This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Tran Thi Mai Huong - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The uterus is an organ of the female reproductive system. It is shaped like an inverted pear and has thick walls. The main function of the uterus is to house and nurture the fetus until it is ready to be born.
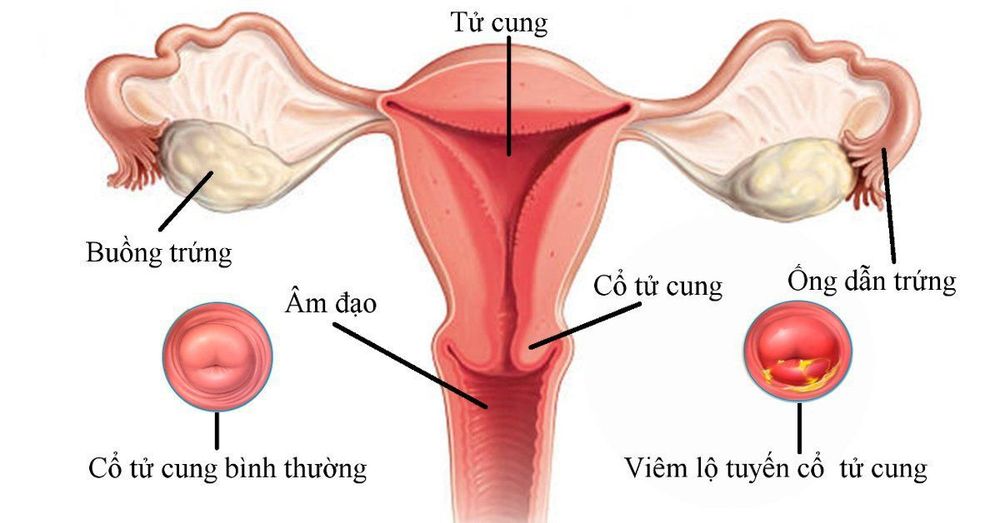
1. Position of the uterus
The uterus is located in the middle of the pelvis, behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. The actual position of the uterus in the pelvis varies from person to person. Each position has its own name:
Anterior reclining position: Uterus with head slightly forward Reclining position: Uterus slightly bent backward Both of these positions are normal and the position of the uterus is correct. can change throughout a woman's life, most often after pregnancy.
Trắc nghiệm: Sự hiểu biết của bạn về kinh nguyệt
Kinh nguyệt có vai trò quan trọng đối với sức khỏe sinh sản, do đó nữ giới cần chủ động trang bị kiến thức để theo dõi và kiểm soát tình trạng sức khỏe. Bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn hiểu hơn về chu kỳ kinh nguyệt của bản thân.2. Uterine components and functions
2.1. Fundus The fundus is the upper part of the uterus. It is wide and curved. The two fallopian tubes attach to the uterus just below this part.
2.2. Uterus Body The uterine body is the main part of the uterus. This part is composed of many muscles and can be stretched to protect the developing fetus. During labor, the muscular wall of the body of the uterus contracts to help push the baby out through the cervix and vagina.
The body of the uterus is lined by a mucous membrane called the endometrium. This membrane responds to reproductive hormones by changing its thickness during each menstrual cycle. If an egg is fertilized, it attaches to the endometrium. If no fertilization occurs, the endometrium sheds its outer layer of cells, and is expelled during menstruation.
2.3. Isthmus The part of the uterus that lies between the body of the uterus and the cervix is called the isthmus. This is where the walls of the uterus begin to narrow toward the cervix.
2.4. The cervix The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus. It is lined with a smooth mucous membrane and connects the uterus to the vagina. Glands in the lining of the cervix normally secrete thick mucus. However, during ovulation, this mucous membrane becomes thinner to allow sperm to easily enter the uterus.
The cervix consists of three parts:
The hole in the cervix: This is the inner part of the cervix, leading into the uterus. Cervical canal: The canal connecting the uterus and vagina. Ectopic opening: This is the outer part of the cervix, which protrudes into the vagina. During labor and delivery, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
3. Common Uterine Problems
3.1. Congenital Uterine Defect The word congenital refers to something that a person is born with. According to the March of Dimes, about 1 in 300 women are born with a birth defect of the uterus. In some cases, birth defects of the uterus cause pregnancy complications.3.2. Some examples of congenital uterine anomalies are: Separation of the uterus. A band of muscle separates the uterus into two separate parts. Two-horned uterus. The uterus has two smaller chambers instead of one large cavity. Double uterus. The uterus has two smaller chambers, each of which has its own cervix. Unicorn uterus. Only half of the uterus is formed Endometriosis.
