This is an automatically translated article.
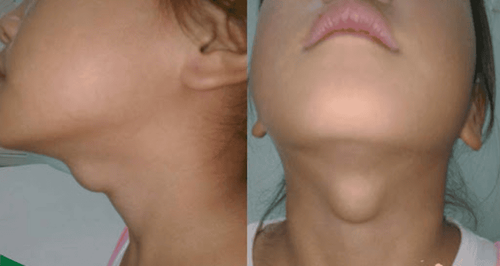
Thyroid cyst is a lump or lump in the neck that is filled with fluid. During pregnancy, the fetal thyroid gland begins to form at the base of the tongue and will migrate to the neck below the thyroid cartilage. Cysts form when part of the thyroid duct does not disappear and persists after birth, leading to the formation of a thyroid cyst.
1. Symptoms of Tongue Thyroid Cysts
Thyroglossal duct cyst usually presents with symptoms between 2 and 10 years of age, although it can also be diagnosed at any age from birth to adulthood. youth. The tumor usually moves when the person swallows or sticks out the tongue. The tumor may not be obvious until the child is older. In some cases, the parent or child may not even notice a lump in the neck until an infection causes the cyst to swell.
Usually, the tumor will appear in the middle of the neck and cause almost no discomfort such as pain, difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Other common symptoms of a thyroid cyst include:
Hoarse voice Difficulty breathing or swallowing A hole in the neck near the cyst causing mucus to drain Red skin around the area of the cyst Redness and pain in the cyst when the cyst becomes infected.
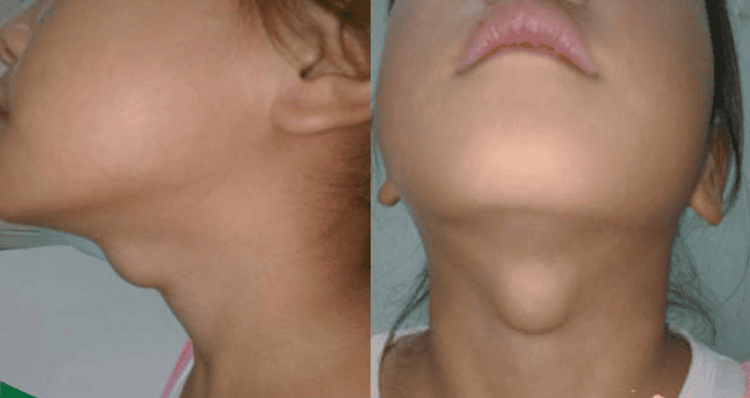
Hình ảnh nang giáp lưỡi ở trẻ
2. Causes of Tongue Thyroid Cysts
Thyroid cyst is a birth defect and currently doctors have not found the exact cause of this malformation. Thyroid cysts occur in both boys and girls and are not associated with other diseases or birth defects.
3. Diagnosis of thyroid cysts
As a first step, the doctor will look and feel on the baby's neck to see if there are any cysts. If a cyst is suspected, your doctor may order blood tests and imaging tests to look for cysts in your neck to confirm the diagnosis.
Blood test: A test to measure the amount of TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) in the blood to determine how well the thyroid gland is working.
Diagnostic imaging:
Ultrasound: This technique uses sound waves to create an image of the cyst. CT scan: This technique uses X-rays to create 3-D images of the tissues in a child's throat. MRI scan: This test uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create images of the tissues in your child's throat. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) test: In this test, the doctor uses a small, hollow needle to be inserted into the cyst to extract cells to be taken to a laboratory for examination and testing. confirm diagnosis.
Xét nghiệm máu giúp chẩn đoán nang giáp lưỡi
4. Treatment of thyroid cysts
Antibiotics If a thyroid cyst is infected with bacteria or a virus, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to help treat the infection. Infection before surgery can make it more difficult to remove a cyst and increase the chance of it coming back, so it's important for your doctor to treat the infection before surgery.
Thyroid duct surgery Doctors recommend to perform surgery to remove thyroid cysts, especially cysts that have become infected or make it difficult for the child to breathe or swallow. This technique is known as the Sistrunk surgery. The procedure for performing Sistrunk surgery is as follows:
General anesthesia so that the child can sleep during the surgery. Make a small cut in the front of the neck to open up the skin and muscle above the cyst site. Removal of cystic tissue in the neck. Remove a small piece from inside the hyoid bone as well as any remaining tissue in the thyroid duct. Close the muscles and tissues around the hyoid bone and open areas with sutures. Close the cut in the skin with sutures. This surgery takes a few hours, so the child will still need to stay in the hospital for at least one night and after leaving the hospital, the child will still need to stay out of school for a few days. While the child is recovering:
Parents should fully and properly follow the instructions given by the doctor in caring for the child's incision. Go for re-examination on time.

Trẻ uống thuốc điều trị nang giáp lưỡi
5. Is thyroid cyst dangerous?
Most thyroid cysts are harmless and do not cause any long-term complications for the child. However, the doctor may still recommend surgery to remove this cyst if it makes the child feel self-conscious due to the appearance of a lump in the neck. Cysts can grow back even after surgery, but with an incidence of only about 3%.
In rare cases, a thyroid cyst can become cancerous and may require immediate surgery to stop the cancer cells from spreading. The rate of cancer in thyroid cysts is about 1%.
References: childrenshospital.org, medicalnewstoday.com, healthline.com
Recommended video:
Fetal screening - A healthy baby is born
SEE MORE Causes and ways to prevent hypothyroidism during pregnancy TSH hormone and its significance in the screening diagnosis of thyroid diseases Common pathologies in the thyroid gland