This is an automatically translated article.
Nicotine produces physical and mood-altering effects, giving the user a temporary feeling of pleasure and satisfaction in the brain. These effects make them addicted to cigarettes and lead to dependence on nicotine in cigarettes.
1. Overview of nicotine in cigarettes
Nicotine dependence is addiction to tobacco products that contain nicotine. When dependent on nicotine, people become addicted to cigarettes and cannot stop using despite knowing the harmful risks of the chemicals and nicotine in cigarettes. Quitting smoking causes unpleasant symptoms and anxiety.
However, nicotine in cigarettes only acts as an addictive substance, the harmful dangers of tobacco actually stem from a number of other substances also found in tobacco. Smokers have much higher rates of heart disease, stroke, and cancer than non-smokers.
Quitting smoking can improve the health of both new and long-term smokers. Currently, there are many effective treatments for nicotine dependence, helping patients control smoking cessation. Therefore, people who are smokers and dependent on nicotine in cigarettes should seek medical help.
2. Signs of dependence on nicotine in cigarettes

Đối với một số người, dù chỉ mới hút một vài điếu thuốc cũng nhanh chóng dẫn đến bị lệ thuộc nicotine trong thuốc lá
For some people, even smoking a few cigarettes quickly leads to nicotine dependence in cigarettes. Signs of this condition include:
Can't stop smoking, have tried to quit smoking one or more times without success; If you stop smoking, you will experience physical and mood-related symptoms, such as cravings, anxiety, irritability, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, depressed mood, frustration, anger, hyperesthesia hunger, insomnia, constipation or diarrhea ; Still smoking and can't stop even though the body is having health problems related to the lungs or heart; Choose smoking over social or recreational activities, for example not going to places where smoking is prohibited or not socializing with family and friends because they are not supportive of smoking. Most smokers have to put in a lot of effort to achieve long-term and stable smoking cessation. Therefore, patients should seek medical advice and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
3. Mechanism of dependence on nicotine causes tobacco addiction
Nicotine is a chemical found in cigarettes that makes it impossible for users to stop smoking. After inhaling cigarette smoke into the lungs, the addictive nicotine is rapidly released into the bloodstream and then travels to the brain within seconds. Nicotine in the brain increases neurotransmitters, which help regulate mood and behavior.
One of the neurotransmitters is Dopamine - released in the "reward nervous system" of the brain, which has the function of improving mood and increasing pleasure. Experiencing these pleasurable sensations from nicotine causes the user to become addicted to tobacco.
The dependence on nicotine in tobacco is related to behavior (including lifestyle, habits and sensations) as well as physical factors. This association can act as a trigger, creating situations or feelings that trigger cravings, even after stopping smoking for a while. Specifically, a person will get used to smoking a cigarette when:
Just woke up in the morning; Drinking coffee in the morning or during your lunch break at work; After meal; Drinking alcohol; In certain places or with certain friends; Talking on the phone; Stressed or frustrated; Seeing or smelling tobacco; Driving. To overcome dependence on nicotine in cigarettes, users need to be aware of the factors that trigger their cravings, and then develop a plan to deal with the behaviors and related habits. to smoking.
