This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by CCII Doctor Bui Thu Huong - Head of Emergency, Day Treatment Unit - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Children with acute diarrhea, if not detected and treated promptly, will lead to dehydration and endanger their lives. Recognizing the signs of dehydration in children will help parents take quick action and protect the safety of their children's lives.
Diarrhea is the passage of loose or watery stools ≥ 3 times in 24 hours.
Acute diarrhea is diarrhea that has an acute onset and lasts no more than 14 days.
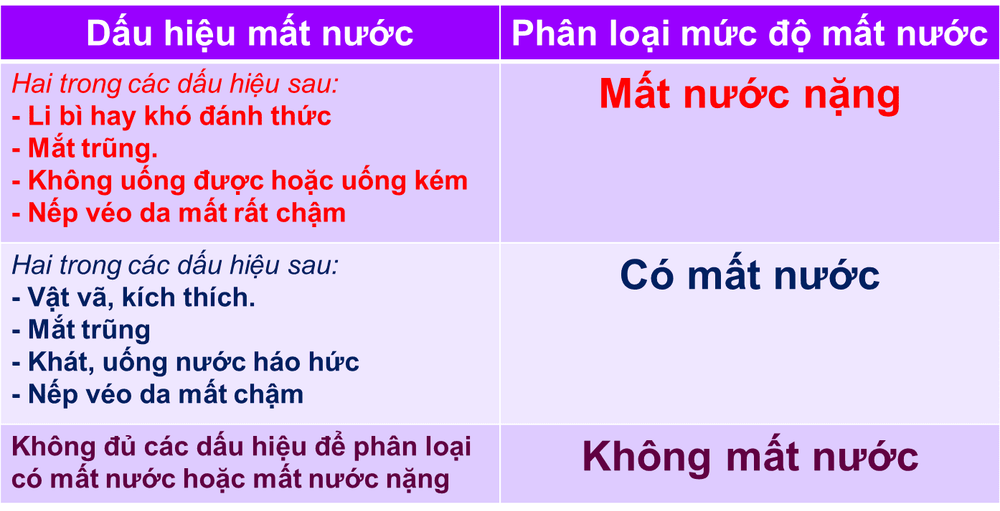
1. Signs of dehydration in children 2 months - 5 years old
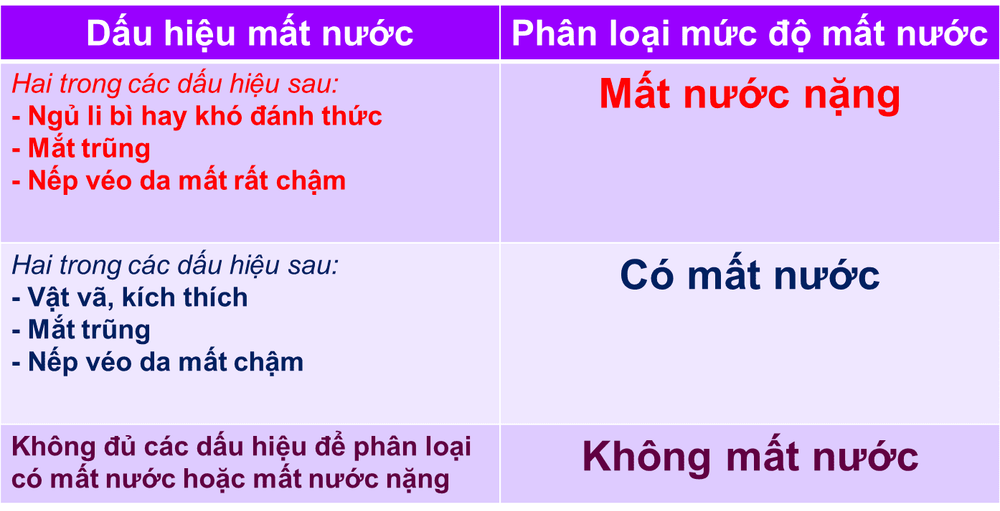
2. Signs of dehydration in babies 1 week - 2 months
3. Treatment of acute diarrhea in children
3.1 Treatment regimen A Treatment of cases of diarrhea without signs of dehydration. Dosage: Give the child water to drink after each bowel movement with the following amount of water:
ORESOL solution (ORS) low osmotic pressure is best