Endometriosis occurs when the endometrium, usually inside the uterus, grows on the outside of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or pelvic lining. It can cause severe pain, especially during menstruation or during sexual activity.
3.3. Uterine Fibroids Uterine fibroids are benign growths on the wall of the uterus. They can range in size from very small (the size of a seed) to quite large (the size of an orange). Although fibroids do not always cause symptoms, some women experience bleeding and pain. In addition, in some cases, larger fibroids can also lead to fertility problems.
3.4 Uterine Prolapse Uterine prolapse occurs when a supporting organ system is dilated or damaged. Uterine prolapse when part of the uterus slides down into the vagina. In severe cases, part of the uterus may slip out of the vaginal opening. There are many reasons for this situation; including childbirth, surgery, menopause, or extreme physical activities.
3.5. Pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It is sometimes caused by the same bacteria that cause gonorrhea and chlamydia, although other bacteria can also be to blame.
The main symptoms of PID are pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain during intercourse and urination. Other symptoms may include unusual vaginal discharge, fatigue, and unusual bleeding. If left untreated, PID can cause infertility and increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
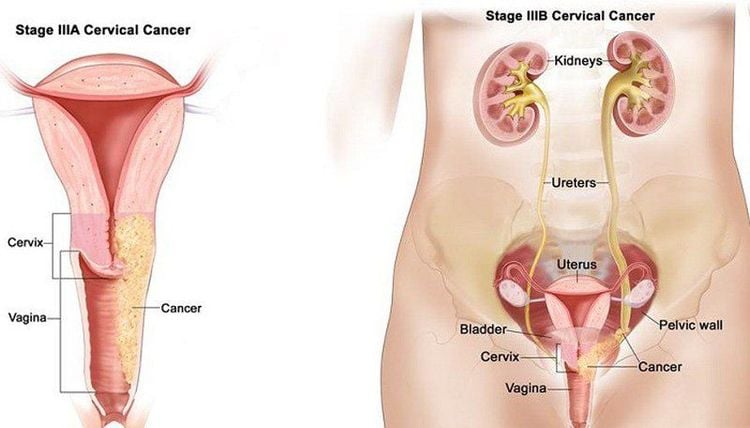
3.6. Cancer Although uterine cancer can begin anywhere in the uterus, it is most common in the endometrium. Certain conditions increase a woman's risk of developing endometrial cancer, like being obese or taking estrogen without progesterone.
Cancer can also affect the cells of the cervix, causing cervical cancer. Doctors are uncertain about the exact causes and risk factors of cervical cancer, but smoking and sexually transmitted diseases appear to be a factor, plus having a system A weakened immune system also increases the risk.
Common symptoms:
Heavy menstrual bleeding Intermenstrual bleeding Unusual or unpleasant vaginal discharge Pelvic or lower back pain Menstrual pain or pain during sex Pain when urinating or bowel movements See your doctor if you notice any of the above symptoms. With a medical history and physical exam, doctors can narrow down what's causing the condition.
4. The secret to a healthy uterus
4.2. Get routine HPV vaccinations Pap smears Pap smears can detect precancerous changes in the cervix, along with other uterine problems. . The American Cancer Society recommends:
All women 21-29 years old should have a Pap smear every three years Women over 30 should have a Pap smear, along with an HPV test every five years through Age 65, once vaccinated against HPV Women over 65 years of age can stop having a Pap smear if they have had it periodically in the previous 10 years, unless the woman is at high risk for uterine cancer. Cervical cancer screening is one of the methods to help screen and detect the disease early for treatment and prevention. The gynecological cancer screening package at Vinmec will assist customers in performing tests and ultrasound of the uterus to detect abnormalities early for a treatment plan.
4.2 Get vaccinated against HPV The HPV vaccine can protect you against 9 strains of the virus. Females between the ages of 9 and 26 can get the HPV vaccine. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration rates this vaccine as preventing up to 90% of cervical, vaginal, and anal cancers. Vinmec International General Hospital always provides HPV vaccines, especially women who need HPV vaccination before becoming pregnant to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
4.3. Using a condom during sex Using a condom during sex prevents the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, which increase the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease or cervical cancer for women.
4.4. Don't smoke Smoking is linked to certain types of cervical cancer.
4.5. Healthy diet

Folic acid rich foods, such as asparagus, broccoli and other green vegetables. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as oranges and grapefruit. Foods rich in beta carotene, such as carrots, squash, and cantaloupe. Foods rich in vitamin E, such as whole grain breads and cereals.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com