This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Dam Thi Quynh - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Symptoms of acute respiratory failure in infants, if detected early and treated promptly, will help improve treatment effectiveness and limit possible complications that affect the health of the child.
1. What is acute respiratory failure in infants?
Respiratory failure in newborns is a condition in which the respiratory apparatus fails to guarantee the gas exchange function, leading to hypoxia and increased CO2 in the blood, showing low PaO2 and or high PaCO2. It is a very common syndrome in the neonatal period, especially in the first days after birth, during the time when the child adapts to the external environment. Premature infants are more susceptible to respiratory failure than term infants. Respiratory failure is one of the leading causes of neonatal mortality.
2. Warning signs of acute respiratory failure in infants
Neonatal acute respiratory failure is a very common medical condition in newborns. But without experience, recognizing early signs of respiratory failure in infants is not easy. Sometimes children have signs of severe respiratory failure such as breathing cessation, cyanosis, whining, lethargy ... just discovered.
Normal infant's breathing rate is 40-60 times/minute, the baby is breathing smoothly with no signs of exertion, no cyanosis. Newborns, especially premature babies, have an unstable breathing rate or have short pauses in breathing < 15 seconds, if they stop breathing for > 15 seconds, recurrence can lead to respiratory failure.
Assess the degree of postpartum respiratory failure based on the Silverman index, including 5 clinical symptoms: chest and abdomen movement, intercostal muscle contraction, sternal depression, rising and falling nostrils, moaning. Depending on the patient's condition there is a corresponding clinical respiratory rate.
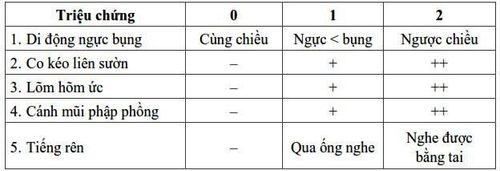
Chỉ số Silverman giúp đánh giá tình trạng suy hô hấp
Manifestations of children with acute respiratory distress syndrome usually appear early, within 24 hours of birth. Regardless of the cause, neonatal respiratory failure includes the following three symptoms:
Tachypnea > 60 breaths/minute or slow breathing < 40 breaths/minute, or apnea. Signs of respiratory traction: Contraction of intercostal muscles, retraction above and below the sternum, chest-abdominal breathing, movement of the chest and abdomen in the opposite direction. Purple around the lips, cyanosis of the extremities or the whole body. Purple occurs when the PaO2 in the blood falls below 70 mmHg or the reduced Hb level is above 5g%. Other signs: Irritability, fussiness, lack of or poor feeding, lethargy, fever...

Trẻ sơ sinh quấy khóc bỏ bú
3. What is the cause of acute respiratory failure in infants?
The leading cause of acute respiratory failure in infants is premature birth. In addition, there are a number of other factors associated with this condition such as: C-section babies, infants born to mothers with diabetes, second twins, premature babies, babies born to infected mothers pregnancy, children born from mothers with stress during pregnancy, children with birth defects (congenital heart, diaphragmatic hernia, congenital air cocoon...).
The diagnosis of causes is based on: gestational age, clinical signs, obstetric history, radiology ...
Sinh non là nguyên nhân hàng đầu gây suy hô hấp cấp ở trẻ sơ sinh
4. How should the infant be treated with acute respiratory failure?
Treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome in infants is considered a great challenge because this condition requires the child to be monitored and cared for continuously with a professional medical team along with treatment methods. , proper care, right. One of the decisive factors for success in treatment is early detection of signs of respiratory failure and appropriate and timely treatment.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, all newborns are greeted by experienced doctors in neonatal resuscitation when they are born. Therefore, the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome is usually started as soon as the newborn is born in the delivery room or operating room. Treatments include respiratory support with oxygen delivery, non-invasive or non-invasive ventilatory support, and alveolar surfactant replacement therapy (Suractant pump, which can be performed at the site). delivery room, operating room), or other supportive treatments. Thereafter, all neonates with signs of acute respiratory distress syndrome were rapidly transferred to the intensive care unit – the neonatal department. Here, children will be received by neonatologists, continue to treat and care for children.

Trẻ được điều trị tại khoa Sơ sinh - Bệnh viện Vinmec
The Neonatal Department of Vinmec Times City hospital is conducting a less invasive method of pumping Surfactant for children with respiratory failure due to lack or inactivation of Surfactant. This is a new technique with limited intervention to children, initially bringing benefits and high efficiency. Ensuring a healthy pregnancy as well as controlling maternal risk factors (preterm birth, multiple pregnancy, gestational diabetes, vaginitis ...) play an important role in limiting depression. acute respiratory failure in neonates.
Acute respiratory failure is a very common syndrome in infants. In case the child has respiratory failure, the child needs immediate support with the right method and correct technique. It plays an important therapeutic role and is decisive for success in the treatment of acute respiratory failure in infants.
For more details on Surfactant pumping technique to treat neonatal respiratory failure at Vinmec, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE
MORE:
Depression Acute respiratory failure in premature infants: Risks and complications Symptoms of respiratory distress in the newborn Differential diagnosis of the cause of acute respiratory failure in the neonate