This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Le Anh Viet - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.And Master, Doctor Nguyen Hong Hai - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Thyroid cancer is a common endocrine tumor and, if diagnosed, treated early can effectively prevent the progression of thyroid cancer. Accordingly, the rapid differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules at the outset is imperative, and this can be achieved by applying the value of ultrasonography and the TIRADS classification.
1. What is a thyroid nodule?
Thyroid nodules are solid, dense, thyroid tissue that form within the thyroid gland. If the block is small in size, it is called a thyroid nucleus. In contrast, when the patient has many thyroid nodules or a single or large nodules, it is called a thyroid nodule.Most thyroid nodules cause no significant symptoms, so patients often won't know they have thyroid nodules until a doctor finds out during a routine physical exam. When large, the goiter becomes visible or causes pressure around or makes it difficult to swallow or breathe. However, a small percentage of thyroid nodules are thyroid cancer (malignant cells in the thyroid gland).
Therefore, the treatment options depend on the type of thyroid nodule the patient is suffering from. Accordingly, the correct diagnosis of thyroid nodules is of crucial importance. When evaluating a lump or nodule in the neck, one of the doctor's main goals is to rule out the possibility of cancer. In addition, your doctor will also want to know if your thyroid is functioning normally through a local thyroid exam, a physical exam for symptoms of hyperthyroidism, and tests to check your thyroid function. Ultrasonography or fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid tissue to give clear results, distinguish the possibility of benign and malignant thyroid nodules.
2. What is a thyroid ultrasound?
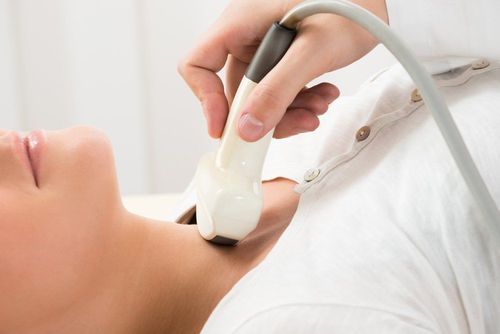
Ultrasound is a non-invasive medical tool that helps doctors diagnose diseases safely and painlessly. This technique creates images of the inside of the body using sound waves through a transducer and gel that is placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves pass from the transducer through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the echoes of the sound waves. The computer uses those sound waves to create images. Ultrasound does not use radiation like X-rays, so there is absolutely no risk of exposure. Also, because images are taken in real time, ultrasound makes it possible to show the structure and movement of organs inside the body, like the speed at which blood flows through the blood vessels.For thyroid ultrasound, this order is ordered when imaging of the thyroid gland and adjacent structures in the neck is needed. The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland; This structure is located in the front of the neck just above the collarbone and has a butterfly-like appearance, with the two lobes on either side of the neck connected by a narrow band of tissue called the isthmus.
Thyroid tissue is thin and soft, located just below the surface of the skin but is rarely of any concern. Up to 5 to 10% of adults will have a nodule (nodule) in the thyroid gland that a doctor can identify on examination. However, if indicated, the ultrasound value will be very sensitive and show many palpable nodules in the thyroid gland, giving detailed information:
Size of the thyroid nodule Density inside the thyroid nodule (filled with liquid or solid) Features suggestive of thyroid cancer instead of a benign nodule such as irregular margins, microcalcifications... Are the lymph nodes in the neck affected? what or not. As age increases, up to 70% of adults will find nodules on ultrasound, but most of these contain benign thyroid tissue, which does not pose a health risk. The rest may doubt the ability to confirm the diagnosis of malignancy on thyroid ultrasound if there are features such as solid structure, hypoechoic, irregular margins, large axis perpendicular to the skin surface, microcalcifications. However, the definitive diagnosis is by fine-needle aspiration thyroidectomy (FNA).
