This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Umbilical cord ultrasound, placental ultrasound are ultrasounds of the fetal appendages that play an important role in detecting abnormalities affecting the fetus.
1. Umbilical cord ultrasound
1.1. Normal umbilical cord ultrasound The normal umbilical cord ultrasound has the following characteristics:Location: The umbilical cord plugs in the center of the placenta, sometimes the umbilical cord can be inserted at the center or edge. Size: The umbilical cord is 12-15mm in diameter. Structure: The normal umbilical cord has a structure of 3 blood vessels, in which there are 2 arteries and 1 vein, 2 arteries twist around the veins to form the helix. The umbilical cord has an average of 12 turns. 1.2 Abnormalities in umbilical cord ultrasound Abnormalities in umbilical cord ultrasound are classified into insertion site abnormalities, size abnormalities, and structural abnormalities.

Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có biết thai nhi tuần 6 phát triển như thế nào không?
Thai nhi tuần 6 đánh dấu một mốc tăng trưởng với tốc độ phi thường. Mẹ chắc hẳn đang rất hạnh phúc và tò mò về sự phát triển của con từng ngày. Để biết bé phát triển ở mức độ nào, mẹ có thể làm bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2. Ultrasound of the placenta

2.1.1 Structure The normal placental structure is semicircular, located adjacent to the uterine wall and can be clearly identified from 11 weeks. The placental ultrasound showed a normal placental structure consisting of The three distinct parts are the basement membrane, chorion, and placental tissue. The placental structure develops throughout pregnancy. 2.1.2 Biometric indicators The thickness of the placenta increases with gestational age, at term the placenta has a maximum thickness of 45mm. 2.1.3 Clinging position The position of each other that can be attached is bottom, front, back, right or left side. On ultrasound of the placenta, the attachment position is normal if the distance between the endocervical opening and the inferior edge of the placenta is > 4 cm.
2.2 Abnormalities in placental ultrasound
Pathological images of placental ultrasound show abnormalities in fetal structure, location and morphological features.2.2.1 Structure Abnormalities in the chorion of the placenta include: subamniotic lesions and subchondral lesions.
Subamniotic cysts include:
Subamniotic cysts : There may be a single cyst or a polycyst. A single cyst probably won't cause any harm to the unborn baby. In the case of many large cysts and cysts in the placenta, it can cause fetal growth retardation. Subamniotic Hematoma: A placental ultrasound showed a subamniotic hematoma containing fetal blood and adjacent to the umbilical cord, which was the result of rupture of blood vessels exiting the chorion. Subchoroidal lesions include:
Pancreatic monolayer cyst: If present, a single cyst is not pathological. If it appears polycystic and large in size, it can cause underdevelopment of the fetus. Subchorionic Hematoma: A placental ultrasound shows a subchondral hematoma containing fetal blood and often located adjacent to the umbilical cord, as a result of rupture of a blood vessel exiting the chorion. Subchondral Thrombosis: Subchondral thrombosis is a dangerous abnormality that can cause fetal death in utero.
Partial ovum: This abnormality is also known as triploid syndrome. The placental ultrasound image shows an enlarged placenta with many internal cavities, the fetus present is often underdeveloped and sometimes malformed. Placenta Comb: This abnormality can appear from the 11th week of pregnancy. The placental ultrasound showed large blood pools, the pregnant woman had a history of cesarean section. Placental ultrasonography helps in early detection of interdental placenta
Villi space: In most cases, this villi is not pathologically significant, however in a few cases It will cause fetal underdevelopment if blood lakes appear early (before 25 weeks) in large numbers (>3) and large in size (>2cm). Intervilliary thrombosis: When the amount of blood clots is high and with infarct lesions, it can cause poor fetal growth. Placental Infarction: This abnormality is the result of one or more placental uteroplacental arteries cease to circulate and the fetus is often detected in pregnant women with vascular disease. Placental Mesothelial Dysplasia: This lesion can be detected by placental ultrasonography and has progressed normally with pregnancy, possibly threatening preterm delivery, preeclampsia, intrauterine growth retardation, fetal death in utero, Wiedeman-Beckwith syndrome (granulomatosis, gigantism, abdominal wall defect, risk of severe neonatal hypoglycemia, predisposition to development of fetal tumors in infancy small).