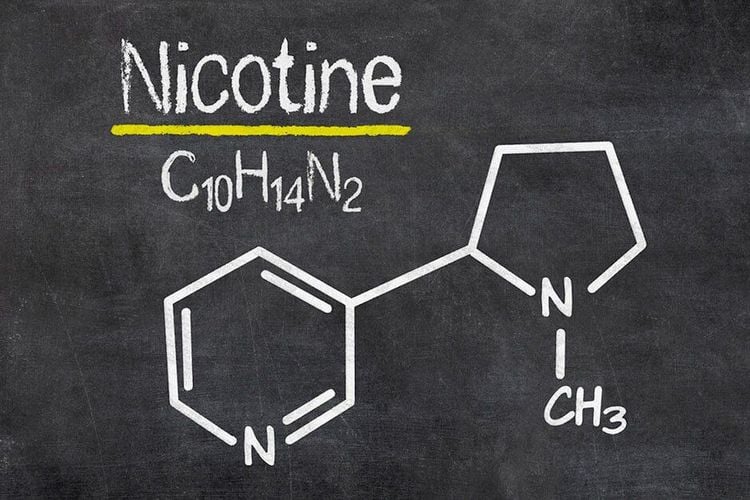
Nicotine là hóa chất có trong thuốc lá khiến người dùng không thể ngừng hút thuốc
4. Risk factors for nicotine dependence in cigarettes
Anyone who smokes or uses other forms of tobacco is at risk of nicotine dependence. High risk factors for nicotine dependence in cigarette users include:
Genetics: Certain genetic factors can affect how receptors on the surface of neurons in the brain respond to dose. high nicotine in cigarettes ; Family, friends and society: Children who live in homes where relatives smoke or play with friends who smoke are more likely to try tobacco. In addition, images of smoking in movies and on the Internet can also induce young people to try smoking; Age: Most people start smoking in their teens. The younger the age to start smoking, the more likely it is to become addicted to heavy cigarettes in adulthood; Depression or other mental illness: Many studies show that people with depression, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or certain other mental illnesses are more likely to be smokers; Substance use: People who abuse alcohol and use drugs are more likely to be addicted to tobacco as well.
5. Harm of tobacco addiction
Tobacco smoke contains more than 60 cancer-causing chemicals and thousands of other harmful substances. Even cigarettes advertised as "all natural" or "herbal ingredients" contain chemicals that are harmful to the health of the user.
Smoking adversely affects almost every organ of the body and weakens the immune system. About 50% of regular smokers will die from tobacco-related diseases.
Both women and men who are dependent on the nicotine in cigarettes have the same risk of dying from lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cardiovascular disease from tobacco use. Specific negative health effects are:
Lung cancer and lung diseases: Tobacco abuse causes almost 9 out of 10 cases of lung cancer, as well as other lung diseases, including bronchitis chronic management and worsening of asthma. Certain types of cancer: Smoking is a major cause of cancers of the esophagus, larynx, throat (oropharynx) and mouth. In addition, smoking has also been linked to cancers of the bladder, pancreas, kidney, cervix, and some leukemias. Overall, smoking leads to 30% of all cancer deaths; Cardiovascular and circulatory problems: Just smoke 1 - 4 cigarettes a day, the risk of cardiovascular disease will increase, even death from heart attack and stroke. Cardiovascular conditions, such as heart failure, will worsen if the patient smokes. Quitting smoking within the first year reduces the risk of a heart attack by up to 50%; Other diseases: Including diabetes, eye problems (cataracts and vision loss due to macular degeneration) and impaired senses, infertility in women and impotence in men, chance of pregnancy and newborn complications, colds and flu, or diseases of the teeth and gums (gingivitis, periodontitis), ... In addition, smoking at a young age also causes premature aging, forming wrinkles and making teeth yellow, affecting aesthetics. Smokers also pose risks to other family members, putting them at higher risk of lung cancer and heart disease from secondhand smoke. In particular, the children of subjects who are dependent on the nicotine in cigarettes are also more likely to develop sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), which worsens asthma, ear infections and colds.
Adhering to a treatment plan that focuses on both the physical and behavioral aspects of nicotine dependence can aid in the withdrawal process. Besides, working closely with the doctor and using some more drugs will also increase the chances of successful detoxification significantly. For example, the introduction of a smoking cessation therapy called “nicotine replacement” – providing patients with a nicotine replacement product (which is not tobacco and does not contain harmful chemicals in smoke) helps reduce symptoms. irritability and cravings.
However, to successfully quit smoking, the first and most important factor is still the consciousness and consistency of the smoker.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: mayoclinic.org