This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Doctor Vu Thi Hanh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Trans fontanelle ultrasound is a safe and painless test that uses ultrasound waves to create images of the brain. Ultrasonography of the fontanelle is only performed in children under 6 months of age, the skull bones are not fully developed, the skull joints have not yet healed.
1. How is a trans- fontanel ultrasound performed?
During the test, an ultrasound machine sends ultrasound waves into the head and images are recorded on a computer. The black and white images show the internal structure of the brain, including the brain parenchyma, ventricles, and blood vessels.
2. Why do fontanel ultrasound?
Doctors order fontanograms when there is concern about neurological problems in infants. Premature infants requiring intensive care frequently require head ultrasound to rule out neurological complications of preterm birth, such as cerebral hemorrhage or periventricular white matter damage due to asphyxia.
The doctor may also order an ultrasound of the baby's head with:
Abnormal increase in head size Puffy fontanel

Trẻ xuất hiện thóp phồng cần được chỉ định siêu âm đầu
Any neurological symptoms Head ultrasound can often help diagnose:
Bleeding in brain tissue or in the ventricles Hydrocephalus A mass in the brain, such as a tumor or cyst Suspected complication of meningitis
3. Prepare before doing fontanel ultrasound
You don't need to do anything special to prepare your child for a head ultrasound. You should tell the doctor about any medications your child is taking before having an ultrasound.
4. Perform an ultrasound
An ultrasound of the fontanelle will be done in the radiology department of a hospital or in a radiology center. Parents can often accompany their child for reassurance and support.
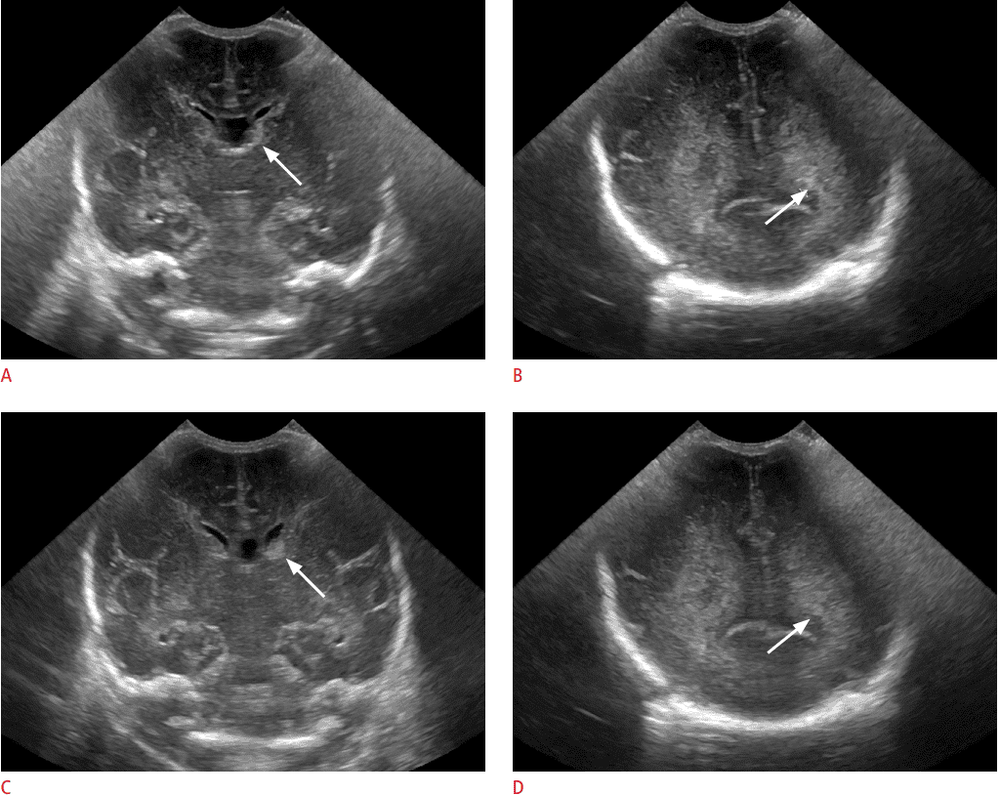
Kết quả siêu âm qua thóp ở trẻ sơ sinh
If your child is in the hospital and cannot easily be brought to the radiology department, a portable ultrasound machine can be carried to the bedside. This is usually done in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
A fontanel ultrasound can be done with the baby on the belly or back, or even in the parent's arms, if needed. The room is usually dark enough to see clearly on the computer screen. The sonographer will spread a clear, warm gel over your baby's scalp. This gel helps to transmit sound waves.
The sonographer will then move the transducer over the gel. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves, and the computer measures how the sound waves bounce off the head. The computer changes those sound waves into an image to be analyzed. The examination usually takes 15-30 minutes.
5. Benefits vs Risks?
Benefits: Most ultrasound scans are non-invasive. Sometimes, the ultrasound exam can be temporarily uncomfortable, but it is not painful. Ultrasound is common, easy to use, and less expensive than most other imaging methods. Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and does not use radiation. Ultrasound scans give clear images of soft tissues that do not show up well on X-ray images. Risks Ultrasound of the fontanelle is unlikely to have harmful effects in children.
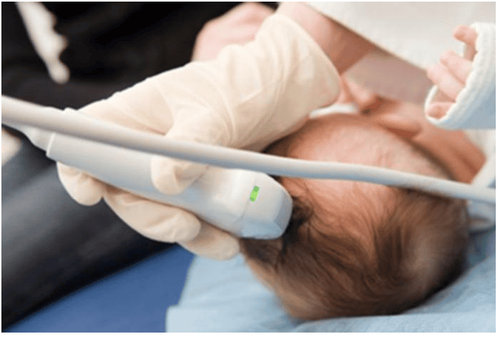
Siêu âm thóp hoàn toàn an toàn với trẻ nhỏ
6. What are the limitations of cranial ultrasound?
Ultrasound exams are very sensitive to movement, and an active or crying baby will delay the test. You can feed your baby, or provide a pacifier or favorite toy for comfort.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.