This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor CKII Nguyen Thi Tam -Children Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Paracetamol, also known as Acetaminophen, has the most widely used antipyretic and analgesic effect in the world. At therapeutic doses, it is a highly safe drug, but overdose can lead to acute liver necrosis and death. Currently, there are many different medicinal products that contain paracetamol, which is available without a doctor's prescription, so it is easy to buy and use.
1. Manifestations of paracetamol poisoning
Paracetamol poisoning tends to increase in our country. This is a common type of poisoning that is easy to miss, with a delay in diagnosis, especially when patients abuse paracetamol to self-medicate with repeated overdoses. Poisoning is the main manifestation of hepatitis due to hepatocyte necrosis, which can lead to liver failure, acute kidney failure, respiratory failure, circulatory failure, if not timely intervention will be life-threatening, even life-threatening. lead to death.
If diagnosed early, adequate and prompt treatment with the simple antidote N-acetylcysteine (NAC) can also easily save the patient's life.

Ngộ độc paracetamol có thể dẫn đến suy hô hấp
2. Paracetamol toxicity and metabolism
Paracetamol tolerability in children (mg/kg body weight) is higher than in adults. The dose to reduce fever and pain is usually 10-15 mg/kg/time, every 4-6 hours. The maximum dose is 90 mg/kg/24 hours. Therapeutic doses may have few side effects. The toxic dose is >= 150 mg/kg/24 hours. Paracetamol is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, reaching a peak in plasma after 30-60 minutes. Paracetamol is metabolized mainly in the liver and to a small extent in the kidney by conjugation with Glucoronic and Sulfonic and then excreted by the kidneys. Less than 5% of Paracetamol is metabolised by Chytocrom P-450 to a highly toxic intermediate metabolite, N- Acetyl- P. Benzoquinoneim is rapidly inactivated by conjugation with the Sulhydryl group of Glutathion and then excreted through the body. kidney or bile. When using Paracetamol in therapeutic doses, the amount of Glutathion is sufficient to combine and eliminate, so it is safe. When taking large doses of Paracetamol, it will deplete the liver's Glutathion stores, the highly active intermediates will be redundant and firmly attached to hepatocytes, causing hepatocellular necrosis. In areas of Glutathion deficiency such as malnourished children, obese children, diabetics, adults who drink alcohol or are taking some drugs that induce metabolic enzymes, drugs that increase the production of mediators with high toxic activity such as group of anticonvulsants such as Phenobacbital, Carbamazepine, phenyltoin... and Rifampicin the liver is more susceptible to toxicity. Children with a family history of hepatotoxicity with Paracetamol have an increased risk of toxicity.
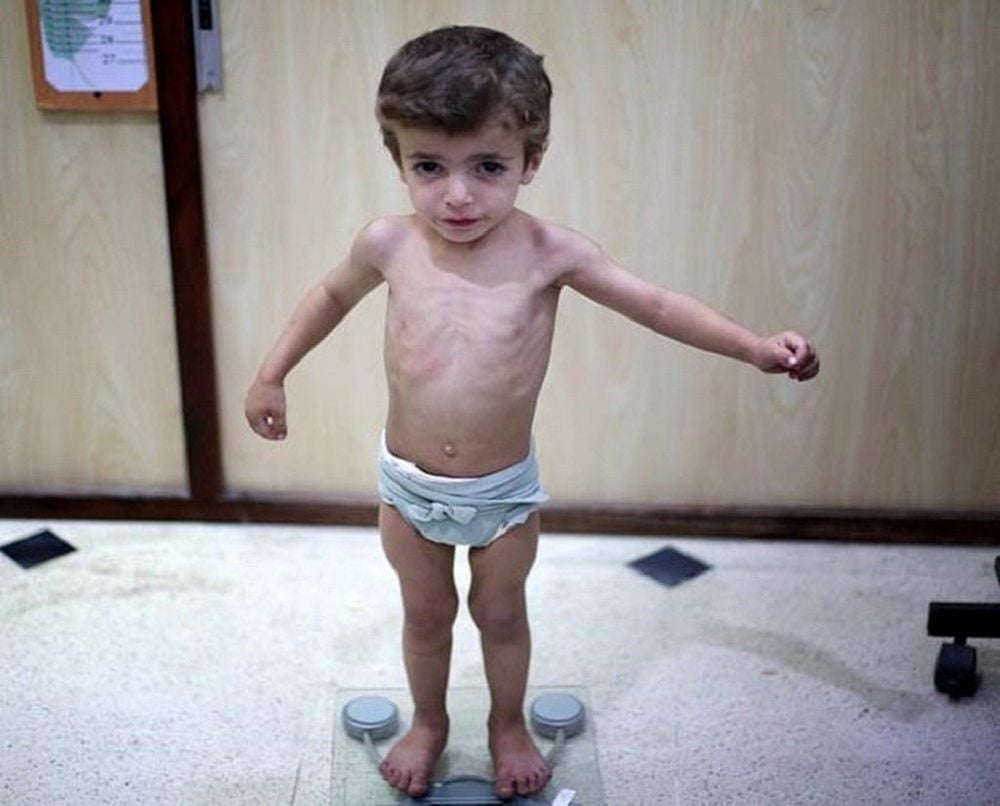
Trẻ suy dinh dưỡng dễ có nguy cơ ngộ độc paracetamol
3. Evolution of paracetamol poisoning
Paracetamol poisoning has a very poor initial presentation, which is easy to pass, so it requires vigilance and prompt diagnosis and screening. After 1-3 days, new symptoms of poisoning may be evident with the main disease being hepatitis, liver failure. Symptoms of poisoning can be divided into 4 stages: .
