This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Ta Son - Doctor of Fetal Medicine - Department of Fetal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Sacrococcyx is a tumor that develops before birth in a baby's coccyx – known as the tailbone. It is the most common neonatal tumor, with an incidence of about 1 in 35,000 to 40,000 live births.
1. What is a sacroiliac tumor?
Sacrococcygeal teratoma is the most common neonatal tumor. This tumor is usually covered by the skin, but may also be covered by a thin, transparent membrane of tissue. Most tumors have many blood vessels that feed them. They come in different sizes, and they can sometimes grow out from behind or toward the baby's belly.
SCT is classified based on location and severity, specifically:
Group I: Tumor is outside the body and attached to the tail bone. Group II: Tumors both inside and outside the body. Group III: can be seen from the outside, but most of the tumor is inside the baby's abdomen. Group IV: is the most dangerous group, cannot be seen from the outside. They are located in the body at the level of the tailbone. SEE ALSO: Common congenital tumors in children
2. Diagnosis of sacral teratoma
Signs and symptoms of sacrococcygeal teratoma depend on the size and location of the tumor. Some tumors can be diagnosed prenatally with ultrasound.
Accordingly, the abnormally large abdomen is the first common sign suggesting the fetus has a tumor. A larger-than-normal uterus may be due to a large tumor or polyhydramnios. Less common manifestations include maternal preeclampsia. Tumors of the fetal sacrum can be cystic, solid, or mixed on ultrasound images. The heterogeneous density profile of the tumor may be due to mixed areas of tumor necrosis, cystic degeneration, hemorrhage, or calcification.
It may take the mother several days to evaluate and confirm the diagnosis of a sacroiliac tumor. The medical team will then explain the diagnosis and discuss treatments.
If the fetus is diagnosed with teratoma, the mother will continue to be monitored to evaluate the growth of the tumor or the change in the baby's health status to be able to intervene promptly if need. Your baby may need surgery to remove the SCT mass if the size and severity of the tumor causes complications such as fluid retention – putting the baby or mother at high risk.
Other tumors may not be discovered until after the baby is born. After birth, a baby may have symptoms indicative of SCT such as an inability to urinate or increased bowel movements because the tumor presses on the bladder or rectum. In addition, some children have no symptoms at all.
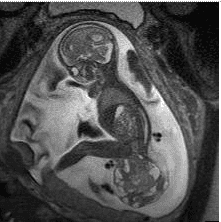
3. Risks and complications of sacroiliac teratomas
When antenatally diagnosed SCT is accompanied by fluid accumulation, the tumor can pose a threat to the health of both mother and baby.
In severe cases, the tumor "steals" blood from the fetal circulation, causing the fetal heart to work too hard and possibly leading to heart failure. Heart failure manifests as fetal edema, fluid accumulation in the fetal body cavities. Accordingly, the fluid accumulation that often accompanies SCT usually progresses rapidly and almost has a poor prognosis.
On the maternal side, there is a risk of “mirror syndrome” where maternal edema is similar to fetal edema. When this condition is present, the mother may experience fetal-like edema along with signs of preeclampsia – which is gestational hypertension, protein in the urine and edema caused by fluid retention.
4. Monitoring and planning the birth of a fetus with a diagnosis of sacrococcygeal teratoma
If the baby's condition is stable and there is no hypervolemic heart failure (oedema), the mother will be monitored with routine fetal ultrasound. If the teratoma is small in size, it is possible to give birth vaginally at full term.
If the SCT is large or polyhydramnios, elective cesarean section should be done early to avoid tumor rupture as well as the risk of preterm labor and delivery.
If the fetus is edematous, you may consider the indication for fetal surgery.
5. Treatment of sacroiliac teratomas
Treatment of SCT involves surgical removal of the tumor. Depending on the diagnosis and the severity of the tumor, surgery may be needed before birth or after birth. Accordingly, antenatal hysterectomy is only indicated when there is edema, putting the baby in a high-risk state.
6. Long-term follow-up
Most fetal sacrococcygeal tumors are less likely to be malignant and the prognosis is generally good after resection.
Is one of the rare tumors, but the disease can be detected early from the first trimester of pregnancy by using ultrasound to diagnose fetal malformations. Accordingly, early diagnosis is extremely important for the fetus to have the opportunity to monitor, laser ablation surgery to cut off the feeding vessel to make the tumor size smaller, providing a good prognosis for the child.
However, early diagnosis of birth defects as well as fetal tumor abnormalities is one of the difficult procedures, in order to detect pregnant women, it is necessary to choose reputable medical facilities. system of modern facilities, a team of specialists, capable of in-depth consultation and life-saving intervention in emergencies.
Understanding the psychology of parents who want to give birth to a healthy baby, in the examination process, Vinmec International General Hospital has equipped medical equipment for accurate image diagnosis today. such as the high-end 4D ultrasound system GE Voluson E10. With the new technology - Radiance System Architecture, this device enables enhanced imaging performance, 4 times the ultrasonic path of the previous generation for outstanding penetration, volume speed and high resolution. In addition, with the combination of the 3.0 Tesla MRI scanner system with a higher magnetic field, it allows the machine to quickly survey and reproduce detailed 3D images, so it can very clearly define the boundary (invasion level) of the tumor. teratoma, fetal amputation, as well as other birth defects.
In particular, at Vinmec, there is a team of doctors who specialize in ultrasound screening for fetal malformations, have performed prenatal diagnostic procedures, treated interventions right in the fetal period and are able to provide genetic counseling. Specialized transmission of rare diseases. With many years of experience in the management of high-risk pregnancies, doctors at Vinmec have diagnosed and "rescued" many fetuses with very severe birth defects with good prognosis and stable quality of life. after.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.