Chorionic villus tumours : Vascular tumors due to abnormal proliferation of villi blood vessels creating a network of arteriovenous connections in the placenta, which can be detected by ultrasonography. placental sound with hemangioma size up to 4cm. This abnormality can cause complications in both mother and baby. Choroidal choroidal angiomas: In some cases, choroidal angiomas present avascular, however, do not pose a threat to the fetus. Monitoring the vascular status of the lesion with placental ultrasound can help predict abnormality. Complications for the mother can occur is polyhydramnios, causing premature rupture of membranes. Complications for the fetus are anemia, heart failure, fetal edema, placental abruption, severe fetal death in utero. Partial ovum: The placental ultrasound shows that the placenta is generally large, partly normal and partly with fluid cavities, amniotic cavity, embryo or fetus with low mobility, fetal growth retardation and often multiple deformities. There is an abnormal number of triploid chromosomes. However, this abnormality has a non-malignant prognosis. Abnormalities in the basement membrane of the placenta include:
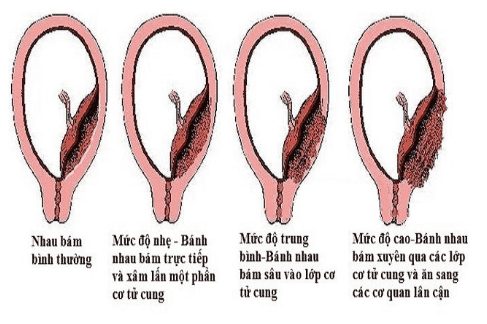
Fibrin deposition: Fibrin deposition, if abnormal, causes calcification of the entire basement membrane and is associated with other abnormalities such as infarction and thrombosis between the villi, leading to fetal growth retardation. The placental abruption consists of a posterior decidual hematoma and a hematoma at the edge of the posterior decidua. This abnormality is often associated with cleft lip or placenta previa. Placenta Comb: Factors that increase the risk of placenta accreta include previous uterine surgery, history of curettage, and multiple pregnancies.
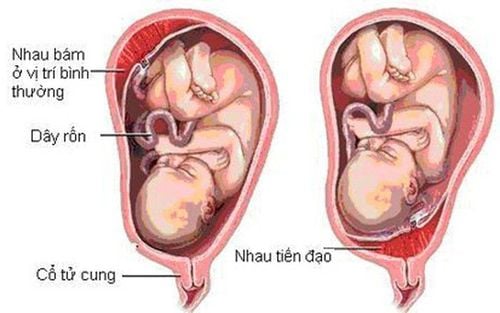
Placenta praevia: Used to refer to the placenta completely or partially attached to the lower part of the uterus. The low complication rate of placenta previa, which causes vaginal bleeding in the third trimester of pregnancy, increases the risk of bleeding for the mother and baby from placental abruption. Placenta previa can be diagnosed on clinical examination, or discovered incidentally during routine obstetric examination and placental ultrasound. The following factors are thought to increase the risk of placenta previa: a history of previous pregnancies with placenta previa, multiple pregnancies, an older woman, a history of uterine surgery or an abortion. , history of endometritis, multiple pregnancy, uterine malformation, submucosal fibroids, or the mother smoked during pregnancy. 2.2.3 Morphological features
Morphological abnormalities of the placenta (usually very rare, accounting for 5%) include: accessory placenta, two-lobed placenta, and extrachorionic placenta, which can be detected by ultrasound of the placenta. together .
Ultrasound of the fetal appendages including the umbilical cord and the placenta helps to timely detect abnormalities in pregnancy, from which the doctor will advise on appropriate treatment and health care for the mother and baby.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package Maternity Care Program for pregnant women right from the first months of pregnancy with a full range of antenatal care visits, periodical 3D and 4D ultrasounds and routine tests to ensure that the mother is healthy and the fetus is developing comprehensively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.