This is an automatically translated article.
Postpartum infection is a medical condition and is one of the five common dangerous obstetric complications, especially in places with poor education and facilities. Postpartum infections can cause serious infections that can include conditions such as generalized metritis, bacteremia, peritonitis...1. Outline of Postpartum Infections
Postpartum infection is a medical condition and is one of the five common dangerous obstetric complications, especially in places with poor education and facilities. The development and emergence of antibiotics and the introduction of new generations of antibiotics have contributed to alleviating the consequences of postpartum infections. However, serious infections still persist and this is a cause that can easily lead to maternal death if not diagnosed and treated promptly.Causes of severe obstetric infection may be due to retained placenta, amniotic fluid infection, intrauterine procedures that do not ensure aseptic principles... Obstetric procedures may be the cause of infection. Severe as: Miscarriage, postpartum or after cesarean section. Bacteria that cause common postpartum infections such as E. coli, S. aureus, S. pyogenes, C. perfungeus, C. seucellii... Postpartum infections can cause serious infections including: to conditions such as total inflammation of the uterus, bacteremia, peritonitis ...

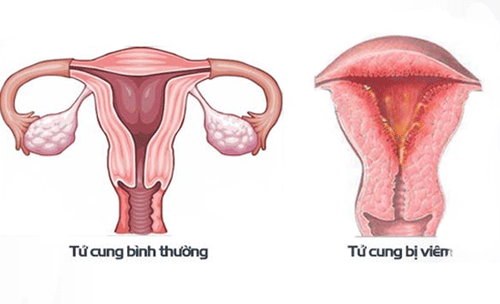
Nhiễm khuẩn hậu sản là một tình trạng bệnh lý và là một tai biến sản khoa nguy hiểm thường gặp
2. Symptoms of postpartum infection
2.1. Generalized metritis is a complication of endometritis or endometriosis. High fever, fatigue, malaise. Little or no discharge. When stretching the uterus, there is a rotten, black discharge (especially on the 8th, 10th day). Uterine compression is painful. Progression to peritonitis, sepsis. 2.2. Generalized peritonitis Occurs after endometritis, total uterine inflammation, pelvic peritonitis, or adnexitis. Time: 7-10 days after giving birth or caesarean section. Body as a whole: Signs of infection, intoxication. Vomiting, abdominal pain: Intestinal obstruction or semi-obstruction. Diarrhea with stools. Physical: Abdomen distended, peritoneal reaction. Subclinical: Unprepared abdominal X-ray shows water-vapor levels. Prognosis: Early diagnosis and surgery have good prognosis, if delayed surgery, poor prognosis and possibly death. 2.3. Sepsis Secondary to postpartum infection mainly from the placental area in the uterus. Body as a Whole: Continuous or fluctuating or prolonged high fever, fatigue, weakness, lethargy. Possible shock, coma, oliguria, dyspnea, jaundice. The discharge is foul, with blood and pus. Uterus is enlarged, slow contraction and tenderness. Hepatosplenomegaly, abdominal distension... Diagnosis: Blood culture (at high fever), fluid culture from uterine cavity, urine culture. Red blood cells are decreased, white blood cells are increased or decreased. Severe prognosis, high risk of death.
Nhiễm khuẩn huyết là một nhiễm trùng nặng trong sản khoa tiên lượng nặng
3. Treatment of postpartum infections
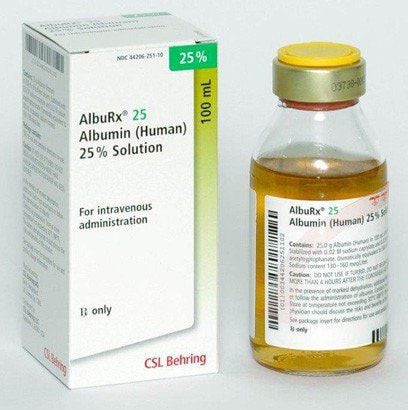
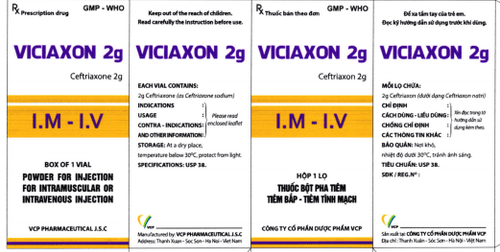
3.1. Principle Blood culture, fluid culture and urine culture prior to antibiotic therapy. Broad-spectrum combination antibiotics when no antibiogram is available. If there is an antibiogram, then treat according to the antibiogram. Translation compensation. Use vasopressors if hypotension is not reversible after rehydration. Breathe oxygen. Resolve infection. 3.2. Use of antibiotics Combination of three antibioticsCeftriaxon 1g intravenous / 24 hours. Azithromycin 500mg IV/24 hours. Metronidazole 500mg IV every 12 hours. If penicillin allergy
Combination drug
Gentamycin IV 4-6mg/kg for the first dose, the next dose is based on renal clearance. Clindamycin 600mg IV every 8 hours. Or a combination of IV Gentamycin 4-6mg/kg for the first dose, the next dose based on renal clearance. Lincomycin 600mg IV every 8 hours. 3.3. Surgery Remove the source of infection. When the temperature returned to normal, a partial hysterectomy was performed. For generalized peritonitis: Laparotomy, partial hysterectomy and abdominal drainage.
Nhiễm trùng nặng do sản khoa là nguyên nhân này dễ dẫn đến tử vong cho mẹ nếu không được chẩn đoán và điều trị kịp thời
4. Postpartum infection prevention
Attention should be paid to aseptic work during examination and active treatment of postpartum infections.Currently, Vinmec has deployed the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package. This examination package can detect inflammatory diseases early, making treatment easy and inexpensive. When registering for the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package, customers will receive:
Gynecological examination. Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries. Bilateral breast ultrasound. Tests such as: Treponema pallidum rapid test, Chlamydia rapid test, taking samples for cervical-vaginal cytology, bacterioscopic staining (female vaginal fluid), HPV genotype PCR automated system, total analysis Automated urine collection.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: kcb.vn