This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Huynh An Thien - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.
Cerebral infarction accounts for about 85% of stroke cases, is one of the leading causes of death in the world. The disease often leaves severe sequelae, creating a burden on the family and society. The issue of time and treatment method plays a decisive role in the treatment of cerebral infarction.
1. Methods of treating cerebral infarction
Currently, there are 2 methods for first aid for cerebral infarction: injecting fibrinolytic drugs and removing thrombus with mechanical instruments. In order to implement these two measures, patients must go to the hospital early in the "golden hour", the time from the stroke to the time of receiving thrombolytic drugs is < 4.5 hours from the onset, the time to Mechanical thrombectomy was < 6 hours from onset. Before performing the above emergency measures, it is necessary to take computed tomography of the brain and cerebral blood vessels for the patient to determine the condition of the brain damage and locate the blocked blood vessel in the brain.
1.1 Thrombolytic injection Thrombolytic injection is performed by inserting an arterial catheter into the site of the thrombus and then injecting the fibrinolytic agent and/or removing the thrombus from the vessel. Many studies have shown that arterial fibrinolytic therapy increases the clinical recovery rate in acute ischemic stroke.
Intravenous fibrinolytic drugs: Indicated when the patient arrives early < 4.5 hours after onset. The most commonly used drug is Alteplase (rtPA). Intra-arterial fibrinolytics: Indicated for < 6 hours for the internal carotid system or < 12 hours for the basilar artery system. The drug is injected before - during - after the thrombus through a microcatheter that is threaded to the thrombus. 1.2 Collecting thrombus with a mechanical device
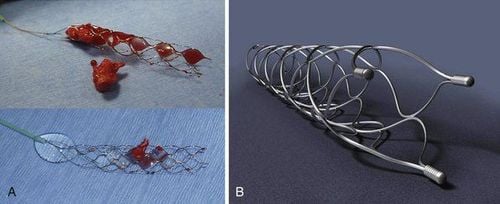
Lấy huyết khối bằng dụng cụ cơ học
Mechanical thrombectomy: Using specialized tools to pull the clot out of the body, thereby restoring the flow. Instrument types in use include:
Thrombus suction system: Penumbra Thrombotic traction device: Merci Thrombotic traction and flow re-opener: Solitaire The key is still to treat the underlying cause of the disease. to avoid recurrence. Usually, the main cause is often cardiovascular diseases such as stenosis - regurgitation of heart valves; Diseases requiring the use of multiple anticoagulants reduce the risk of cerebral infarction but increase the risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
2. Indications for treatment
Acute cerebrovascular occlusion comes before 6 hours with occlusion of the internal carotid system and 8 hours with occlusion of the basal vertebral system from the time of symptoms, even 12 hours with the basal system depending on the severity of clinical damage and images. Severe focal neurological signs (NIHSS ≥8) or extensive ischemic area On angiogram detected embolism Acute cerebral embolism before 3 hours (intravenous fibrinolysis is contraindicated).
3. Contraindications to treatment
High diastolic blood pressure >185mmHg or systolic blood pressure >105mmHg (if unresponsive to beta-blockers) Mild neurologic signs (NIHSS <5) Intracranial bleeding. Large area of cerebral infarction (>1/3 area of middle cerebral artery blood supply) Clear attenuation on computed tomographic images No gloom-light areas on images Newly had major surgery in about 2 weeks Yes bleeding that has not been completely treated, such as a ruptured brain aneurysm. Relatively contraindicated in patients with contrast allergy and renal failure.
4. Follow-up after treatment of cerebral infarction
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to assess progression and look for bleeding complications. Magnetic resonance angiography to evaluate flow recirculation.
5. Prevention of cerebral infarction recurrence

Chóng mặt, đau đầu có thể là dấu hiệu cảnh báo đột quỵ
Treatment of high-risk causes of cerebral infarction such as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia. Follow a diet to reduce fat, reduce salt (THA), reduce starch and sugar (DM), eat lots of green vegetables, exercise 30 minutes a day, stop smoking, alcohol, avoid obesity. Periodic re-examination and treatment according to the doctor's instructions Go to the hospital as soon as there are signs of suspicion of stroke. Vinmec Danang Hospital is currently applying the treatment of cerebral infarction by mechanical thrombectomy with a success rate of over 95%, and a complication rate of less than 5%.
The hospital is equipped with superior equipment, serving the interventional technique to remove cerebral artery thrombosis such as: DSA GE, MRI 3.0, CT 640 ranges, especially CTP that other hospitals do not have.
The team includes leading doctors and team in the region including:
Dr. Dr. Ton That Tri Dung Ths.Bs Huynh An Thien Ths.Bs Nguyen Thanh Nam . To register for examination and treatment of cerebral infarction at Vinmec Danang International General Hospital, customers can contact hotline: 0236 3711 111 or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Brain infarction: What you need to know Cerebral infarction, cerebral hemorrhage: 2 dangerous types of cerebrovascular accident Escape from the "death door" after a stroke.