This is an automatically translated article.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted virus. HPV virus can cause many dangerous diseases for men such as genital warts, anal cancer, penile cancer,... Most men infected with HPV do not notice any abnormal signs. about health.1. What is HPV virus?
HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) is a virus that is transmitted sexually or through skin contact.
There are more than 100 strains of HPV virus. Most strains of the HPV virus are harmless, cause no symptoms, and go away on their own. However, there are still about 40 strains of HPV that cause disease in the genitals and anus.
Some low-risk strains such as HPV-6 and HPV-11 can cause genital warts; HPV-2 and HPV-1 cause warts on the hands and feet. There are 15 high-risk strains of HPV (especially strains 16 and 18) that can cause precancerous, cervical, anal, and other genital cancers.
2. What disease does the HPV virus cause in men?
Most men infected with HPV do not notice any unusual signs of health. However, some strains of HPV virus in men can cause many dangerous diseases such as:
2.1 Genital warts
Genital warts (also known as genital warts) are visible warts on the genital area of men: the foreskin, the shaft of the penis, the urethral opening, the scrotum, the pubic area, around the anus,. .. caused by HPV infection. Even warts can appear in the mouth or throat of someone who has oral sex with an infected person.
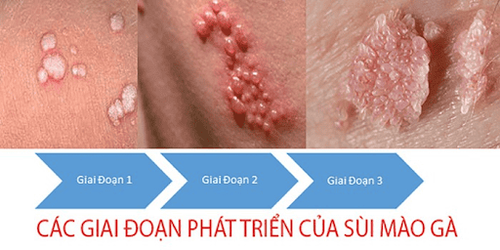
Mụn cóc sinh dục ở nam giới thường do virus HPV
Some warts are close together forming a cauliflower-like appearance, causing itching or discomfort in the genital area and bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Genital warts appear due to HPV-6, HPV-11 or some other strains such as HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-31, HPV-33, HPV-35,...
To treat the disease, Patients can receive medication, cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen, or surgical removal of the wart. However, the patient needs to consult with a specialist to know the condition of the disease and have the most appropriate treatment plan.
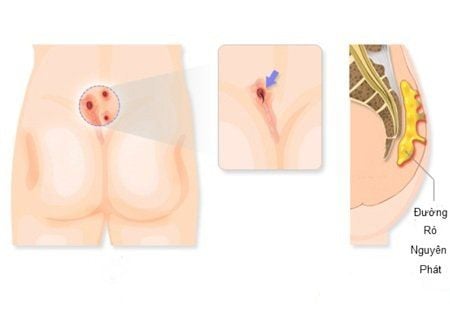
2.2 Anal cancer
Is one of the most serious complications of HPV infection in men, caused by strains of HPV-16 and HPV-18. If a man has a history of genital warts, the risk of anal cancer is very high.
Many men have no obvious symptoms of anal cancer except for mild pain and swelling. Others may experience some symptoms such as: anal bleeding, enlarged groin lymph nodes, anal pain, swelling, itching or bleeding.
To detect the disease, the patient can do cytology and anal biopsy to detect abnormal cells.
2.3 Penile cancer
Some patients with penile cancer have no obvious symptoms until the disease has reached an advanced stage. If the penis has sores, changes in color or boils, the patient should go to a reputable medical facility. To determine if penile cancer is present, the patient needs to have a penile cell biopsy.

Ung thư dương vật là một biến chứng nguy hiểm sau nhiễm HPV
3. How to reduce the risk of HPV infection
Get vaccinated against HPV. Living in fidelity, monogamy, few sexual partners. Correct use of condoms is the best method of protection against sexually transmitted diseases. Men who were vaccinated with 9vHPV, 4vHPV, or 2vHPV before age 15 and received 2 doses of HPV vaccine according to the recommended dosing schedule (0.6 - 12 months) or 3 doses of HPV vaccine according to the recommended schedule ( 0, 1 - 2, 6 months), is considered fully vaccinated.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.