This is an automatically translated article.
Breast cysts are a common condition among women, making them one of the most common reasons women visit a breast clinic. These cysts can be completely asymptomatic and only discovered incidentally. Finding a cyst in the breast can be worrying, but most breast cysts are not dangerous, they are not cancerous. Even so, you should see your doctor for an accurate diagnosis.1. How are breast cysts formed?
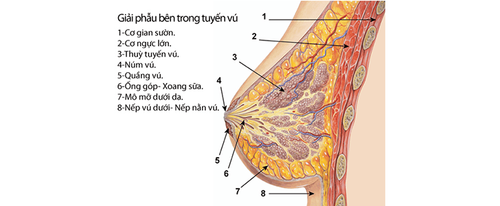
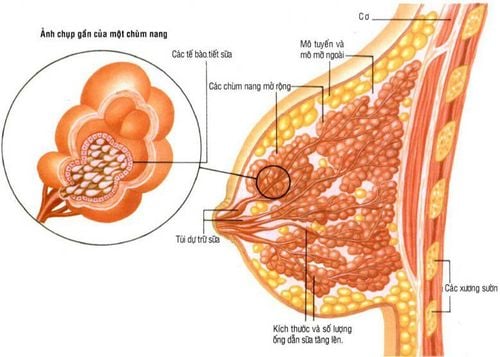
Breast cysts are part of the benign pathology of the mammary gland - cystic fibrosis. This disease process includes all fibrous and cystic changes in the breast tissue. A breast cyst simply forms as an aberration in the natural development of the breast, composed of a cavity lined by an inner layer of fluid-filled epithelial cells, surrounded by surrounding breast parenchyma. Breast cysts can vary in size from small to large, and can be single or multiple. The connective tissue around the cyst proliferates with fibrous cells that cause the cyst to harden, also known as cystic fibrosis.Many studies report a high incidence of cystic fibrosis in women, showing that more than 70% of women develop cystic fibrosis changes during their lifetime, with 20% of these having symptoms.
Breast cysts usually develop in women between the ages of 30 and 50. The rate of cyst formation increased during these years, then decreased significantly. Since cyst growth is related to hormone levels in the body, most benign cysts will disappear and new cysts will not form for a year after menopause.
Breast cysts often appear on both sides at the same time, this is the most common case;
Common types of cystic fibrosis: mammary cyst, fibrocystic disease, and ductal hyperplasia.
2. Detecting breast cysts based on what?
The vast majority of breast cysts, as well as cystic fibrosis, are discovered incidentally, with only 20% of cysts found in women with cyclical pain.Possible signs and symptoms of breast cysts include:
A rounded or oval breast lump, well-defined, smooth, easily mobile. Increased tenderness or tenderness in the breast just before a period is called cyclical pain. Breast pain or tenderness in the area where the cyst is palpable. Increase in size of follicles before menstruation. Reduced cyst size and postmenstrual symptoms. When there are suspected clinical symptoms, going to the hospital is necessary, but you should not be too worried.
The doctor will ask about the history, risk factors, physical examination as well as order tests and imaging facilities to evaluate the breast.
Breast ultrasound is often the first-line method because it is simple, easy to perform and inexpensive, but it evaluates most of the breast tissue structure, detects lesions, and helps to distinguish simple cysts or cysts. complex.
Mammography is not as useful as ultrasound in identifying between cysts or cysts, but is more appropriate for breast evaluation in patients over 35 years of age. Patients under 35 years of age often have denser breast tissue, which is better evaluated by ultrasound.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also an imaging modality used. However, because of cost and availability, it is not used as routine as ultrasound or mammography.
Histopathological assessment by fine needle aspiration (FNA) or core needle biopsy. FNA is performed when there are symptomatic cysts or cysts with suspicious solid bud components.
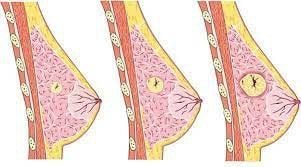
Nang vú có nguy hiểm không là thắc mắc của nhiều chị em mắc nang vú
3. Direction to handle breast cysts
If your doctor diagnoses as a simple breast cyst, then you need not worry as most simple breast cysts are not dangerous, are benign and do not require further treatment or diagnosis. Breast cysts may remain stable for many years or may resolve on their own.Unless the cyst is particularly large, causing discomfort or pain, the cyst can be drained with a fine needle. Drainage usually only takes a few minutes for each cyst, and it can cause mild discomfort or pain. If the cyst recurs, it can be evaluated again with mammography and ultrasound of the breast, and drainage is considered again. The fluid inside the cyst may be clear or colored, but this is nothing to worry about.
Some complex breast cysts may require other diagnostic measures such as fine-needle aspiration or biopsy to rule out breast cancer but most are benign. Aspiration can both diagnose and remove the cyst at the same time. Or your doctor may ask to see you every 6-12 months for 1-2 years to check on this complex cyst.
If at any point your doctor feels the cyst has suspicious features that suggest it might actually be breast cancer, he or she may order a biopsy to make sure any solid The inside of the cyst is benign.
4. Is breast cyst dangerous?
Nearly all "simple cysts" are not as dangerous as the name suggests. They are almost never associated with a higher cancer risk.The only possible exception in which cysts may show a cancer risk is when other cancer risk factors, such as family history, on further imaging tests shows several solid shoots within or along its walls.
According to the American Cancer Society, simple cysts do not increase the risk of developing breast cancer, although there is a small chance that complex cysts can develop into breast cancer.
A 2019 study: Trusted Source found that 30% of breast cancer cases are in people with a history of benign breast disease. If you're concerned about your risk of breast cancer or have a family history of breast disease, talk to your doctor about how and when you should have the screenings you should have.
You should see your doctor if the following changes occur in your breasts:
You feel a new lump in your breast or armpit. Part of your breast feels thick or swollen. The skin on your breast is dimpled or irritated, red. Your nipples are sore, pulled in, or oozing discharge. The size and shape of your breasts have changed. Your breasts are still sore. Having these symptoms does not mean you have breast cancer. But it does mean you should see a doctor and follow up more closely with your doctor.
Nang vú có nguy hiểm không còn phụ thuộc vào loại nang lành tính hay ác tính
5. Summary
Breast cysts are quite common, most of them are benign, especially for people in their 40s. With the question, is cystic fibrosis dangerous? Usually, cystic fibrosis is not dangerous, is benign, and does not require treatment. If you feel any lump in your breast, it's important to see your doctor for an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital applies the aspiration treatment of benign breast tumors by the assisted biopsy technique of the ultrasound-guided vacuum suction device (VABB), which has opened up a new direction. overcome the disadvantages of traditional surgical methods. Thanks to this method, instead of having to open surgery to remove the tumor as before, the doctor only needs to insert the needle of the VABB machine to cut the tumor and suck the tumor out. Patients will experience less pain and no scarring. Especially, it does not cause breast deformation, does not require hospitalization. The patient does not need to undergo many incisions to remove the tumor, but only one needle is needed to treat the tumors, even treat many tumors at the same time.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.