How to give drinking: Children < 2 years old, give each spoonful, older children give sip by cup or bowl. If the child vomits, stop waiting for 5-10 minutes and then continue to give it again. 3.2 Treatment regimen B Treatment of acute diarrhea in cases of moderate and mild dehydration, give ORS to children based on weight or age (if it is not possible)
Amount of ORS given to drink in the first 4 hours (ml): Amount of water (ml) = Patient weight x 75 ml.
How to give drink:
Children 2 years old, give each spoonful, every 1-2 minutes, give 1 spoonful, for older children, take sips by cup. If the child vomits, stop drinking for 10 minutes, then give it more slowly. After 4 hours reassess dehydration; if dehydration symptoms disappear, switch to regimen A, children still show signs of moderate and mild dehydration, continue with regimen B. If it worsens, switch to regimen C.
3.3 Treatment regimen C Applied in cases of severe dehydration Intravenous infusion immediately 100ml/kg Ringer Lactate solution (or physiological saline solution) divided the amount and time as follows

Every 1-2 hours reassess the patient. Transmit again with the same amount and time if the circuit is weak or not picked up. If dehydration is not progressing well, the infusion is faster. As soon as the patient can drink, give ORS (5ml/kg/hour). If infusion is not possible, insert a nasogastric tube for ORS at 20ml/kg/hour (total 120ml/kg) Resume feeding as soon as the child is able to eat such as continuing breast-feeding or giving other foods nutritious

Cha mẹ cần pha thuốc theo đúng liều lượng theo hướng dẫn của bác sĩ
4. Supportive treatment
Zinc supplementation in the treatment of acute diarrhea. Children 1 - < 6 months old: 10mg/day x 10-14 days Children ≥ 6 months old: 20mg/day x 10-14 days S. Boulardii: 200-250mg/day x 5-6 days in combination with rehydration and full electrolytes. Racecadotril: 1.5mg/kg/time x 3 times/day in combination with adequate rehydration, electrolytes and not more than 7 days Do not use antiemetics, take stools Ensure nutrition: Continue breastfeeding mother or previous milk, do not dilute the milk, avoid carbohydrates
5. Prevention of acute diarrhea in children
Breastfeeding Use of preventive vaccines: Fully vaccinated according to the expanded immunization program. Specific prevention of diarrhea with vaccines: Rotavirus, cholera, typhoid. Improve eating habits Use clean water for hygiene and eating Practice safe food hygiene when preparing or storing food Wash hands often when caring for children Use hygienic latrines Pediatrics department At Vinmec International General Hospital system, it is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children,. ...With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
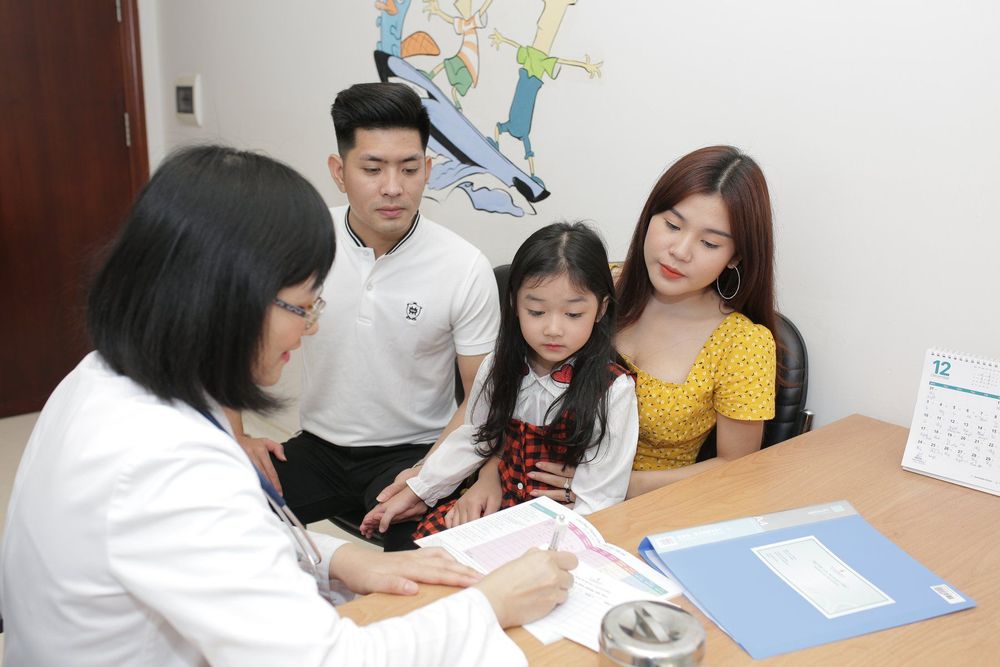

Khi trẻ bị tiêu chảy kéo dài cha mẹ nên đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ Nhi khoa để được thăm khám và điều trị
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
READ MORE
Prevention and treatment of acute diarrhea in children What is acute diarrhea caused by Rotavirus in children? Guidelines for rehydration for children with diarrhea