This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist II Bui Le Phuoc Thu Thao - Radiation Oncologist - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Treatment of central nervous system lesions by brain radiosurgery (STEREOTACTIC RADIOSUGERY – SRS) at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital is a completely new technique in Vietnam. This technique has only been applied at the world's leading radiation therapy centers for about 10 years now. This is considered the most modern brain radiotherapy technique in Southeast Asia, bringing positive signals in the treatment of cancer.
1. Introduction to SRS . radiosurgery
Radiosurgery (translated from Stereotactic radiosurgery), sometimes also called stereotactic radiotherapy, is radiation therapy that delivers high doses of radiation to a tumor with the help of a mass localization system. multidimensional tumor with accuracy <1mm. Therefore, patients only need 1 to 5-6 times of radiation therapy to finish the treatment, which is very convenient for the patient. However, this radiation technique requires special radiotherapy systems, complex navigation systems and highly trained personnel.
Although, the name refers to a specific surgical technique, but radiosurgery is not a surgery at all. It is so named because radiosurgery can act as a replacement for the scalpel blade, which can "vaporize" the tumor without significantly affecting the surrounding healthy tissue.
Initially, this method was developed to treat some tumors of the central nervous system (SRS). This technique was later expanded, and could be applied to treat some cancers located in other parts of the body, such as some malignancies in the lungs and liver. At that time, the technique of radiosurgery was called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT).
2. In what cases is radiosurgery indicated?
Not all cases of tumors can be performed radiosurgery. For the central nervous system, the following are some possible indications for radiosurgery:
2.1 Nonproliferative lesions Intracerebral arteriovenous malformations Intracerebral arteriovenous fistulas Trigeminal neuralgia
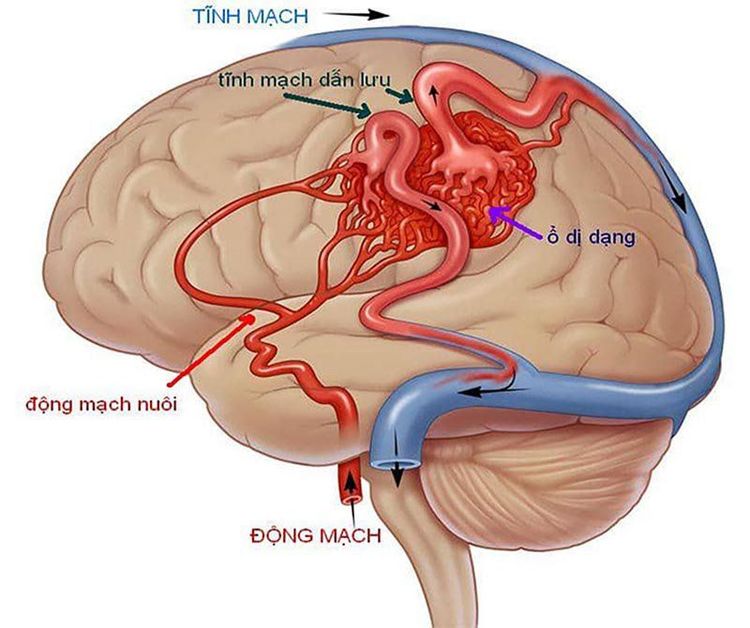
Previously, radiation therapy for metastatic cases was mainly whole brain radiation with 2D or 3D techniques. Some recent studies show that if the number of metastases is small and small in size, SRS radiosurgery alone gives better control results than whole brain radiation and has less impact on the patient's cognitive ability, from That improves the patient's quality of life. Some even report that radiosurgery can be performed in patients with multiple lesions (up to 10-20 lesions). This shows the absolute superiority of radiotherapy (specifically, SRS radiosurgery) over surgery.
3. How is radiosurgery performed?
Radiosurgery techniques can be performed with some radiotherapy systems such as Gamma Knife, Cyber Knife or some newer accelerators.
