This is an automatically translated article.
Genital prolapse is a fairly common disease in women in ancient times. Nowadays, due to higher knowledge and better quality of life, this disease tends to decrease much. This disease is not life-threatening but affects daily life and activities.1. What is genital prolapse?
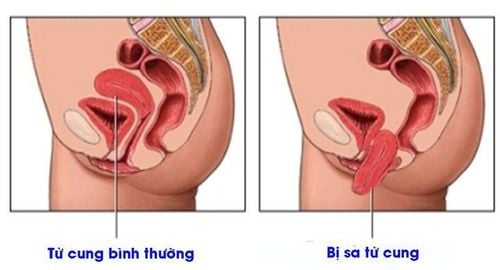
Genital prolapse occurs when the pelvic floor muscles and ligaments stretch and weaken, unable to hold the uterus. Therefore, uterine prolapse can cause the uterus to prolapse and protrude into the vaginal area. However, in many cases, not only the uterus, but also the anterior vaginal wall with bladder prolapse and the posterior vaginal wall with the rectum.Genital prolapse is a disease with a higher rate in rural areas, it is common in people who have many pregnancies, give birth too early, too thickly, and have not been delivered safely and with proper technique in previous births. .
Genital prolapse is divided into 3 levels according to the prolapse location of the cervix, so that appropriate surgery can be indicated. Specifically
Genitourinary prolapse I: The cervix is low in the vagina but has not reached the vulva. Genital prolapse II: Cervix prolapse vulva. Grade III genital prolapse: Uterus, low cervix, and cervix completely prolapse outside the vulva.

Sa sinh dục xảy ra khi cơ sàn chậu và dây chằng căng ra và suy yếu, không thể giữ được tử cung
2. Causes of genital prolapse
There are many causes of genital prolapse including:Multiple births, thick births, home births. The delivery was not delivered safely and with proper technique at a qualified and specialized medical facility. Perineal laceration was not sutured. Heavy labor, labor early after giving birth, presses on the soft perineum, which easily causes genital prolapse. Other causes of increased intra-abdominal pressure such as heavy occupation, chronic constipation, prolonged cough, etc. In addition, it may be due to congenital anomalies in people who have never given birth.
3. Some things to know about genital prolapse
Genital prolapse should be detected when the following symptoms are present:Detect prolapse of the vulva, perineum. Initially, the size of the prolapsed mass was small, the prolapse was infrequent, appeared when working or walking a lot, lying down, the mass dropped into the vagina or could be pushed up on its own. Later on, the prolapsed mass was frequent and could not be pushed up anymore. Severe pain in the lower abdomen Symptoms of urinary disorders (due to bladder and urethral prolapse): Difficulty in urination, painful urination, urinary incontinence, blood in urine, urinary retention. Disturbances of bowel movement (due to rectal prolapse): Difficulty defecation, constipation, or a feeling of straining or heaviness in the anal area. Bleeding, fluid from the cervix due to cervical inflammation, rubbing. The patient should be assessed for the size, extent, and composition of the genital prolapse by physical examination. The examination process needs to evaluate:
Whether the cervix has ulcerative lesions, hypertrophy or not. Let the patient sit or cough so that the genital prolapse appears more clearly (if the prolapse is not frequent). Assess their degree of adhesion in the case of old incisions, thereby predicting and predicting surgical methods. Rectal examination: the purpose is to assess the degree of rectal prolapse and the thickness of the rectal-vaginal part to help perform the surgery safely, to prevent rectal injury. Assess the condition of the perineum and anal levator muscle. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for genital prolapse. Medical treatment only applies to genital prolapse of grade I or prolapse of II, III but the patient is too old, too young, or has a systemic disease that contraindicates surgery.
4. How to prevent – prevent genital prolapse

Cần lưu ý không nên mang thai và đẻ quá gần nhau, tránh trường hợp sa sinh dục
Do not give birth at home. Pregnancy should be monitored during pregnancy and labor at reputable medical facilities to deliver birth safely and with proper technique. Closely monitor the labor process to not make labor too long, do not push for too long. Pregnant women need to be instructed on how to push properly. Obstetric procedures must be done according to indications, correct techniques and qualified to avoid trauma to the vagina and perineum. If the perineum is torn, it needs to be stitched. After giving birth, the mother needs to rest, avoid strenuous activities, heavy labor, early manual labor. Do not give birth thickly. For chronic diseases that often cause increased pressure on the abdomen (permanent constipation, prolonged cough...), it should be detected and treated early. In order to help customers detect and treat gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International Hospital has a basic gynecological examination and screening package, helping customers detect early infectious diseases and help treat easy, inexpensive. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, has no age limit and may have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Having menstrual problems: irregular menstrual cycle, irregular menstrual cycle Irregular vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Vaginal pain and itching Female clients have several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, Unsafe sex, abortion,... Female customers have other symptoms such as: Abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the private area, abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.