscles in the uterus to grow and contract. Contractions help during childbirth, and they also aid the uterine wall shedding dead tissue during menstruation. Cervical: Estrogen helps to regulate the flow and thickness of endometrial secretions. This enhances the movement of sperm cells to the egg to facilitate fertilization. Mammary glands: Estrogen has a relationship with other hormones in the breast. They are responsible for breast growth during adolescence, the pigmentation of the nipples, and help stop milk production when the baby is no longer nursing. Estrogen is responsible for the difference between male and female bodies. In the female body:
Estrogen makes bones smaller and shorter, pelvis wider and shoulders narrower. Increases fat storage around the hips and thighs, which means more curves and contours. Estrogen helps to slow down female growth during puberty and increase insulin sensitivity. Insulin affects body fat and muscle growth. It affects body hair becoming softer, while making women's hair more permanent. Estrogen makes the larynx smaller and the vocal cords shorter, giving females a higher voice than males. Estrogen inhibits the action of glands in the skin that produce sebum. This reduces the likelihood of acne in women. Other parts of the brain where estrogen has an impact include:
Brain: It can help maintain body temperature, regulate the part of the brain involved in sexual development, and enhance the effects of "feel-good" substances. "for the brain. Skin: Estrogen improves the thickness and quality of the skin as well as collagen content which prevents aging. Bones: Estrogen helps preserve bone strength and prevent bone degeneration. Liver and heart: Hormones regulate cholesterol production in the liver, helping to protect the heart and arteries.
3. Consequences of estrogen deficiency for women
Changes in beauty: the skin becomes dry, wrinkled and loses elasticity, spots appear, age spots. Changes in appearance: the first round is less firm, excess fat is more concentrated in the abdomen. Menstrual disorders, decreased sex drive, vaginal dryness, pain during sex may appear. Changes in health: increased risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure, diabetes, cancer.
Thiếu hụt estrogen sẽ làm da trở nên khô nhám, mất tính đàn hồi và nhiều nếp nhăn
4. Foods that boost estrogen
Some foods contain phytoestrogens, which can affect the level of estrogen in the body. Includes cruciferous vegetables, soybeans and some foods containing soy protein, berries, seeds and whole grains, nuts, fruit, wine.A common misconception is that phytoestrogens can negatively affect health, but several studies confirm that the phytoestrogen-containing foods listed above can reduce the risk of cancer. hot flashes, improves other menopausal symptoms and provides other health benefits.
5. Application of estrogen products to women
Synthetic estrogens, bioidentical estrogens and estrogens derived from pregnant mares (Premarin) are used for a variety of medical purposes.The most common uses of estrogen are as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) for menopause.
5.1. Birth control pills
Birth control pills are the most commonly used method of birth control in the United States. The estrogen contained in oral contraceptives combines with the hormone progestin.Many women take low-dose birth control pills, which contain 20 to 50 micrograms (mcg) of estrogen.
The estrogen in the birth control pill sends feedback to the brain. This feedback causes a range of effects in the body, including:
Preventing the pituitary gland from secreting follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stopping production of luteinizing hormone (LH) Preventing ovulation Supporting the lining of the uterus to stop heavy bleeding during menstruation Some doctors may prescribe birth control pills for alternative use, including:
Regulate menstrual cycles Reduce severe cramps and heavy bleeding Reduce the risk of cancer ovarian cancer and the development of ovarian cysts Protects against ectopic pregnancy Reduces perimenopausal symptoms Helps reduce the severity of hormone-related acne Taking birth control pills comes with many risks, such as heart attack, palpitations, causing blood clots, pulmonary embolism, nausea and vomiting, headache, abnormal bleeding, weight changes, tender and swollen breasts.
Long-term use can also lead to a higher risk of breast cancer.
5.2 Hormone replacement therapy
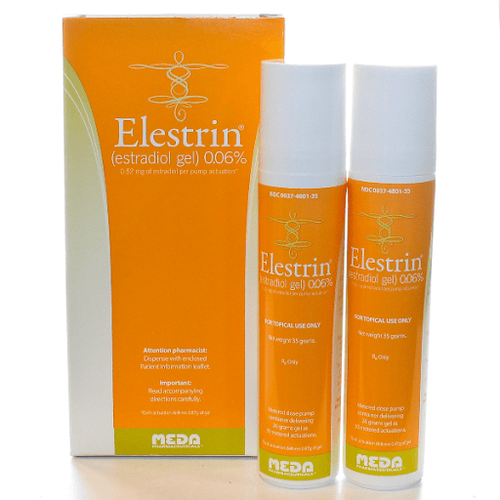
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) aims to relieve some of the symptoms of menopause by bringing female hormone levels back to normal. Treatment may be given as estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progestin.For women, the hormone progestin is used with estrogen to prevent overgrowth of the uterine lining, which can lead to endometrial cancer. HRT is available as a pill, nasal spray, patch, skin gel, injection, vaginal cream.
HRT can help relieve menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, painful intercourse, mood swings, sleep disturbances, anxiety, decreased sex drive.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends that HRT be used at the lowest dose for the shortest time needed to achieve the therapeutic goal.
This can help avoid some side effects, such as bloating, sore breasts, headaches, mood swings, nausea, water retention.
Women who use or are considering using hormone therapy after menopause should discuss the possible health benefits and risks with their doctor.
Hormone therapy is also used to help transgender people who want to transition between sexes, with estrogen often prescribed to help transgender women who are looking to develop female sexual characteristics.
Because of the risks posed by this type of therapy, it is important that a course of hormone therapy is followed under the close supervision of doctors.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source Acog.org