Stage 1: Usually present < 24 hours. Children are tired, nausea, vomiting, irritability, sweating, abdominal pain, loss of appetite and often impaired consciousness. Stage 2: From 24-48 hours after taking the drug. In addition to symptoms of stage 1, liver symptoms worsen, children have right lower quadrant pain, increased pain sensation, enlarged liver, jaundice, may urinate less, increased Bilirubin, liver enzymes and decreased blood clotting. Stage 3: Usually 72-96 hours: This is the full-blown stage with the most intense manifestations of poisoning: Child fatigue, nausea and vomiting, irritability. Liver failure with jaundice, hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, coagulopathy, hepatic encephalopathy. Renal failure and cardiomyopathy presenting with heart failure and arrhythmias. Stage 4: From 7-8 days after drinking. Children may recover or progress to death from total liver failure, hyperammonemia, hemorrhage, hypoglycemia, and renal failure. Paracetamol poisoning may present with CNS depression, shock, hypothermia, and metabolic acidosis.
4. Laboratory test results
Elevations of liver enzymes AST and ALT begin 24 hours after a toxic dose, peaking at 72-96 hours. When AST and ALT increase > 1000 IU/l, it is a sign of severe liver damage. Bilirubin increased in stage 2 and clearly increased in stage 3. Blood sugar decreased. Increased NH3 is related to the degree of liver dysfunction. When NH3 > 1.5 times, the prognosis is poor. PT decreased from day 2 and decreased sharply on day 3. Blood gases indicated acidosis. Renal function may be disturbed, Urea, blood creatinine increased, urine proteinuria and erythrocytosis may increase blood amylase when poisoning causes acute pancreatitis. CT of the brain may present with cerebral edema in comatose patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Paracetamol quantification 4 hours after oral administration (200 mcg/ml), after 15 hours (30 mcg/ml) will show hepatotoxicity. Paracetamol poisoning is diagnosed based on 3 criteria:
Children take an overdose of Paracetamol, the amount from >= 150 mg/kg/day. There are clinical symptoms: Digestive disorders, impaired liver function, blood clotting disorders, kidney failure... Test: Liver enzymes increased, Bilirubin increased, blood sugar decreased, thrombin time decreased. Quantification of plasma Paracetamol concentration after 4 hours reaching > 200 mcg/ml, after 15 hours reaching 30 mcg/ml, there will be signs of liver toxicity. For a definite diagnosis, 2-3 of the above criteria are needed. In children at high risk of toxicity, the dose may be lower.

Ngộ độc Paracetamol cần được chẩn đoán trên nhiều tiêu chuẩn
5. Treatment of Paracetamol poisoning
It should be conducted at the hospital with the following principles: Urgent and coordinated emergency measures for poisoning.
Elimination of toxins from the body Specific detoxification Treatment of functional disorders Specific treatment:
Initial management:
Induce vomiting if the child arrives before 1 hour after taking a toxic dose.
Gastric lavage if up to < 6 hours. Drink activated charcoal after gastric lavage. Treatment at the hospital:
Ensure maintenance of vital functions: Respiratory, circulatory, nervous. Specific detoxification by N-Acetyl cysteine is a precursor of Glutathion, oral form (Mycomyst) or injection form used for vomiting and gastrointestinal bleeding in children. Early use before 10 hours can prevent liver damage. Other supportive treatment measures: Blood transfusion and fresh plasma transfusion in the presence of anemia and coagulation factor supply. Give vitamin K if PT is < 70%. Inject hypertonic sugar if blood sugar drops. Treatment of water-electrolyte and acid-base disorders. Anti-infection. Ensure care, nutrition and provide enough calories, give the child a sonde or intravenous nutrition... Paracetamol used to reduce fever with therapeutic doses is usually highly safe. But if overdosed can lead to acute liver necrosis and death. When a child has a fever, it is an immune response of the body to pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. In case the child has a fever < 38.5 degrees Celsius, let the child wear thin, loose clothes, stay in a cool place, drink plenty of water, apply a warm towel to the forehead, armpits in the groin and wipe the body... Only use to reduce fever when the child has a fever. ≥38.5 degrees Celsius or ≥38.0 degrees Celsius in children with a history of febrile convulsions to avoid dangerous complications such as convulsions, delirium...
When a child has a fever, it is necessary to use antipyretics. prescription and doctor's advice.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline HERE for support.
READ MORE
What does Paracetamol do? Note when using Paracetamol Paracetamol dosage for children according to weight