This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Thi Hau - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging including magnetic resonance, CT and ultrasound.X-rays of the sinuses help doctors observe the state of sinus congestion, thereby helping to diagnose sinusitis without the need for a sinusoscopy, helping to treat it appropriately.
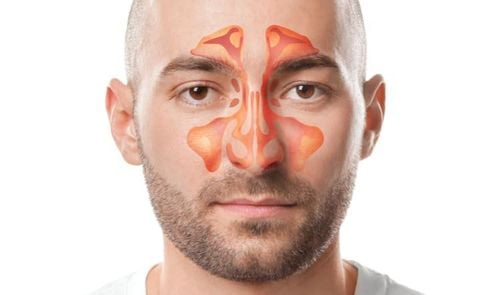
1. Anatomy of the Sinus
Sinuses are cavities located in the bones of the skull. In the sinus cavity, which is lined by respiratory mucosa, the secretions of the sinuses are poured into the nasal cavity through small openings (nasal-sinus openings).The sinuses all have holes connected to each other, so when one sinus inflammation lasts for a long time, it can easily lead to other sinuses called polysinusitis.
The facial sinuses are divided into 2 groups:
Anterior group of sinuses Including the maxillary sinuses, anterior ethmoid sinuses, and frontal sinuses surrounding the eye sockets.
This group of sinuses is the respiratory area of the nasal cavity, open to the outside, so it is easy to get infected and easily cause eye complications. The maxillary sinus has an opening with a wide nasal cavity, and is closely related to the upper teeth, so the anterior sinuses are often infected with acute bacterial infection and pus.
Posterior group of sinuses Including posterior ethmoid and sphenoid sinus deep below the skull base, related to the posterior orbit, optic nerve, cavernous sinus, pituitary gland.
Posterior ethmoid sinus is more private, less infiltrated by external pathological causes. The posterior sinuses have an opening with the nose behind the superior fissure, so secretions often flow down the throat and are less prone to acute inflammation, but often chronic inflammation.
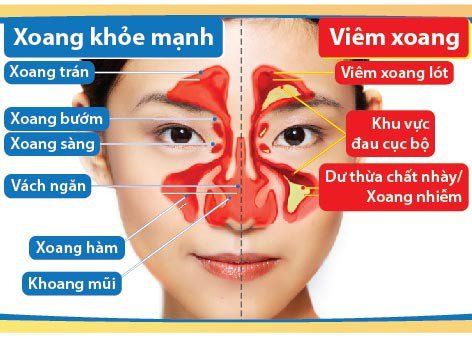
2. Common sinus diseases
Acute sinusitis Acute anterior sinusitis. On the X-ray film taken in Blondeau position, the sinuses are evenly blurred, solid or have a solid area below. Acute ethmoid sinusitis in children. Osteomyelitis - maxillary myelitis (masquerading as acute maxillary sinusitis). Chronic sinusitis: Is caused by irreversible changes of the sinus mucosa, causing dysplasia, polypoid form, exudation, mucus secretion or purulent inflammation. On X-ray film in Blondeau and Hirtz position, it is valuable in definite diagnosis: sinusoidal opacity or arc, polyp...3. Sinus X-ray for what?
Sinus X-ray is an imaging technique that has been used for a long time.The purpose of this method is to help the doctor observe the condition inside the sinus cavities without having to resort to surgery, thereby helping to accurately diagnose the type of sinusitis based on radiographs.
4. Is there any harm in taking a sinus X-ray?
X-rays can cause radiation to the body, but the diagnostic dose of a single x-ray is guaranteed to be within safe limits and most of the time it will not cause any significant health effects. Therefore, patients do not need to worry about the risk of cancer due to radiation exposure.However, the doctor also advises the patient, in order to avoid radiation exposure due to repeated X-rays, the patient should bring along the X-ray film taken before, so that the doctor can rely on the diagnosis without having to new film.
5. X-ray positions for sinusitis and its role in diagnosis
5.1. Blondeau pose (nose – chin – film) This posture helps diagnose diseases of the maxillary sinuses, frontal sinuses and nasal cavities.The patient lies in the prone position with the nose and chin touching the film and the mouth maximally open. At this point, the X-ray goes from back to front.

Normal sinus condition: Observing the X-ray film of the sinuses, the nasal cavity can be seen with a clear space of the airways. The frontal and maxillary sinuses are evenly lit relative to the orbit and the bony walls are clearly visible. In case of disease: If you have sinusitis, the breathing space of the nasal cavity is lost, the nose is too big or narrow. The frontal sinuses or the maxillary sinuses on the X-ray film are blurred due to swelling or edema of the mucosa. In addition, blurred sinuses can be caused by purulent fluid in the sinus cavity, mucosal degeneration, irregularity due to thick mucosa or thick margins. It is important to observe the bone wall for any loss. If the bone wall is not clearly visible, it may be suspected that malignancy is caused. In addition, if a foreign body is suspected, the doctor will conduct an additional cranial position to determine the exact location of the foreign body.
5.2. Schuller position (temporal-atrial) This sinusitis X-ray position helps diagnose inflammation in the mastoid sinuses.
The patient lies on his side, similar to the cephalometric scan. At this time, the beam source is 25-30 degrees relative to the axis of the 2 ears. At that time, the ray passing through the ear canal on the side and the ear on the side must always be bent forward so that the image does not press on the mastoid bone.
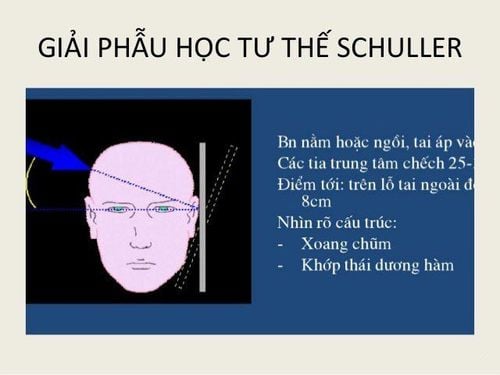
Normal: The film image will clearly show the septum and their lumen. Pathology: Imaging studies show opacities and septal opacities if the patient has acute mastoiditis. Or in the case of chronic mastoiditis, the septa and septum disappear. 5.3. Hirtz position (chin-top position) Hirtz position helps diagnose inflammation of the posterior ethmoid sinus, anterior ethmoid sinus, and sphenoid sinus.
The patient lies on his/her head so that the head is released from the table and the top of the head touches the film. X-rays go from top to bottom.

Normal sinus case: The posterior ethmoid, anterior ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses are bright and the cell septum is clear. In case of sinus disease: The sieving cells are blurred, which can be caused by fluid, pus or by thick mucosa, polyps in the sinuses. And the septum of the sieve is not clear or can also be destroyed or lost by malignancy or nasal polyps. Thus, relying on X-ray films of the sinuses helps doctors accurately diagnose the pathology in the sinus cavity, making treatment easier and bringing better results.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, all dental services are performed according to strict infection control standards, ensuring maximum safety and hygiene for customers. Radiographs and diagnostics were carried out with fully digital radiography machines (Digital Radiography). This reduces radiation dose by up to 50% compared to previous “traditional” X-ray machines. Thereby ensuring maximum safety and efficiency in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.