This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Specialist I Pham Thi Suu - Pediatrician - Vinmec Royal City International Clinic
Measles is an acute infectious disease caused by the measles virus, circulating commonly in children. The disease is transmitted from person to person mainly through the respiratory tract. The disease occurs all year round but usually occurs in winter - Spring.
1. What is Measles (Morbilli)?
Measles is an acute respiratory disease caused by a virus of the genus Morbillivirus of the family Paramyxoviridae. Characteristics to recognize measles in children are fever, inflammation of the respiratory and digestive tracts, conjunctivitis of the eyes, and a red maculopapular rash spreading in order from the face to the limbs and the whole body.
Measles is a widespread disease, so the disease constantly appears in the community, plus the spread of the disease is very fast, so it is easy to break out into an epidemic.
Age of disease is mainly in children under 10 years old, especially children under 5 years old. However, now the disease has appeared in adults because they have not been vaccinated or have been vaccinated but have not been vaccinated.
To date, measles is still a dangerous infectious disease causing epidemics and is one of the leading causes of death in children under 5 years old. The disease has a very high rate of infection, especially in the group of people who have not been immune to measles because they have not been vaccinated against measles, have never had measles before.
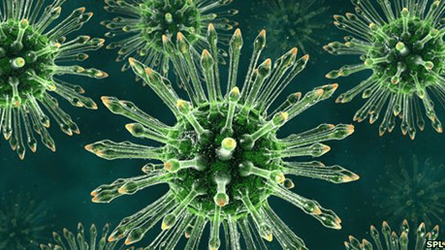
Virus thuộc giống Morbillivirus của họ Paramyxoviridae là nguyên nhân gây ra bệnh sởi
2. Symptoms of Measles
The disease has initial symptoms: fever, conjunctivitis, runny nose, cough and koplik nodules in the oral mucosa. Erythema appears from the 3rd to 7th day of illness. Initially from the face, then spread to the whole body and lasts from 4 to 7 days. Sometimes the disease ends in desquamation; Leukopenia is a common symptom of the disease.
The disease is more severe in children and adults. Complications of the disease can be caused by viral replication or bacterial superinfection including: otitis media, pneumonia, diarrhea, croup and encephalitis. Death is mainly in children under five years of age with the main cause being pneumonia, sometimes from encephalitis.
Measles is endemic disease in urban communities and can cause epidemics in 2-3 years. The majority of cases are in children who have not been immunized.
3. How measles is transmitted
The disease is transmitted by the air contaminated with droplets containing the virus, usually by direct contact with the secretions of the nose and throat of the patient. And sometimes, it can be spread by newly contaminated objects, nasopharyngeal secretions of the patient.
Measles is the most contagious infectious disease and the population immunity in the population needs to reach over 94% to cut off the transmission of the disease in the community.
Bệnh sởi lây truyền bởi không khí bị nhiễm các hạt nước miếng có chứa virus
4. How long is the incubation period for measles?
The incubation period for measles is about 10 days, but can range from 7 to 18 days from exposure to onset of fever, usually 14 days until rash appears, very rarely incubation period longer or shorter.
The disease is contagious from the beginning of the prodromal period until 4 days after the rash, at least 2 days after the rash. The vaccine virus has proven to be non-transmissible.
5. Subjects susceptible to measles
All people who have not been infected or are not fully immune to infection. Immunity is established after a sustained illness.
Infants born to mothers who have had measles in the past will receive passive maternal immunity between 6 and 9 months of age, or longer depending on the amount of maternal antibodies remaining during pregnancy , and the rate of reduction of antibodies in maternal blood. Immunization of infants at 9 months of age results in an immunity rate of 95-98%, re-immunization with an additional dose can increase the level of immunity up to 99%.
Babies born to mothers who have been immunized with the vaccine have fewer passive antibodies. These children are still susceptible to measles and need to be immunized earlier.

Trẻ sinh ra từ người mẹ từng mắc bệnh sởi sẽ được miễn dịch thụ động do mẹ truyền cho
6. Measles Prevention
Fully vaccinated according to the instructions of the Ministry of Health Isolate people with measles, avoid crowded places when there is an epidemic. Patients and those in contact with the patient should wear a medical mask. Wash hands before and after contact with the patient. Environmental hygiene, personal hygiene regularly. Improve physical condition, complete and balanced nutrition. In short, vaccination is the most effective way to prevent measles in children. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is providing a Package Immunization Program with a variety of vaccines for different subjects, from infants, young children, adults, and women before and during during pregnancy. In which, there is MMR II & Diluent Inj 0.5ml vaccine of MMD company in the US. Vaccines are imported and stored in a modern cold storage system, with a cold chain that meets GSP standards, keeping vaccines in the best conditions to ensure quality. Underwent general supervision before, during and after vaccination at Vinmec Health System and always have an emergency team ready to coordinate with the vaccination department to handle cases of anaphylaxis, respiratory failure - circulatory arrest, ensuring Ensure timely and correct handling when incidents occur.
In addition, the hospital also provides a full range of vaccines for everyone from children to adults, women before and during pregnancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:
Measles symptoms and vaccination against measles