This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Tung Hoanh- Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.In 1880, the French scientist Louis Pasteur proved that it was bacteria that were the real cause of many diseases. Infections are very common health conditions that can affect patients of all ages.
1. What is an infection?
Definition of infection (also called infection) is the proliferation of bacteria, viruses or parasites... to the body, leading to cellular, organizational or systemic reactions. Usually, the clinical manifestation is a syndrome of infection and toxicity.Infection can be at a fixed location or spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. However, some microorganisms that naturally live in the body are not considered infections, for example, bacteria that reside in the mouth and intestines. Bacteria and viruses are invisible to the naked eye, they can cause similar symptoms and often spread in the same ways. This is the only similarity between bacteria and viruses. Distinguishing between bacterial and viral infections is important for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases:
Bacteria are a unique organism, they are very complex cells and can survive on their own inside or outside the body. body. Most bacteria are not harmful. In fact, there are many bacteria that reside on our skin and in our bodies, especially in the intestines, which help in the digestion of food. Viruses are smaller in size and have a non-cellular structure. Unlike bacteria, viruses need a host such as a human or an animal to multiply. Viruses cause infection by entering the nucleus inside healthy host cells.
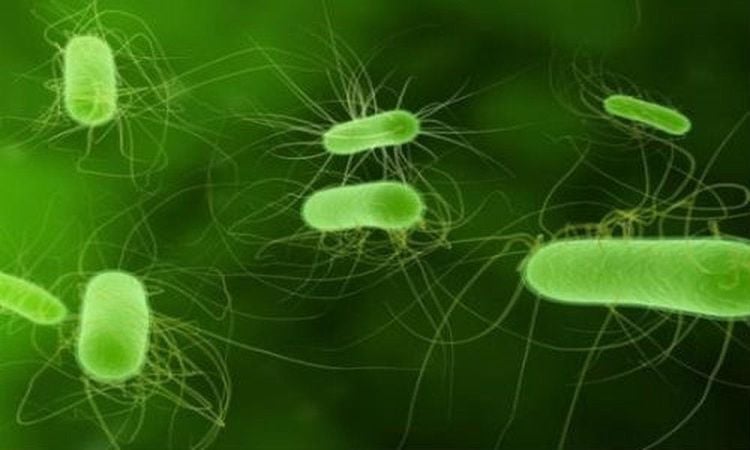
Nhiễm khuẩn do vi khuẩn
2. What is nosocomial infection?
Nosocomial infections are infections that occur in patients during a hospital stay. These patients were completely free of potential infections prior to admission.Infections within the first 48 hours of patient admission are not nosocomial infections. In contrast, some patients did not get sick when they were admitted to the hospital, but after being discharged from the hospital for a while, the disease appeared, this is most likely a nosocomial infection. For example: hepatitis B or C virus, HIV infection, osteoarthritis caused by intramedullary nailing... diseases with a long incubation period.
3. What are the symptoms of an infection?
Common symptoms of infections (bacterial and viral) are coughing and sneezing, fever, inflammation, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and cramps. All of the above reactions are ways in which the immune system tries to get rid of the disease-causing organism. However, bacterial and viral infections are not exactly the same, mostly because of differences in the structures of the organisms and how they respond to drugs. Patients can experience a wide variety of symptoms for an infection.4. Classification of infections by disease location
Infections can be classified according to the anatomical site of the infected organ, including:Urinary tract infections Skin infections Respiratory tract infections Infections originating in or around the teeth Infections Vaginal Amniotic fluid infection.
5. Classification of infectious diseases
Isolated infection: an infection caused by a single pathogen. Combined infection: infection caused by two or more pathogens. Secondary infection: an infection in the body weakened by another infection (secondary candidiasis in HIV/AIDS patients...). Local infection: the infection is concentrated in a certain location. Systemic infection. Acute (acute) infections: influenza, dysentery... Chronic (permanent) infections. Other types of infection such as: recurrent infection, embryonic infection (congenital syphilis), typical and atypical infections, delayed infections (HIV virus infection), molecular infections (due to acids) nucleic. of viruses entering the body can cause disease).
Nhiễm trùng cấp tính
6. General Infection Treatment Methods
Treating bacterial infections Doctors usually treat bacterial infections with antibiotics. Antibiotics can kill bacteria or stop them from multiplying. However, since bacteria are increasingly resistant to antibiotics, the latest generation of antibiotics are indicated for serious infections.Treatment of viral infections Control the symptoms with different medicines. For example, take paracetamol to reduce fever. Using antiretroviral drugs to stop the virus from replicating, For example, taking medicine for HIV/AIDS. Antibiotics will not be effective for treating viral infections.
7. Measures to prevent infections
Wash your hands thoroughly often (best way to avoid catching a cold) When shaking hands with someone with a cold is a risk factor, avoid rubbing your eyes or nose immediately afterwards. Because bacteria or viruses can spread disease through touching or shaking hands with another person. Food should be cooked or cooled as quickly as possible, avoiding staying at room temperature for too long. Vegetables and meat must be stored separately, using different cutting boards for raw and cooked foods. Meats should be cooked clean. Some organisms will die when food is cooked, but they can still leave behind toxic substances that cause diarrhea and vomiting. Body fluids, such as blood, saliva, and semen, can contain disease-causing and disease-transmitting microorganisms. Use protection during sex to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted diseases. Do not arbitrarily use antibiotics without a doctor's prescription. When using drugs, it is necessary to adhere to the correct treatment regimen: take the right drug, at the right dose and for the prescribed time. Prevention of diseases caused by viruses by vaccination such as: hepatitis A, B, influenza, Japanese encephalitis...Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.