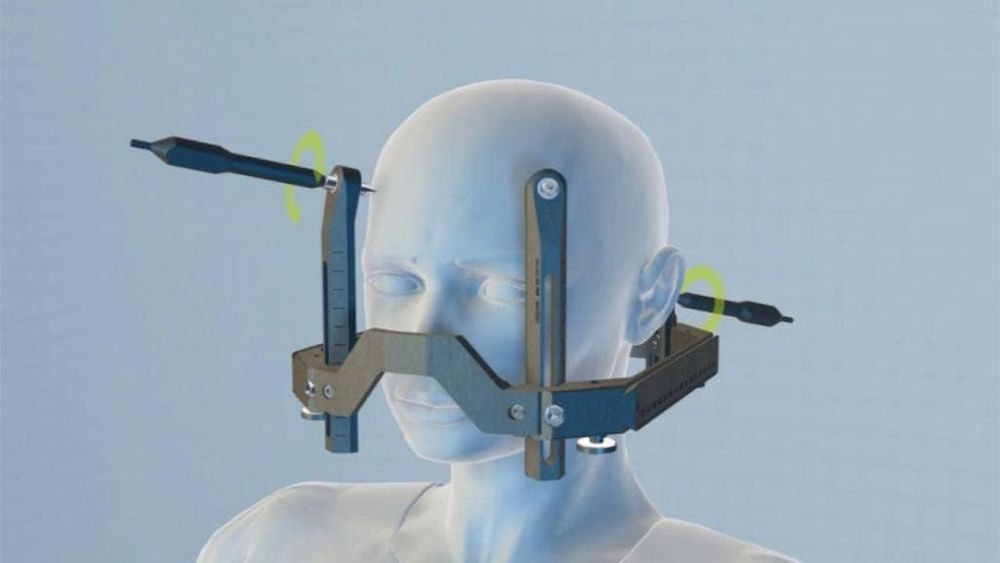
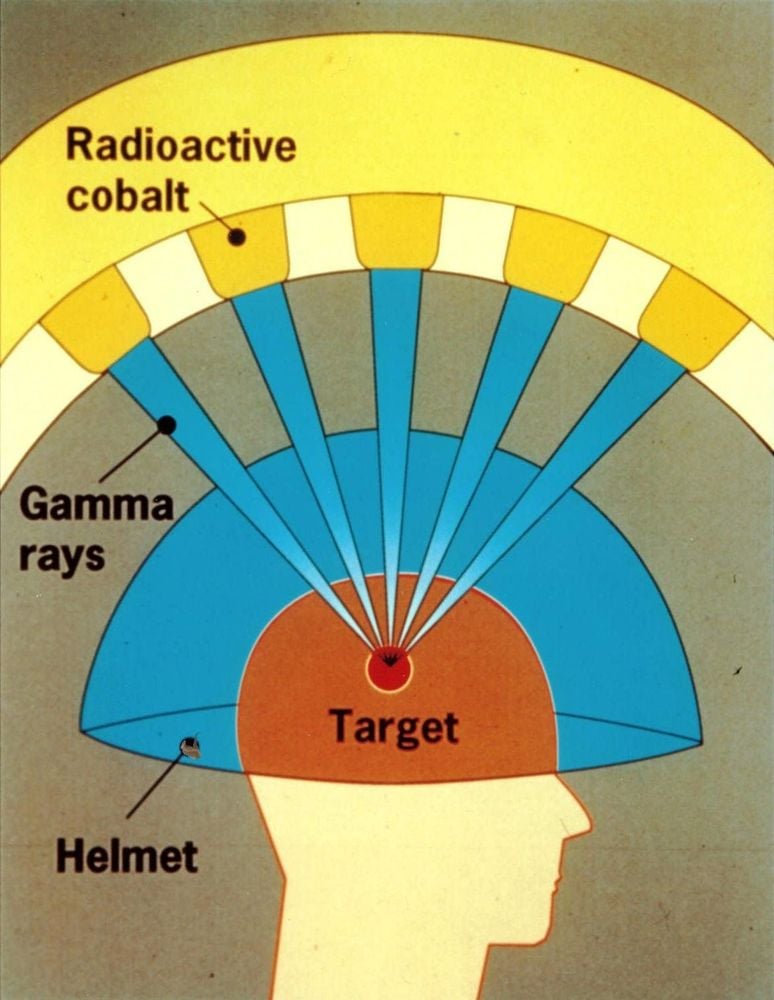
With the Gamma Knife: The patient is immobilized with an external fixation frame. The patient then undergoes an MRI or CT simulation to help the doctor clearly identify the tumor, its shape, size, location, and plan treatment. The original Gamma Knife system used 201 Cobalt 60 radioactive sources mounted on a hemispherical frame controlled by a computer system to focus on gamma rays to focus on the location of the lesion requiring radiation therapy. The Gamma Knife machine only performs radiosurgery for brain lesions and cannot treat sites other than the brain.
Cyber Knife radiosurgery: consists of a miniature accelerator attached to a robot control arm and an image guide system to ensure accuracy when beaming. The image guidance system helps to monitor the movement of the tumor during radiation, to guide the movement around the tumor of the robotic arm carrying the radiation accelerator. This technique helps to deliver radiation beams to the tumor by many different angles, focusing high doses on the tumor and limiting the dose to healthy organs.
