This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Congenital syphilis is caused by an infection from a mother with syphilis that is transmitted through the placenta or during childbirth. Congenital syphilis can cause death or birth defects in an unborn baby. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to prevent mother-to-child transmission of syphilis.
1. What is congenital syphilis?
Syphilis is an infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. This is a sexually transmitted disease mainly caused by not using protection when having sex.A mother with syphilis can transmit to the fetus through the placenta, causing fetal infection, increased risk of miscarriage, premature birth, stillbirth. During pregnancy, the fetus will be infected with syphilis from the mother and when born, the baby will have congenital syphilis. Newborns are also infected from their mothers when they are born by vaginal delivery.
2. How is syphilis transmitted from mother to child?
Most syphilis symptoms in pregnant women are difficult to recognize because they are not as obvious as in non-pregnant women, so they are often not detected in time.
Besides, the lesions of second stage syphilis often do not have their own characteristics, so it is difficult to detect. Therefore, the mother easily transmits the disease to the fetus and causes congenital syphilis. Studies also show that, during the first 4 years of having syphilis, if a woman is left untreated, there is a high risk of infecting her unborn baby.
Mother-to-child transmission of syphilis occurs between the 4th and 5th months of pregnancy because this time the placenta allows the mother's blood to easily exchange with the fetal blood, which creates an opportunity so that spirochetes can enter the fetus through the umbilical blood vessels and spread the disease.
3. Manifestations of congenital syphilis
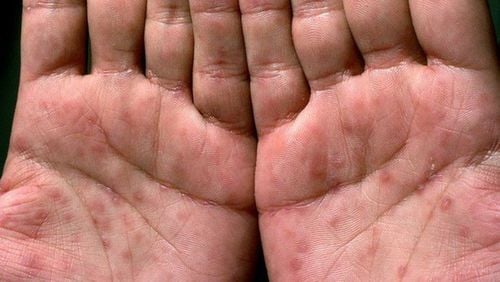
Children with congenital syphilis transmitted by the pregnant mother will have syphilis in many different forms, including early congenital syphilis and late congenital syphilis. Depending on the severity of the infection, the symptoms of congenital syphilis will have different features.3.1 Manifestations of early congenital syphilis Early congenital syphilis usually appears in the first 2 years of a child's life; In mild cases, infants with congenital syphilis at birth appear normal, but after a few days or 6 to 8 weeks later, syphilis lesions appear similar to those of secondary syphilis. : blisters on palms and feet, cracks in the edges or around the nostrils, runny nose with blood, difficulty breathing...; In particular, in the first 6 months after birth, children infected with congenital syphilis may experience inflammation of the bones and cartilage in the long bones with manifestations such as: large bones, pain at the ends of bones, hindering movement extremities or osteochondritis pseudochondral parrot - with pain in the long bones at night because the ends of the bones leave the body, leading to paralysis; When a child is 2 years old, inflammation of the bones and periosteum may appear in the knuckles and toes. 3.2 Manifestations of late congenital syphilis Late congenital syphilis usually appears when children are over 3 years old, sometimes it is not until 5-6 years old or in adulthood that symptoms appear. At this time, the disease has symptoms similar to syphilis in the third or second stage. There are cases where the disease has no clinical symptoms, so it is also called the closed syphilis period; To diagnose congenital syphilis, it must be based on positive serologic test results or on the basis of manifestations such as: iritis appearing at puberty starting with symptoms of eye pain, photophobia, glare. eyes on one side then spread to both sides, which can lead to blindness; Bilateral watery knee arthritis, painless, appeared quietly between 10 - 20 years old; Deafness in both ears beginning at age 10, often accompanied by interstitial iritis; Bone lesions with perforated palate, flat nose, protruding forehead, tibia blade.
4. How dangerous is congenital syphilis?
If the fetus is infected with spirochetes massively, the fetus will not live and there is a risk of miscarriage at 5-6 months of pregnancy; If the fetus has a milder spirochete infection, it may be born prematurely and is also very difficult to survive.5. How to prevent congenital syphilis
In fact, most of the cases of pregnant women with first and second stage syphilis give birth to babies with congenital syphilis, most dangerously many babies die when they are born. recently born or shortly after.However, there are also cases in which a pregnant woman has syphilis during the latent period, where the baby may not be born with congenital syphilis or have a separate, milder form of syphilis and are not at risk. affect life after birth.
Therefore, in order to prevent children from being born with congenital syphilis, affecting their health and future, it is necessary to strictly follow the following notes:
Go to medical facilities for examination and tests. experience before planning pregnancy and childbirth;

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.