3. What is the TIRADS classification?
Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (TIRADS) assesses the risk of malignancy of thyroid nodules based on imaging features on ultrasound from which to determine the following attitude. monitoring and appropriate treatment. Different organizations will issue different TIRADS classifications, but the commonly used TIRADS classification tables are:ACR TIRADS - 2017 EU-TIRADS - 2017 K-TIRADS - 2016 Currently, National General Hospital Vinmec is applying the new and most complete classification according to ACR TI-RADS. Tumor description and classification according to ACR TI-RADS (American College Of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems)
Based on 5 characteristics:
Follicular or quasi-cystic composition: 0 score Spongiform cystic degeneration : 0 points Both dense and dense: 1 point Solid or almost solid: 2 points Acoustic structure (Reverb) Drum: 0 points Amplified or homophonic: 1 point Dimphonic: 2 points Very hypoechoic (strongly reduced sound) ): 3 points Shape Wider than tall: 0 point Higher than wide: 3 points Coastline Smooth: 0 point Unknown border: 0 point Lobular or irregular: 2 points (57% positive diagnostic value) Thorny fringe: 3 points. Calcification No or large comet tails (concentrated colloidal calcification): 0 points. Coarse calcification: 1 point (low malignancy) Borderline calcification: 2 points Punctate Echogenic Foci: 3 points Based on sonographic features, thyroid nodules will be evaluate TI-RADS from 1 to 5 with different levels of suggestive of malignancy, thereby making recommendations for each nodule.
TI-RADS 1: Benign. There is no need for a smear test (FNA).
TI-RADS 2: No doubt. There is no need for a smear test (FNA).
TI-RADS 3: Low suspicion. Aspiration cytology (FNA) check if nucleus ≥ 2.5cm
Monitor if nucleus ≥ 1.5cm.
TI-RADS 4: Moderately suspicious. Aspiration cytology (FNA) check if nucleus ≥ 1.5cm
Monitor if nucleus ≥ 1cm.
TI-RADS 5: High suspicion. Aspiration cytology (FNA) check if nucleus ≥ 1cm
Monitor if nucleus ≥ 0.5cm.
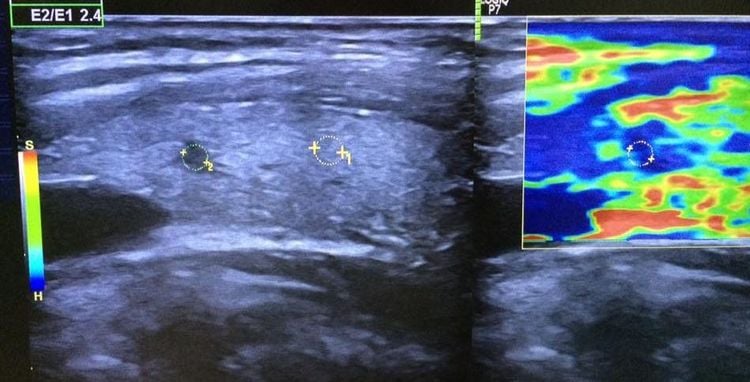
4. Value of ultrasound and application of TIRADS classification in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules
To date, there have been a series of studies verifying the effectiveness of using the TIRADS classification for the diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules according to the features noted on thyroid ultrasound. Therefore, this tool has been considered as a simple laboratory analysis method, supporting the clinical data to distinguish benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Furthermore, in order to reduce the dependence on the subjective judgments of the physician, the ultrasound imaging data has been further enhanced, in addition to the clinical symptoms, to be used to support support diagnostic decision making in practice.Currently, the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules is mainly based on initial imaging. Biopsy should only be performed in cases where the possibility of cancer diagnosis by ultrasound and TIRADS classification is suspected, as it is an invasive tool and may also pose certain risks. With large sample size retrospective observational studies, the sensitivity and specificity of the combination of thyroid ultrasound and the TIRADS classification in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules as cancer have high value. Since then, this combination has become an objective factor with the judgment of the clinician, achieving the top patient goal, quickly finding a definitive treatment because of the nature of thyroid cancer. has a pretty good prognosis.
In summary, along with thyroid ultrasound, when combined with the TIRADS classification, cases of patients with thyroid nodules will be supported in making more accurate clinical decisions. From there, the distinction between benign and malignant thyroid nodules will be more convenient and faster, including making a treatment plan and long-term follow-up.
Periodic health check-ups help detect diseases early, thereby planning treatment for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy.
The results of the patient's examination will be returned to the home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties right at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment of neurological diseases at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.