This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Xuan Thang - Deputy Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine and Head of Internal Medicine Unit - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalNodular goiter usually refers to an abnormal growth of thyroid cells forming a mass. Understanding well about the thyroid nodules tirads 3 and thyroid nodules 2 lobes tirads 3 will help the treatment become more effective for the patient.
1. Epidemiology of nodular goiter
The subjects and incidence rates of nodular goiter are assessed as follows:
Prevalence is about 7% in the adult age group The detection rate is about 5% in women and 1% in men The rate of nodular goiter increases with age. Age, depending on the epidemiological area, iodine deficiency is more common in women than in men. However, the rate of malignancy is usually higher in men than in women.
Trắc nghiệm: Hiểu biết của bạn về tuyến giáp đến đâu?
Tuyến giáp đóng vai trò gì đối với cơ thể, tại sao phụ nữ thường gặp các vấn đề về tuyến giáp nhiều hơn nam giới? Đó là những thắc mắc thường gặp khi tìm hiểu về tuyến giáp. Hãy làm thử trắc nghiệm dưới đây để kiểm tra hiểu biết của bạn về tuyến giáp đến đâu nhé!
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. Clinical of nodular goiter
Most thyroid nodules have no clinical symptoms, are only discovered incidentally during ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, or only cause a sensation of swallowing or a slight lump in the neck. The rate of palpable thyroid nodules is only about 3-7%, while thyroid nodules are detected.
Thyroid nodules can be single or multiple, palpable on clinical examination or not detected only on thyroid ultrasound, can be solid or cystic, size or small, benign or cystic. malignant. This thyroid function can be euthyroid, hyperthyroid, or hypothyroid. Most are benign. The malignancy rate of nodular goiter is only about 5% - 10%
Nodular goiter needs to be evaluated to consider appropriate treatment. Thyroid ultrasound is required in all patients with known or suspected nodular goiter.
3. The nature of human armor
Basically, the nature of thyroid nodules is specifically divided as follows:
Benign: Thyroid aneurysm, colloid cyst, hemorrhagic cyst, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, thyroid cyst (colloid cyst), Follicular adenoma, Huthle cell Malignant : Carcinoma: papillary (75%), Follicular (10%), Medullary (5%), Anaplastic (less than 5%), Limphoma (5%), Sarcoma (rare), metastatic thyroid cancer.
4. Risk factors for thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer status is determined by the following risk factors:
Childhood neck radiotherapy Local goiter Hashimoto's thyroiditis Personal or family history of thyroid adenoma Familial adenomatous polyposis Familial thyroid cancer family
5. Clinical features suggestive of malignant thyroid nodules
In the case of malignant thyroid nodule, it can be recognized by clinical features such as:
Rapid growth, firm, hard, sticky or poor mobility Difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing Hoarseness of voice Neck lymphadenopathy
6. Methods of surveying thyroid nodules
Thyroid function test, calcitonin (when FNA results suggest medullary cancer), thyroglobulin
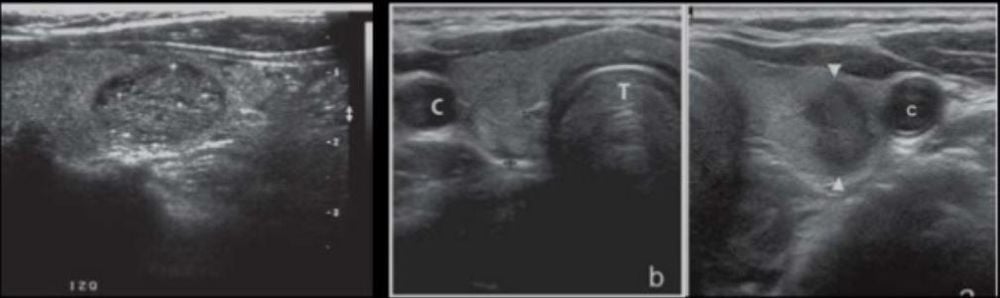
6.1 Thyroid ultrasound Thyroid ultrasound is usually easy to perform, does not bleed, and is highly effective for screening for goiter core. Low cost, no discomfort. Small kernels detected. This is also an important diagnostic method for nodular goiter. The characteristics of lesions on ultrasound will help assess the possibility of malignancy of the thyroid nodule, guide the next method of exploration, appoint fine needle aspiration thyroid nodule.
Thyroid size. Thyroid parenchyma is homogeneous or not, thyroid nodule or not (Number, location, size, individual characteristics)
Whether or not cervical lymphadenopathy with lymph node characteristics. Based on features on ultrasound, the European Thyroid Association (ETA) has made recommendations for risk stratification for malignant thyroid nodules. The recommendation is also endorsed by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) as well as the European Society of Thyroid Imaging and Data Systems (EU - TIRADS; Europian Thyroid Imaging and European Union). Reporting Data). The recommendation outlines thyroid ultrasound concepts and criteria for the concepts of benign, low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk nodules.
Ultrasound features suggestive of malignant thyroid nodule:
Nodule height greater than width Poor echogenicity, irregular margin Microcalcification in nucleus spiky margin, invasive proliferation Having diseased lymph nodes Management Features that suggest low risk:
Cysts (over 80% of fluid) Spongiform nucleus Clear halo sign Moderate risk nucleus:
Slightly less echogenic than thyroid tissue Round oval shape, poorly defined margins Yes vascular proliferation in the nucleus Marginal calcification or macrocalcification Rate of malignancy according to TIRADS (European Thyroid Association 2017 guidelines):
EU - TIRADS 1: Normal, no risk of malignancy EU - TIRADS 2: Benign Very little risk of malignancy, close to zero EU - TIRADS 3: Low risk of malignancy 2 - 4% EU - TIRADS 4: Moderate risk 6 - 17% EU - TIRADS 5: High risk 26 - 87%
Indication for biopsy is based on:
Patient's risk factors Presence of suspicious features on ultrasound. There are many cytological classifications: Pathologists of the Royal College of England, Australia, Italy, Japan and the United States. In which, the updated American Bethesda 2017 classification is highly clinical, accompanied by guidelines to guide further treatment for patients.
6.3 Thyroid scan Basically thyroid scan is indicated in cases
Diagnosis of hot nodules Determine thyroid size Evaluation of multinodular goiter function Evaluation of substernal goiter Determine thyroid tissue Ectopic In iodine-deficient areas, scintigraphy helps to exclude autonomic nodules for mononodular and multinodular goiters with normal TSH. CT scan of thyroid is needed in some complicated cases
7. Treatment of goiter
The treatment will depend on the nature of the thyroid nodule
Medical treatment with LT4. However, it is necessary to pay attention to the possibility of recurrence after stopping treatment and the side effects of the drug. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with benign nodules. Injection of Ethanol PEI (Percutaneous Ethanol Injection) with cystic thyroid nodules and mixed thyroid nodules with abundant, benign fluid component. Not indicated for solid nodule, toxic nodule and toxic multinodular goiter. Radiotherapy with hyperthyroid nodules Surgery: Used for malignant nodules, suspected malignancy, symptoms of compression and nodules larger than 4cm. In most cases, only periodic follow-up may be necessary. In order to bring the best quality examination and examination results, Vinmec International Hospital currently uses the SPECT/CT Discovery NM/CT 670 Pro system, with the most modern 16-sequence CT technology of the device manufacturer. GE Healthcare (USA), helps to provide high quality images, accurately assess thyroid diseases.
Thanks to good facilities and a team of qualified staff and doctors, the hospital has now successfully treated and treated many thyroid patients, bringing them good health and good health. stable quality of life.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.