This is an automatically translated article.
The article is advised by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease caused by the proliferation of skin cells, which causes old and new skin cells to fail to replace, piling up to form thick, red, scaly patches of white or silver. .
1. Common types of psoriasis
The characteristic symptom of psoriasis is thick red patches covered with white or silver scales. In addition, depending on the location and characteristics of the lesion, there are separate symptoms for each disease such as:
Plaque psoriasis: patches of skin appear on the elbows, knees and lower back. Pustular psoriasis: pustules appear on the skin of the hands and feet. Droplet psoriasis: teardrop-shaped lesions appear all over the body, often in children, after an episode of streptococcal pharyngitis. Psoriatic arthritis: swelling of joints of fingers, toes or spine, knees... Nail psoriasis: thick nails, with small holes on the nail surface. Scalp psoriasis: on the scalp there are scales or thick silvery white patches of skin. Folded psoriasis: occurs in obese people, lesions in the folds of the skin such as armpits, groin, buttocks ...
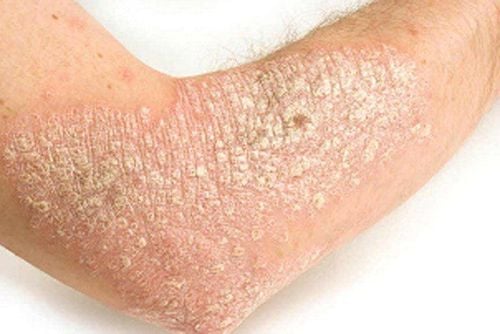
Vảy nến thể mảng là dạng thường gặp
2. Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is a skin disease that is not caused by a virus or bacteria. Therefore, psoriasis is not contagious from person to person through mutual contact. We can completely hold hands, hug, kiss, share items, clothes with people with psoriasis without having to worry. However, psoriasis has been shown to be hereditary (10% of children get the disease if one parent is sick, 40% of children get it if both parents have it).3. How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Psoriasis is identified mainly through physical examination. A dermatologist will examine the skin, nail, and lesion sites to pinpoint psoriasis. In cases where the skin lesions are not obvious, the doctor will biopsy the damaged skin to make an accurate diagnosis. Do not do blood or urine tests because these tests do not help diagnose psoriasis. However, for treatment with immunosuppressive drugs, the doctor may order blood tests to monitor drug side effects.4. Complications of psoriasis

Bệnh nhân cần được điều trị để kiểm soát tình trạng bệnh
Psoriasis is an unstable disease, if not properly cared for and treated, the patient may have the following complications: generalized redness, pustular psoriasis, arthritis, skin infection... Recent research suggests that psoriasis is a risk factor for metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease (ie, greater susceptibility to metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease), especially for people with severe psoriasis.
Currently there is no cure for psoriasis completely. The main goal of treatment (drugs, biologics, phototherapy...) is to reduce inflammation and control skin cell proliferation, to help patients prolong stabilization time and prevent maximal prevention. complications of the disease. Therefore, patients need to follow the treatment instructions of the skin specialist as well as know what to do and not to do every day, in order to better control and live peacefully with the disease.