This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor of Dental - Jaw - Facial - Doctor of Dental - Jaw - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Aphthous ulcers are painful, localized, shallow, round or oval sores in the mouth with a gray base. Oral canker sores are one of the most common causes of mouth ulcers. This is a disease that causes a lot of discomfort for the sufferer and can cause dangerous complications if not treated promptly.
1. What is an oral canker sore?
Oral aphthous ulcers are painful ulcers in the mouth with small ulcers less than 1cm, oval or round with red margins. Commonly found in the inner mucosa of the mouth. About 20-40% of the population has an aphthous ulcer at least once in their life, many of whom can have multiple recurrences. The disease occurs most often in adolescents and less often in the elderly. White people, people with high socioeconomic status are more susceptible to the disease. The disease is not contagious.
2. Causes of canker sores
2.1. Genetic factors Genetic factors may play an important role in canker sores . About 40% of patients have a family history of aphthous ulcers. These people often have an earlier onset and a more severe illness. There is an association between human leukocyte antigens (HLA) and disease. In people with aphthous ulcers there is an increased frequency of HLA type A2, A11, B12 and DR2 antigens. This association varied by ethnic and racial origin.
2.2. Mechanical trauma Trauma to the oral mucosa due to mechanical factors such as numbing injections, sharp teeth, rough toothbrushes or dental interventions can trigger the onset of aphthous ulcers.
2.3. Tobacco Several studies have shown a negative association between smoking or inhaling tobacco smoke and aphthous ulcers. The cause may be because smoking increases the process of keratinization of the mucosa, creating a protective barrier, preventing injury and invading germs. Nicotine is considered a protective factor because it stimulates the production of adrenal steroids by acting on the hypothalamus, causing decreased production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1, interleukin 6. Therefore. Nicotine replacement therapy is recommended for patients with aphthous ulcers who have stopped smoking.

2.4. Medications Several drugs have been implicated in the development of aphthous ulcers, such as captopril ACE inhibitors, gold salts, nicorandil, phenindion, phenobarbital, and hypochloride solutions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as propionic acid, diclofenac, and piroxicam can cause aphthous-like mouth sores.
2.5. Anemia The deficiency of hematopoietic factors such as iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid is two times higher in people with aphthous ulcers than in controls, suggesting a link between anemia and aphthous ulcers. mouth . However, some argue that anemia is caused by a poor diet when suffering from aphthous ulcers.
2.6. Hormonal changes The relationship between aphthous ulcers and hormonal changes in women is controversial. Some authors have found that aphthous ulcers often occur during the onset of menstruation or during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. McCartan et al did not find an association of the disease with any of the women's hormonal changes (participation, perimenopause, menopause).
2.7. Stress Mental stress was once considered a etiological factor in aphthous ulcers. It indirectly causes aphthous ulcers through daily actions that contribute to an increased risk of soft tissue trauma such as lip biting, cheek biting. Several recent studies have shown no correlation between stress level and the severity of aphthous ulcers. Therefore, psychological stress plays a role in promoting disease rather than etiological factors in individuals with a history of aphthous ulcers.
2.8. Aphthous and streptococcal ulcers Oral streptococci are considered to be microorganisms directly involved in the pathogenesis of aphthous ulcers. It contributes to aphthous ulcers and acts as an antigen, stimulating the body to produce antibodies. These antibodies cross-react with the oral mucosa. The species of alpha-hemolytic streptococcus that causes aphthous ulcers is Streptococcis sanguis (later isolated as Streptococcus mitis).
2.9. Helicobacter pylori and Helicobacter pylori have been implicated in the pathogenesis of aphthous ulcers. This bacteria is present in dental plaque, but its role is unclear.
2.10. Viruses Some viruses may be involved in the pathogenesis of aphthous ulcers, such as human cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus.
3. Clinical symptoms of oral aphthous ulcers
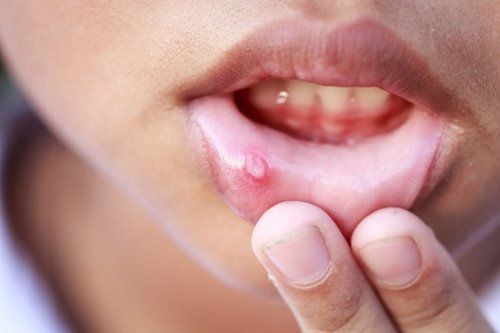
There are several types of canker sores, including minor, canker sores, and herpetiform.
3.1. Small sore mouth sores Most common sore mouth sores:
Less than about 1/2 inch, or 12 mm (mm) in diameter. Ellipse. Heals without scarring in 1-2 weeks. 3.2. Large mouth sores This is less common:
Larger than about 1/2 inch, or 12mm, in diameter. Has irregular edges. It can take up to six weeks to heal and leave a scar. 3.3. Herpetiform canker sores Usually develop later in life:
No larger than about 1/8 inch, 3 mm, in diameter. Usually clusters of 10 to 100 ulcers occur. Has irregular edges. Heals without scarring in 1-2 weeks. 3.4. Other symptoms Occasionally, other signs or symptoms may occur along with the lesions, such as:
Fever. Swollen lymph nodes. Consult a doctor if you experience:
Unusually large sores. Ulcers periodically, with new ones developing before the old ones heal. Persistent sores, lasting three weeks or more. Extensive pain. Pain that cannot be controlled with self-care measures. Extreme difficulty eating or drinking. High fever along with sore mouth sores. See your dentist if sharp tooth surfaces or dental appliances appear to be causing sores.
4. Measures to prevent canker sores in the mouth
Gargle with salt water, baking soda (dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in 1/2 cup warm water), spit this mixture out after rinsing. Try products that contain an anesthetic, such as Anbesol and Orajel. Avoid abrasive, acidic, spicy foods, which can cause further irritation and pain. Apply ice to painful ulcers or allow ice samples to slowly dissolve next to the ulcer. Brush teeth gently using a soft brush and a non-foaming toothpaste. Applying a small amount of milk of magnesia a few times a day can relieve pain and may help heal pain faster. Try to avoid foods that can cause mouth irritation such as: nuts, chips, cookies, spices, salty foods and acidic fruits, such as pineapple, grapefruit and oranges. Be sure to avoid any food sensitivities or allergies. Choose healthy foods. To help prevent nutritional deficiencies, eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Regularly eating yogurt containing beneficial bacteria or can also help avoid sore mouth sores. Do not chew and talk at the same time as this can cause minor trauma to the cell layer of the mouth.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.