This is an automatically translated article.
Invasive ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which fetal tissue invades the uterine muscle due to uncontrolled fetal growth. If not treated in time, it can progress to squamous cell carcinoma.1. What is invasive egg pregnancy?
An oocyte is an abnormal development of the placenta. Normally, the placenta is responsible for nourishing the fetus, but for some reason, the placenta overgrows, creating many complications such as invasive egg pregnancy or trophoblastic cancer. This is a malignant cancer with a very high mortality rate.
In most cases, the ovum does not have a fetus and is called a complete ovum, in some cases, the ovum has a fetus but does not survive and it is called a partial ovum.
Usually about 80% of ova are benign and the disease will clear up after curettage or hysterectomy in people who no longer want to have children.
2. Symptoms of invasive egg pregnancy
When having an invasive egg pregnancy, pregnant women will have the following symptoms: Vaginal bleeding and abnormal discharge, grape-shaped placental hairs, lower abdominal pain, vomiting or nausea, abnormal nipple discharge often.
The lower abdomen is as big as pregnancy, the belly does not shrink after giving birth. If the disease progresses to a late stage, the patient will have signs of shortness of breath, convulsions and leading to paralysis.
3. How to treat invasive egg pregnancy?
The general principle of invasive fetal ovum treatment is to remove the maximum amount of abnormal egg tissue from the body, then combine with chemotherapy to eradicate the malignant ovum tissue.
Điều trị thai trứng xâm lấn như thế nào
The doctor will remove the ovum from the body using aspiration or hysterectomy for patients who still need to give birth. Hysterectomy is indicated for patients who are elderly (≥ 40 years) and no longer intend to have children, or patients have extensive invasive complications causing heavy bleeding or have received chemotherapy but not effective. For the case of benign ovum, the patient after curettage will be monitored for about six months.
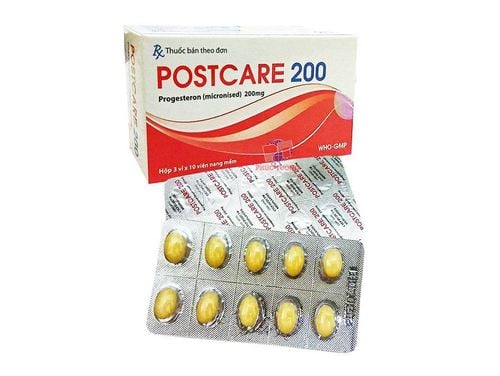
In the case of invasive oocyte pregnancy with high risk of turning into trophoblastic cancer, the patient should be treated with chemotherapy and closely monitored. The most commonly used chemical is Methotrexate combined with Folinic Acid. If this chemical is resistant during treatment, it will switch to a combination of chemicals such as EMA-CO, EMA-EP,...
Invasive pregnancy is a dangerous malignancy, so the patient absolutely need to adhere to treatment, closely monitor before and after treatment. Patients need to have beta hCG blood and urine tested every 2 weeks until the hCG level returns to normal. Next, beta hCG will be tested in the urine every 4 weeks. The follow-up period is at least 1 year for early detection of recurrence or distant metastases. If the patient wishes to have a baby, she should only become pregnant after about 1 year from the date of treatment and must have an hCG test at 6 and 10 weeks of pregnancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.