This is an automatically translated article.
Fibrocystic mammary gland (or cystic fibrosis) is a histological change of the mammary gland. If cystic fibrosis is small, just follow-up without surgical treatment.
1. What is a fibroadenoma?
Fibrocystic mammary gland (fibrocystic change of the mammary gland, cystic fibrosis of the breast) is a form of histological change of the mammary gland. This is a benign change, common in women between the ages of 18-40. Most of these tumors are benign, do not turn into cancer.
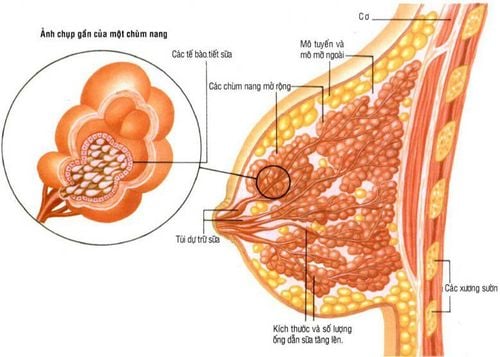
Normally, the lobules of the mammary gland naturally enlarge during adulthood and puberty in girls and are mostly benign. But there will be some solid, hormone-sensitive tumors, especially estrogens, that originate in the epithelium structures located adjacent to the milk ducts outside the lobules. This tumor invades surrounding tissues, pushing these tissues aside without invading them.
Typical fibroadenomas are usually round or long segmented, well-defined, dense, about 1-5 cm in diameter, relatively mobile, so they can move slightly when pressed on the skin. Neighborhoods will see obvious clumps.
These tumors are often discovered incidentally. But there are also cases where a few months or years after surgical removal of the fibroadenoma, the tumor is found in the same breast or even in another breast.
2. Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis of the breast
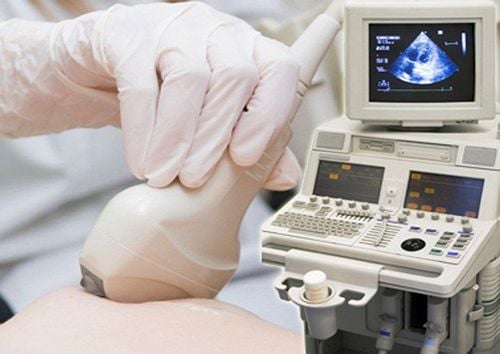
Sóng siêu âm cho hình ảnh bên trong tuyến vú nhằm đánh giá một khối u vú
2.1. Clinical diagnosis Fibroadenomas are firm breast masses and are usually:
Smooth margins, well-defined margins Easy to move Firm or firm Painless. 2.2. Subclinical Several laboratory tests and procedures are used to diagnose cystic fibrosis:
Mammography : A mammogram that uses X-rays to create an image (mammogram) of the suspected breast tissue. have u. A fibroadenoma may be shown on a mammogram as a breast mass with a smooth, rounded margin that is separate from surrounding breast tissue. Breast ultrasound: Ultrasound waves look inside the mammary gland to evaluate a breast lump. Breast ultrasound helps determine if the lump is a solid mass or contains fluid. If it is a solid mass, it is most likely a fibroadenoma, while a fluid-filled mass is more likely to be a cyst. Fine Needle Biopsy (FNA): The doctor inserts a fine needle into the breast and withdraws the contents of the tumor. If fluid is drained, the lump could be a cyst. Core Needle Biopsy (CNB): The doctor, with guidance from the mammogram and from the ultrasound image, uses a core needle to take a tissue sample from the tumor, which is then brought to a laboratory for analysis.
3. Benign breast fibroadenoma treatment
The patient may not need surgery if the fibroadenoma is < 2 cm and is painless. At this point, only clinical follow-up, ultrasonography, and mammography is needed when correctly identified by fine-needle biopsy (FNA) and no medication is required. Regular check-ups every 6 months.
Some other cases that are less common, but need to be treated are:
Severe pain with large cysts causing tension, treatment includes fine needle aspiration and pain medication. If the fibroid is > 3cm, minor surgery can be performed, following the areola line to keep the aesthetics. For giant fibroadenoma, the patient needs to be treated surgically. Procedures to remove cystic fibrosis include:
Lumpectomy or excisional biopsy. In this procedure, the surgeon removes the tumor and sends breast tissue to a laboratory to check for cancer. Cryoablation: The doctor inserts a thin, rod-shaped device (cryoprobe) through the skin to the fibroadenoma. Cold nitrogen gas is injected to freeze and destroy the tissue.

Bệnh nhân có thể không cần phải phẫu thuật nếu các u sợi tuyến vú < 2 cm và không đau
4. The latest method to treat benign breast fibroadenomas
Currently, there are 2 methods of treating breast fibroadenomas that do not leave bad scars like surgery to remove the tumor, which are:
Cryocautery Burning with high frequency waves In these methods, the doctor will use Ultrasound probe to pinpoint the exact location of the tumor and then apply too low or too high temperature directly to the tumor to destroy tumor cells. Only local anesthesia is sufficient. For cryotherapy, the tumor does not disappear immediately, but it will shrink over time. The use of any treatment method should be carefully consulted by a specialist to avoid complications.
After the fibroadenoma is removed, one or more new fibroadenomas may develop. New tumors still need to be evaluated with mammograms, ultrasounds and biopsies - to determine if the tumor is a fibroadenoma or is likely to become cancerous.
Radiofrequency ablation technique has been successfully applied in the treatment of benign tumors at Vinmec International General Hospital. After treatment at the hospital, the rate of patients with postoperative hematoma <20%, tumor size reduced by 30-50% in volume after 1 month, 60-70% in volume after 3 months, >90% volume after 12 months.
To achieve the highest diagnostic and treatment efficiency, Vinmec has equipped the most modern imaging equipment system today, typically the GE Healthcare S9 ultrasound machine with flat transducer, high frequency, HD resolution for clear images.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.