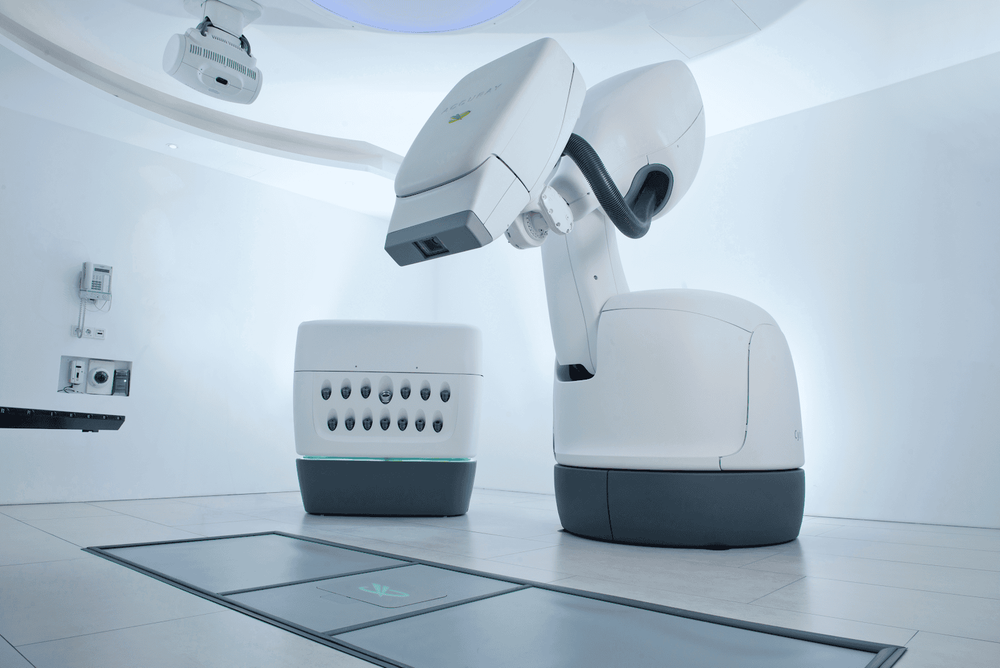
Radiosurgery with TrueBeam at the Radiation Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park Hospital:
Currently, the TrueBeam machine at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital is the most modern accelerator in Vietnam and compared to other countries in the region. This system in addition to performing advanced radiotherapy techniques such as IMRT radiation therapy, VMAT also performs the most advanced radiosurgery techniques such as SRS and SBRT.
With HypercAr technique applied in planning and radiotherapy of brain lesions, it brings optimal results compared to previous radiosurgery techniques. This technique has been used around the world since 2017 and first appeared in Southeast Asia at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. With this technique, the radioactive source will move around the position to be irradiated in a circular arc and continuously emit rays, the arcs are not coplanar to help optimize the dose distribution, uniformity and localization to the limited tumor. Reduce radiation dose to adjacent healthy tissue thereby avoiding maximum complications of radiation therapy.
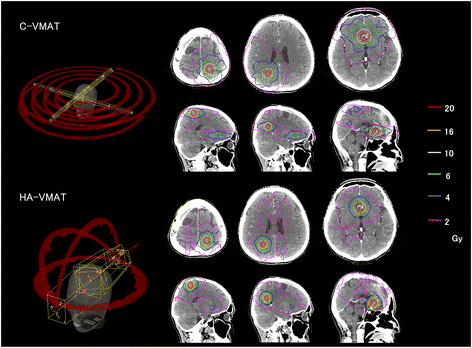
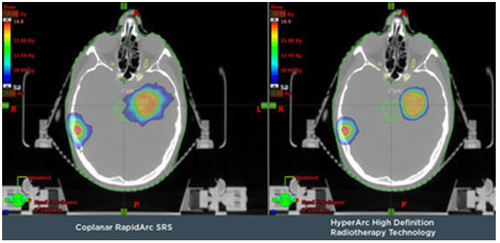
In addition, at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, there is also an Optical Surface Monitoring System (OSMS) that observes the patient's head movement to support accurate beam emission to millimeters. The patient does not need to drill the skull to attach the external fixed frame like radiotherapy with the Gamma Knife system.
In addition, the Encompass dedicated head immobilization system of Qfix (USA) is also specially designed to be used specifically for this SRS radiation system, ensuring the most accurate fixation of the patient's head. but still keep comfort and lightness during radiotherapy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.