This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The mechanism of shock in dengue fever is a dangerous complication and has a high mortality rate. Severe dengue usually occurs as a result of secondary infection with another virus strain.
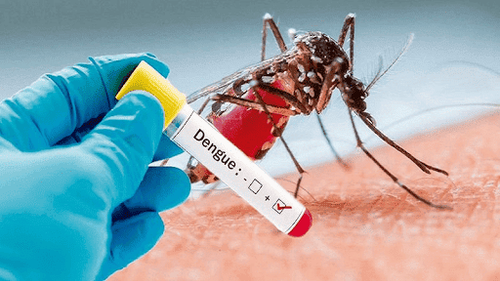
1. What is Dengue Shock?
About 20 million people are infected with the dengue virus each year in tropical and subtropical countries. The mortality rate of this disease is about 1-2%. Symptomatic manifestations of dengue are very broad, ranging from asymptomatic infection or mild symptoms, varying degrees of thrombocytopenia, to severe shock syndrome and multiple organ failure. The most severe manifestation of this disease is dengue hemorrhagic shock syndrome. So what is hemorrhagic shock?Mechanism of shock in dengue fever is a dangerous complication of dengue fever and has a high mortality rate. Severe dengue usually occurs as a result of secondary infection with another virus strain.
2. Shock mechanism in dengue fever
Dengue virus is transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes, mainly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. There are four serotypes of the virus that causes dengue fever. Although called serotypes, they are actually identified as four different species of the Flaviviridae family and the Flavivirus genus.Dengue virus infection has many different manifestations such as viral infection but no symptoms, symptomatic dengue fever is divided into dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever and the most severe is Dengue hemorrhagic fever.
While dengue is a simple disease, Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock are characterized by thrombocytopenia with hemorrhagic manifestations, increased vascular permeability, leading to intravascular volume depletion and shock.
2.1. The pathogenesis of dengue fever So far, the pathogenesis of Dengue hemorrhagic fever has not been fully studied. Currently, there are two main hypotheses put forward to explain the pathogenesis of Dengue hemorrhagic fever:
Virus virulence hypothesis: Dengue virus types with strong virulence cause severe illness and shock. , there is bleeding. Hypothesis on patient background: Due to re-infection with another type of dengue virus and due to the body's pathological immune response, shock phenomenon occurs in patients with dengue hemorrhagic fever. Currently, this hypothesis is supported by more people. The scientists found that antibodies to one type of dengue virus react with other types of dengue but fail to neutralize it, forming an antibody-virus complex. The Fc portion of these antibodies binds to cells carrying FcγRI- and FcγRII, resulting in an increased number of dengue virus-infected cells.

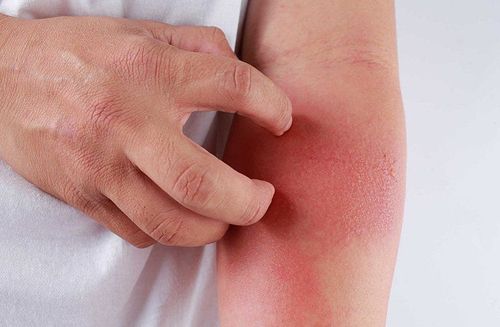
Biểu hiện nặng nhất của sốt xuất huyết là bị sốc sốt xuất huyết
2.2. Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic fever The pathophysiology of Dengue hemorrhagic fever includes two basic disorders:
Increased vascular permeability in dengue due to antigen-antibody, complement reaction, due to Dengue virus Reproduction in monocytes leads to:
Release of vasoactive mediators such as Histamine, Kinin, Serotonin, Anaphylatoxin,... Complement activation Release of organizational Thromboplastin Increase vascular permeability, fluid from the lumen The blood vessels will escape into the intercellular space, resulting in a decrease in the volume of blood circulating in the blood vessels, and the blood will be concentrated, leading to shock. When the circulatory volume is lost 10-15%, the human body can make up for it. If 20 - 30% is lost, shock will occur. If 35 - 40% is lost, the blood pressure is zero. Coagulation disorders in Dengue hemorrhagic fever are caused by some of the following causes:
Damage to the vessel wall and increased vascular permeability Thrombocytopenia Coagulation factors Decreased liver function leading to decreased synthesis of coagulation factors. However, more research is needed to clarify this issue. These two disorders can occur in patients with dengue, they interact with each other leading to severe clinical symptoms such as hemorrhage and shock.
Increased vascular permeability along with coagulopathy, myocardial dysfunction, and dehydration contribute to the development of shock, leading to multiple organ failure. The onset of shock in dengue can be dramatic and progressive. It is very complicated to define the pathogenesis of shock in dengue fever. Scientists already know that endothelial dysfunction is caused by cytokines and chemical mediators.
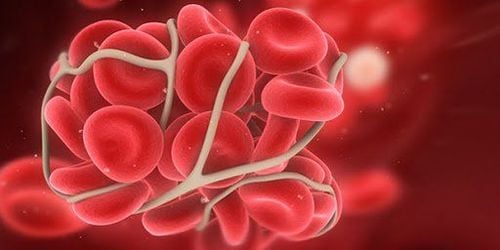
Tăng tính thấm thành mạnh là nguyên nhân gây rối loạn đông máu trong sốt xuất huyết Dengue
At Vinmec International General Hospital, emergency and treatment of many dengue fever cases with severe complications. Accordingly, the medical examination and treatment process at Vinmec is carried out methodically and intensively under the guidance of qualified and experienced doctors. Besides, under the support of modern facilities and advanced medical equipment, the treatment process has achieved high results.
If you have a need to examine and treat dengue fever at Vinmec, please book an appointment directly at the website or contact the hotline for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.