This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Specialist in Pediatric Surgery, Plastic Surgery - Aesthetics - Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Danang International HospitalVaginal malformation is a birth defect in a girl where the rectum, vagina and urinary tract fuse together into one place. In normal anatomy, these openings are separate. The incidence of vitiligo is about 01 in 20,000 to 25,000 girls. The defect is usually diagnosed before birth and the baby will need treatment soon after birth.
1. Symptoms of malformations are still sticky
Symptoms may include:Children without anus Small external genitals with an oversized clitoris No vagina About half of children with malformations with a septum will have a defect affecting their secretions urology and gynecology. Some children have only one kidney or hydronephrosis.
Another problem is fluid retention in the vaginal lumen (hydrocolpos). This is a condition in which fluid builds up inside the vagina and uterus that can press on the neck of the bladder, blocking the ureters, preventing urine from entering the bladder.
About half of girls with malformations with scleroderma will have problems with the gynecological organs that affect reproductive functions later in life, including the ability to give birth.
Other health problems:
Gastrointestinal problems: About 11% of infants with a slurry will develop esophagitis and 3% will develop duodenitis. Heart problems: About 30% of children have heart problems such as an atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, and a patent ductus arteriosus.
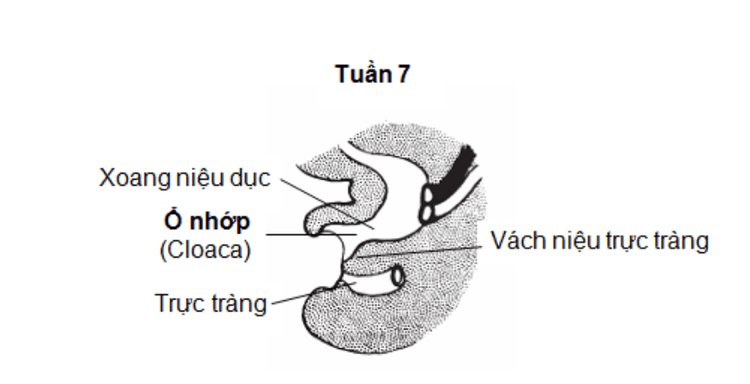
2. Diagnosing malformations with slimy foci in children
Diagnosis and treatment of this malformation requires the collaborative efforts of many different specialists such as: a pediatric surgeon with many years of experience in complex malformations, a pediatric urologist gynecologists, pediatric gynecologists and other specialists. And neonatal slime will be diagnosed during a physical examination immediately after birth.
Then tests will be done to evaluate for related abnormalities 24 hours after birth such as:
Echocardiogram to determine if there is a heart defect. X-ray of the abdomen and spine to evaluate for dilatation of the bowel due to stagnation of waste and to rule out signs of esophagitis or duodenitis as well as extra or missing Sacrum bone. Ultrasound of the kidneys, X-rays of the pelvis and spine to evaluate the kidneys, check for vaginal collapse, and rule out spinal stiffness.
3. Treatment of malformations with sticky sockets
The initial goals of treatment are to stabilize the child and relieve obstruction in the urinary and intestinal tracts, with further goals directed at restoring the anatomy and function of the abnormal organs.
Diagnostic tests for cysts help determine the length and size of the fossa as well as other important factors in determining the best way to correct deformities.
Patients usually fall into one of two groups and each group has different treatments:
The first group involves babies born with a common duct shorter than 3cm or smaller than 2.54cm. For most patients, the ductus can be repaired without making an incision through the abdomen. The second group consisted of patients with a longer common duct. These patients often require laparoscopic surgery or abdominal incision to reestablish and repair the urinary tract and vagina. These types of corrective surgery are best performed at centers that have a team of doctors and specialists with many years of experience in surgery for congenital anomalies in infants.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: childrenscolorado.org, qualitychildrens.org