This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Ngoc Phuong Hoa - General Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Malnutrition directly or indirectly affects a wide range of organ systems including the central nervous system such as protein-energy malnutrition, iodine deficiency, vitamin A deficiency and iron deficiency anemia.
According to the World Health Organization, chronic food shortages affect about 792 million people around the world. More than 15% of life lost to morbidity and mortality (DALYs) globally are estimated to be due to malnutrition, with a major focus on the neurological disorders associated with malnutrition.
1. Why does malnutrition cause neurological disorders?

Macronutrients are nutrients that provide energy including: protein (protein), carbohydrates (sugars) and fats (fats). Micronutrients are vitamins (A, B, C, E...) and minerals (Iodine, Zn, Mg, ...). Macronutrients are capable of providing energy and essential ingredients for body building, while micronutrients are special building items, mainly enzymes that help the body function. can be done well. The term malnutrition is used for both macronutrients and micronutrients. Micronutrient and micronutrient problems often occur together, so patient test results are often combined and cannot be separated.
2. Nervous disorders due to lack of nutrients
The World Health Organization has listed a number of nutrients that contribute to neurological disorders if not provided in an adequate amount and the necessary amounts of those nutrients are recommended by experts for adults as follows: :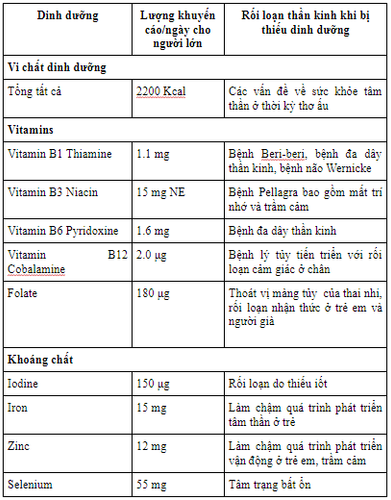
Common diagnoses of patients admitted to the neurological intensive care unit such as traumatic brain injury, stroke, brain tumor, spinal cord injury, degenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease) or movement disorder, Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
During hospitalization, adequate nutrient intake is limited by many factors such as anorexia, rapid satiety, dyspnea, dyspnea, immobility, depression and swallowing disorders, for example breathing difficulties or because the patient needs life support equipment or treatment such as a tracheostomy tube. Or trauma or nerve paralysis, so the patient needs to be nourished by intravenous line or fed through a nasogastric tube.
3. Prevention
Theoretically, preventing neurological complications from malnutrition is as simple as eradicating hunger and reducing poverty. However, most cases of neurological disorders related to malnutrition occur in poor countries. The recognition of poverty reduction is easy to say but difficult to implement. However, the World Health Organization recommends that countries have a number of strategies used to prevent micronutrient deficiencies as follows:
Diversify food and use rich foods micronutrients in the diet. Take a micronutrient supplement, eg a drug or a supplement. This method is used with vitamin A in a large number of low-income countries, such as in Vietnam with a program to prevent vitamin A deficiency, children from 6 to 36 months will be supplemented with vitamin A twice a year. . Fortify adding more micronutrients to a common food. For example, iodized salt is being applied in many parts of the world. The whole world is struggling to deal with diseases caused by micronutrient deficiencies. Adding iodine to all salts is a very successful way to prevent neurological complications from iodine deficiency. Vitamin A supplements are given to children under one year of age to prevent blindness caused by vitamin A deficiency. Or folate-fortified powders have been shown to reduce the occurrence of neural tube defects.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source: who.int, ncbi