This is an automatically translated article.
Protein is an indispensable element in the human body. However, when the total protein in the blood is high, it can warn of some dangerous diseases.1. The role of protein in the body
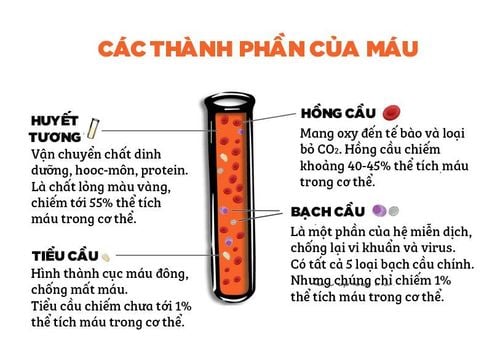
The total protein in the blood consists of 3 components: albumin accounts for 50-55%, globulin accounts for 39-45%, and fibrinogen accounts for 4-6%.Albumin and fibrinogen are proteins synthesized in the liver and account for about 60% of total serum protein.
1.1. Function of Albumin Involved in maintaining plasma oncotic pressure. Ensures the transport of many substances (e.g. Bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones and drugs. These substances are bound to albumin as they circulate in the circulation). Provides amino acids for protein synthesis in tissues. Albumin is an indicator used in the assessment of liver function. Normal Albumin values are around 35 - 50 g/L.
1.2. Functions of Globulin Globulin has 3 main types in the body: Alpha, beta and gamma globulin.
Gamma globulins, also known as immunoglobulins, are produced by B lymphocytes in response to antigenic stimulation. Immunoglobulins include IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM antibodies.
The globulins ensure the following vital functions of the body such as:
Participate in maintaining acid-base balance. Involved in the body's inflammatory response. Plays a key role in the immune defense mechanism and the production of antibodies. Involved in and regulating blood clotting and fibrinolysis.
Globulin đảm bảo nhiều chức năng chính của cơ thể
2. When does the blood protein increase?
There are many causes of high blood protein such as:
2.1. Elevated blood albumin levels The main common causes are:
Acute pancreatitis. Loss of water. 2.2. Increased alpha globulin levels The most common causes are:
Acute infection. Acute inflammatory condition. Carcinoma (carcinoma). Chronic glomerulonephritis. Cirrhosis. Diabetes A disorder of the blood protein (dysproteinemia). Protein loss through the glomerulus. Liver damage. Hodgkin lymphoma. Hypoalbuminemia. Inflammatory diseases. Heart attack. Bone marrow inflammation. Peptic ulcer disease. Pregnant. Kidney disease. Rheumatoid arthritis. Sarcoidosis (sarcoidosis). Stress status. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ulcerative colitis 2.3. Increased blood beta globulin levels The main common causes are:
Acute inflammation. No blood albumin. Diabetes. Dysproteinemia (dysproteinemia). Protein loss through the glomerulus. Increased blood cholesterol. Iron deficiency anemia. Multiple myeloma disease. Nephrotic syndrome. Jaundice due to biliary obstruction. Pregnant. Rheumatoid arthritis. Viral hepatitis.
Nồng độ beta globulin máu có thể tăng trong Hội chứng thận hư
2.4 Increased levels of gamma globulin in the blood The main common causes are:
Advanced stage cancer. Chronic hepatitis. Cystic fibrosis. Liver failure. Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Hypersensitivity reactions. Lexemia disease. Multiple myeloma Rheumatoid arthritis. Severe infection. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Viral infections. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.