This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Minh Thuyen - Pathologist, Pathology Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Cervical cancer can be detected early, and sometimes even completely prevented with regular Pap testing. If caught early, cervical cancer is one of the most treatable cancers. If you've been diagnosed with cervical cancer or are worried about it, you probably have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start.
1. What is cervical cancer?
The cervix connects the body of the uterus (the upper part where the fetus develops) to the vagina (the canal at which the fetus is born). The cervix is made up of two parts and is covered with two different types of cells:
Intracervical neck: The place where the cervix leads into the uterus, covered with glandular cells. Ectopic neck: The outer part of the cervix that can be seen by a doctor during a speculum examination, covered with squamous cells. The place where these two types of cells meet in the cervix is called the dendritic junction (also known as the transition zone, the zone of transformation). The exact location of the transition zone changes as you age and if you give birth. Most cervical cancers originate in cells in the junction.
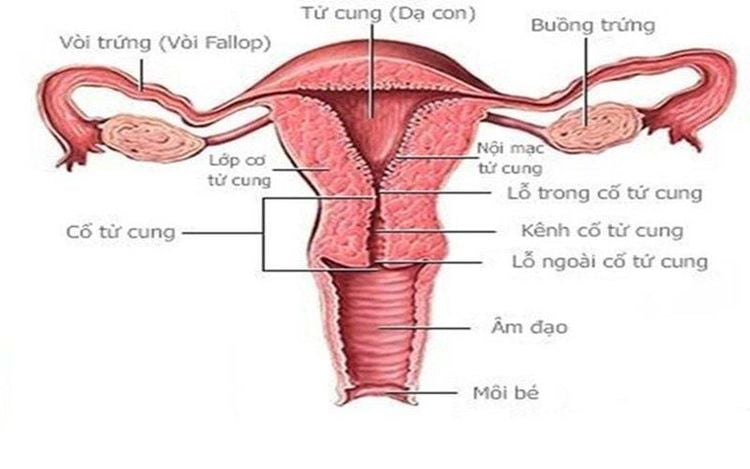
Cấu tạo cổ tử cung
2. What is pre-cervical cancer?
Cells in the transition zone do not suddenly turn into cancer cells. Instead, the normal cells of the cervix first gradually develop abnormal changes known as cervical precancerous changes. Doctors use several terms to describe these precancerous changes, including cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL), and dysplasia.
When identifying precancerous tumors in the lab, they are graded on a scale of 1 to 3 based on the degree of abnormal cervical tissue.
CIN1 (also known as mild dysplasia or low-grade SIL), does not have much abnormal tissue, and it is considered the least severe precancerous lesion of the cervix. CIN2 or CIN3 (also called moderate/severe dysplasia or high-grade SIL), more abnormal tissue; High-grade SIL is the most serious precancerous lesion. Although cervical cancer starts in cells with precancerous changes, only some women with cervical cancer will develop cancer. For most women, the precancerous cells will go away without treatment. But, in some women the pre-cancer turns into actual cancer (invasive cancer). Treating precancerous lesions of the cervix can prevent most cervical cancers.
Precancerous changes can be detected with a Pap test and treated to prevent cancer from growing.
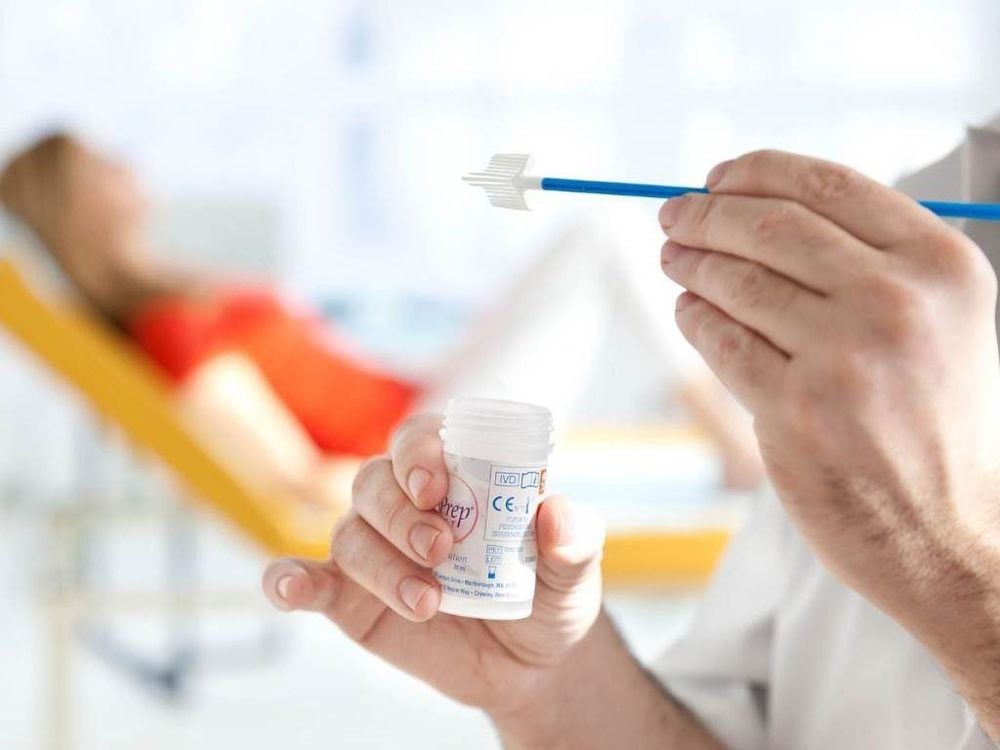
Xét nghiệm Pap giúp phát hiện và điều trị tiền ung thư
3. Types of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer and cervical pre-cancer are classified by microscopic observation. The most common types of cervical cancer are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Most (up to 9 out of 10) cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. This type of cancer develops from cells in the neck outside the cervix. Squamous cell carcinoma usually originates in the transition zone (the junction between the outer and inner cervix). Most of the remaining cervical cancers are adenocarcinomas. This is cancer that develops from gland cells. Cervical adenocarcinoma develops from the mucus-secreting glandular cells of the neck in the cervix. Less commonly, cervical cancer has features of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. These are called squamous-adenocarcinomas or mixed carcinomas. Although most cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas or adenocarcinomas, other types of cancer can also develop in the cervix, such as melanoma, sarcoma, and lymphoma. more common in other parts of the body.

Có nhiều loại ung thư cổ tử cung
To meet the needs of women for gynecological cancer screening, Vinmec International Hospital currently offers a screening package and early detection of gynecological cancer, helping to detect 4 diseases early: Cancer cervical cancer, breast cancer, uterine cancer and ovarian cancer even if the patient has no symptoms.
The subjects who should use the Gynecological cancer screening and early detection package include:
Female customers, over 40 years old Customers wishing to be able to screen for pathology of breast-gynecological cancer (neck) uterus, uterus, ovaries) Customers at high risk of cancer – especially customers with a family history of breast cancer, gynecology Women of reproductive age, perimenopause Menopause and menopause Women are having symptoms of breast cancer, gynecology such as: pain in the breast, lump in the breast, bleeding outside the menstrual cycle, abdominal pain, etc... To register for an examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital You can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
Articles refer to the source: American Cancer Society
MORE:
Signs of cervical cancer women do not ignore Cervical cancer treatment in stages Causes of cervical cancer What is bow?