This is an automatically translated article.
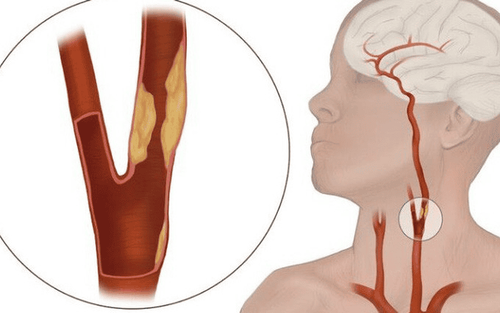
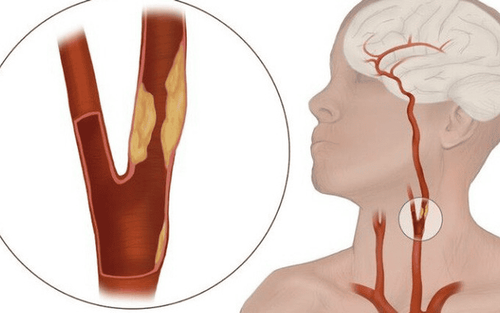
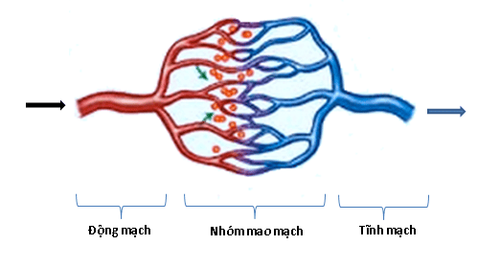
Internal carotid ligation surgery is intended to prevent inflammation from spreading from the blocked or occluded lateral carotid artery, occlusion of the internal carotid artery and its branches, to other parts of the body.1. Indications for internal carotid artery ligation surgery
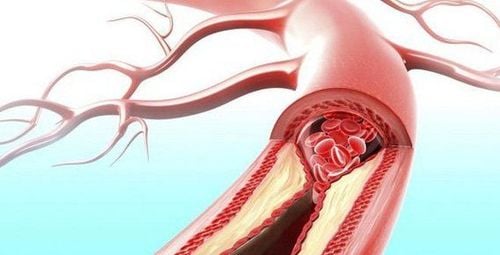
Surgical ligation of the internal carotid artery is indicated when:Once the diagnosis of ruptured internal carotid aneurysm is confirmed, it is necessary to remove the ruptured aneurysm from the circulation. Infection causes partial or complete occlusion of the lateral vein. Carotid occlusion. Inflammation of the internal jugular vein. Perform internal carotid ligation surgery after the diagnosis of ruptured aneurysm of the internal carotid artery is confirmed.
Early surgery before 7 days: patients with good clinical condition WFNS < 3 performed as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. Late surgery after 7 days: patients with WFNS grade ≥ 3, patients with unstable vital signs.
Bác sĩ sẽ chỉ định phẫu thuật khi xác định bệnh nhân vỡ túi phình động mạch cảnh trong
2. Preparing for surgery
Performer: An otolaryngologist, orthodontist or surgeon trained in the internal carotid ligation technique.Facilities: Neck surgery kit (internal carotid artery ligation).
Patient: Be informed and detailed instructions on carotid artery ligation surgery in
Patient record: As a general rule.
3. Carry out surgery
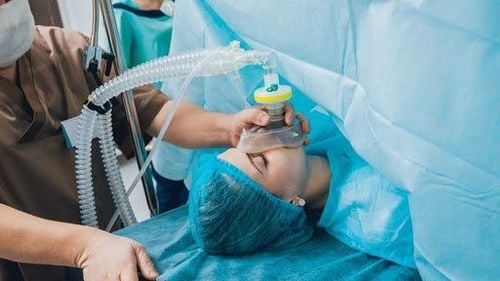
Khi tiến hành phẫu thuật, người bệnh sẽ được gây mê nội khí quản
Patient's position: The patient lies on his back, the shoulder is padded with one pillow, the head is turned to the opposite side.
Stages of internal carotid artery ligation surgery: Stage 1: Find the surgical area. The surgical line goes along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle from the superior border of the thyroid cartilage and the lamina propria. Stage 2: The anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle begins just above the hyoid body and extends down to 8 cm.
3: Find the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle just below the superficial cervical fascia.
4: Separation of the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Then 5: Find the internal carotid artery. Pulling the sternocleidomastoid muscle outward, a large red blood vessel appears, which is the internal carotid artery.
Stage 6: Identify the internal carotid artery and its connecting branches.
Then 7: Ligation of the internal carotid artery. Usually constriction on the trunk of the facet thyroid artery. If the inflammation is extensive, tighten it below the lesion.
Then 8: Stitch the restoration of layers with catgut thread, sew the skin with linen thread.
Possible complications when ligation of the internal carotid artery:
Infection of the incision: after 3-4 days, the incision is red, swollen and painful. Subcutaneous pneumothorax: remove the suture, drain the incision immediately. Regressive nerve palsy: thread trimming. Circulatory disorders: difficult to detect. Internal carotid ligation surgery is a relatively difficult procedure, so the operator needs to have experience and proficiency in internal carotid artery ligation along with a full range of surgical equipment to help minimize the risk of accidents. variables may occur.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
How dangerous is Carotid stenting? Doppler ultrasound of the carotid artery Carotid stenosis: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment