This is an automatically translated article.
Ultrasound and blood tests are the two basic diagnostic tests used to diagnose miscarriage. In the diagnosis of recurrent miscarriage, women need further testing for genetic and genetic problems to determine the cause of the miscarriage.1. What is a miscarriage?
Miscarriage is defined as the premature birth of a fetus before the fetus is viable. According to the World Health Organization, a miscarriage is the end of a pregnancy before 20 weeks or the birth of a fetus weighing less than 500g.More than 80% of miscarriages occur within the first 3 months of pregnancy, the remaining 20% occur in the second trimester. Miscarriages before 12 weeks are called early miscarriages, and miscarriages that occur between 12 and 20 weeks of pregnancy are late miscarriages. Natural miscarriage usually takes place in 2 stages: threatened miscarriage. actual pregnancy and miscarriage.
Miscarriage is divided into 2 types: spontaneous miscarriage and consecutive miscarriage.
Natural miscarriages are miscarriages that suddenly occur in women with normal pregnancies. Repeated miscarriage is when a woman has had 3 or more spontaneous miscarriages in a row. Repeated miscarriage is often rapid, signs of threatened miscarriage are not clear.
2. Clinical diagnosis of miscarriage
2.1. Threatening miscarriage
Trong giai đoạn này điều trị sớm có khả năng giữ được thai
Vaginal bleeding is the main symptom, women have red or black blood, small amount, can last for many days, blood is often mixed with mucus. Most women with threatened miscarriage do not have abdominal pain, only a feeling of pressure or heaviness in the lower abdomen. If the pain is severe and continuous, it means that it is due to uterine contractions, the prognosis is poor, it is difficult to keep the pregnancy.
External physical examination is of little value because the uterus and fetal part are still small, making it difficult to detect symptoms. Vaginal examination: the cervix is long, closed, the body of the uterus is soft and large, corresponding to the gestational age.
Subclinical:
Positive HCG test Ultrasound: there is a phenomenon of dissection of a small part of the placenta or placenta, from the 6th week, the amniotic sac border is clear and even, with echoes of the embryo. The 8th week has a fetal heart rate. 2.2. True Miscarriage Women who have had a miscarriage often experience intermittent, but more frequent, lower abdominal pain due to uterine contractions. Vaginal bleeding heavily, red, thin and clotted indicates that the vegetable has shed a lot, or there may not be much bleeding but persists for more than 10 days.
When examining the vagina, the cervix is thin and open. The lower part of the uterus is enlarged due to the uterus being pushed down towards the cervix, making the cervix look like a gyrus. Sometimes a gestational sac is palpable in the cervical opening.
2.3. Recurrent miscarriage Patients often have symptoms of threatened miscarriage before, then develop more abdominal pain, more bleeding, can detect a piece of tissue expelled from the vagina, however Vaginal bleeding continued and dull abdominal pain persisted.
Vaginal examination shows that the cervix is still open or closed, but the body of the uterus is still larger than normal. The patient may present with an infection. Ultrasound can show residual placenta in the uterine cavity.
2.4. Hemorrhagic miscarriage The common manifestation of hemorrhagic miscarriage is heavy vaginal bleeding, fresh blood. The patient may go into hemorrhagic shock.
Vaginal examination shows a lot of fresh blood and clots, often with a fetal part in the cervix or in the vagina. In case the patient arrives late, the pregnancy has been miscarried, then these symptoms are no longer present but only bleeding symptoms are prominent.
2.5. Infectious miscarriage Pregnant women with prolonged vaginal bleeding accompanied by an infection syndrome: fever, rapid pulse, fatigue, lethargy, increased white blood cell count, increased CRP.
Vaginal examination shows that the cervix is dilated, the vaginal blood is dark, foul. The uterus is soft, painful to press.
Biểu hiện thường gặp của sảy thai băng huyết là ra máu âm đạo nhiều, máu tươi
3. Miscarriage diagnostic test
3.1. Diagnostic test for spontaneous abortion Definitive diagnosis of miscarriage is generally not difficult, mainly based on clinical symptoms and laboratory tests.Tests help determine for sure whether a pregnant woman has a miscarriage or not. Ultrasound and blood tests are two basic tests and techniques to diagnose miscarriage:
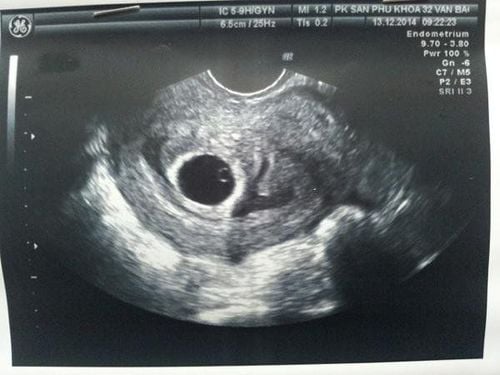
Ultrasound Ultrasound is usually ordered first to check the development of the fetus and see if there is a fetal heart. In most cases, a doctor uses a transvaginal ultrasound by inserting a small probe into the vagina. This may cause some discomfort, but it should not cause pain.
Pregnant women can choose transabdominal ultrasound, but the accuracy is lower. Ultrasound is not harmful to the fetus and does not increase the risk of miscarriage.
Blood tests Pregnant women should have blood tests to measure pregnancy-related hormones, such as Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin ( β-hCG ) and progesterone . Tests may be repeated after 48 hours if:
Concentrations are borderline. Ultrasound results are not clear. Tested too early in pregnancy. Miscarriage is sometimes undiagnosed right after an ultrasound or blood test. For example, when a fetal heart rate cannot be seen on ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy (less than 6 weeks). In this case, you will have another ultrasound and/or blood test after a week or two.
3.2. Diagnostic tests for consecutive miscarriages Repeated miscarriage is when a woman has 3 or more miscarriages in a row, the following tests can be used to find the cause. However, half of all miscarriages have no known cause.
Set up chromosomes If a pregnant woman miscarries for the third time, her doctor will advise her to check for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. If an abnormality is found, then both the mother and the husband should be checked for chromosomes, genetic and genetic problems.
If the cause is from the mother's or her husband's chromosomes, the pregnant woman will be referred to a clinical geneticist for a solution. In some cases, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is a highly effective assisted reproductive method of choice.
Ultrasound Transvaginal ultrasound is used to check for structural abnormalities of the uterus. The second method is 3D ultrasound to survey the lower abdomen and pelvis to help make the diagnosis more accurate.
Ultrasound can also assess whether a pregnant woman has a cleft palate. This can only be done at the start of the pregnancy again, usually between the 10th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
Some cases of fetal growth arrest are diagnosed during routine ultrasound. On ultrasound, it can be seen that the fetal heart is not working or the gestational sac/embryo is shrinking.
Blood tests Blood tests can determine levels of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies and lupus anticoagulants. This test should be done twice, about 6 weeks apart, before a woman wants to get pregnant.
Antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) increase the risk of thrombosis and alter placental attachment. These changes lead to reduced blood flow to the fetus and can cause a miscarriage.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.