This is an automatically translated article.
Patients who find abnormalities in liver function tests, heart disease, kidney disease, lung disease or simply abdominal pain should be diagnosed based on the clinical picture and especially the serological reaction. positive for Cryoglobulin.
1. What is Cryoglobulin?
Cryoglobulinemia is the presence of Cryoglobulin in the patient's serum. Cryoglobulins are immune complexes that precipitate at low temperatures and are deposited in the endothelium. In the human body, Cryoglobulin can damage organs through increasing blood viscosity or causing immune reactions, Cryoglobulin is also the cause of vasculitis in organs such as kidneys, skin, peripheral nerves. record. Depending on the type of disease and the extent of its influence, there are various manifestations such as purpura, joint pain, weakness.According to statistics, mixed cryoglobulinemia has appeared about 1 in 100,000 people, the disease is quite common in southern Europe with patients between the ages of 40 and 60 years old and in women more than men
Since Hepatitis C virus has been found to be responsible in more than 90% of mixed cryoglobulinemia. In addition, the disease can also occur due to genetics or after the patient has been vaccinated with vaccines, especially anti-pneumococcal vaccines.
2. Classification of cryoglobulins in blood
According to Brouet's classification, based on the composition of Cryoglobulinemia can be divided into:
Type I: Cryoglobulins will be formed by monoclonal antibodies (usually IgG or IgM, rarely IgA). This form is commonly seen in patients with multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom's syndrome and a number of other diseases... Type II: Mixed cryoglobulin, is the presence of a polyclonal antibody combined with a monoclonal antibody with the Rheumatoid factor activity: 90% have HCV. Type III: Mixed cryoglobulin, at this time, all immunoglobulins are polyclonal antibodies: Often associated with systemic diseases.
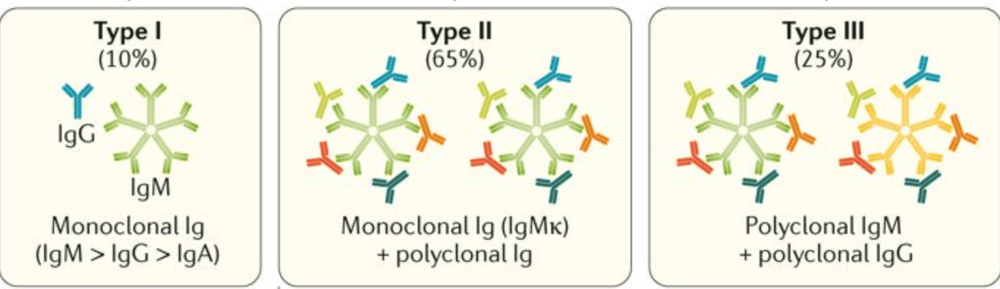
Phân loại cryoglobulin máu theo 3 typ
3. Common symptoms of cryoglobulinemia
Usually, type I Cryoglobulinemia often shows symptoms such as:
The patient has retinal hemorrhage. Arterial thrombosis. Blue purple head limb. Severe Raynaud's phenomenon. Cases of Cryoglobulinemia type II and type III have symptoms such as:
Have immune-complex glomerulonephritis. The patient has pain and arthritis in places such as knee, metatarsal, and ankle joints. Hemorrhagic vascular injury. Some of the symptoms of Cryoglobulinemia in decreasing frequency may be:
Appearance of skin symptoms such as peripheral necrosis, hemorrhage. Joint disease Abdominal pain Kidney disease Neurological symptoms such as peripheral neuropathy. Dry eyes and mouth Swelling of the face Hemorrhage
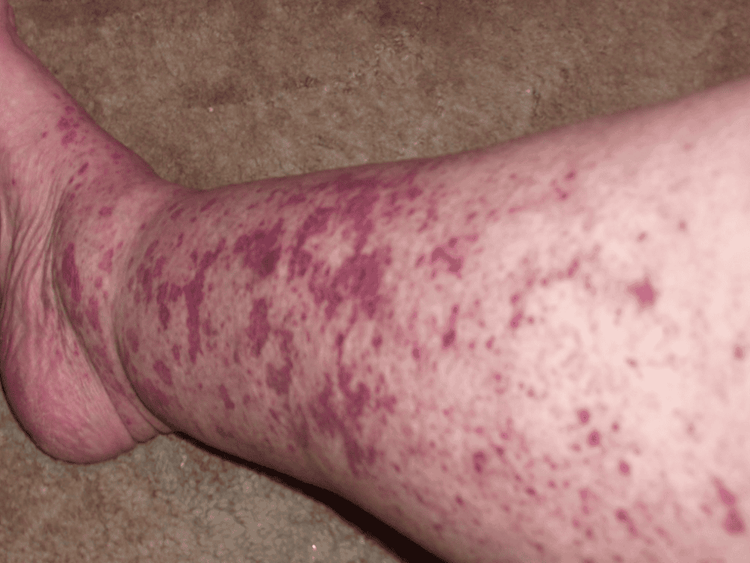
Hình ảnh thực tế trên bệnh nhân mắc chứng Cryoglobulinemia
4. Cryoglobulinemia can be associated with what related diseases?
Cryoglobulinemia is a condition that can be accompanied by a number of other diseases of the infectious disease, cancer or autoimmune disorder groups, but the most common is still hepatitis C.
Most cases of Cryoglobulinemia appear with other diseases. Specific pathology follows:
For type I, there are:
Multiple myeloma Lymphocyte proliferative disorder Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. Type II and III include:
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Autoimmune disorders such as Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis. Infectious diseases such as hepatitis E, hepatitis C, HIV, ...
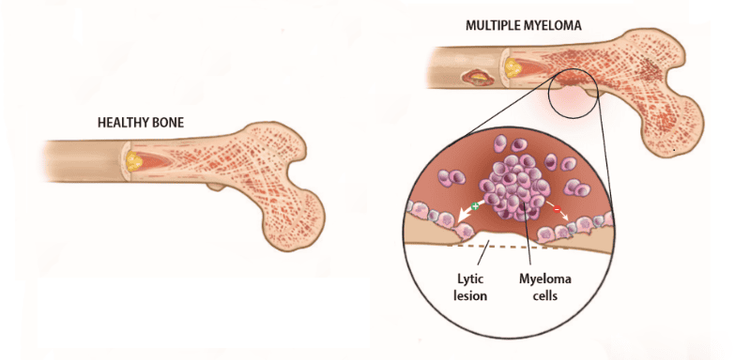
Bệnh đa u tủy xương
5. How is Cryoglobulinemia treated?
According to the advice of specialists, people with Cryoglobulinemia should avoid working or living in cold environments. The therapeutic goals of the disease are to limit cryoglobulin precipitation and inflammation, treat comorbidities (such as hepatitis C), and prevent recurrence.
Cryoglobulinemia treatment plan and regimen will depend on the type of disease, severity of disease and comorbidities. If the patient is asymptomatic, the doctor may recommend careful monitoring without medication. However, if the patient has kidney or nerve damage, a specific treatment regimen will be required. People with symptoms of joint pain and fatigue can use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)...
In addition, plasma replacement therapy is also used in case the patient has dangerous complications. and life threatening.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.