This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Otitis media is a common disease in children, especially acute otitis media, which is classified as acute upper respiratory tract infection. Acute otitis media can be completely cured without leaving complications if detected early and treated properly. In particular, the purulent incision is a treatment method for the pus-stagnation stage of otitis media with some necessary notes.
1. Overview of otitis media
Otitis media is a common name for an infection of the middle ear, specifically the space behind the eardrum. Otitis media is common in children because the inner ear is connected to the back of the throat by a small tube called the eustachian tube, which in children is still incomplete and shorter than in adults, so it is easier to get blocked, leading to fluid. and excess impurities cannot get out of the ear, stagnate and cause inflammation. There are also a number of reasons for otitis media as follows:
Colds often cause upper respiratory tract infections along with otitis media Children living in environments often exposed to cigarette smoke Bottle-fed babies are at risk. Children with otitis media are more likely to get otitis media than breastfed babies because they often lie down to suckle, causing milk to easily spill into the auditory tube causing inflammation Swimming ear infections are common in older children Children with otitis media will have the following symptoms:

High fever 39-40°C with irritability, fussiness, refusal to feed or eat poorly, vomiting, even convulsions Older children who can talk will complain of ear pain while young children will often shake their heads, rub their ears In addition to ear symptoms the remaining symptoms are often non-specific, so they are often ignored by parents, if after 2-3 days, the disease may turn to the stage of rupture of pus, causing perforation of the eardrum, pus draining out of the ear and Chronic inflammation, especially otitis- mastoiditis, causes very dangerous bone loss.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. Clinical forms of otitis media:
Children often encounter clinical forms of otitis media, especially otitis media with fluid retention, otitis media with suppurative otitis media, and necrotizing otitis media. Otitis media with effusion: is an infection of the middle ear that is not caused by an infection, but the fluid that accumulates is usually non-infectious fluid due to the incomplete eustachian tube. When examining the child's ear, there are air bubbles on the surface of the tympanic membrane, the eardrum is opaque and has limited mobility. The main treatment of this form is observation without using antibiotics, the disease will clear up on its own in 4-6 weeks if there is no superinfection.
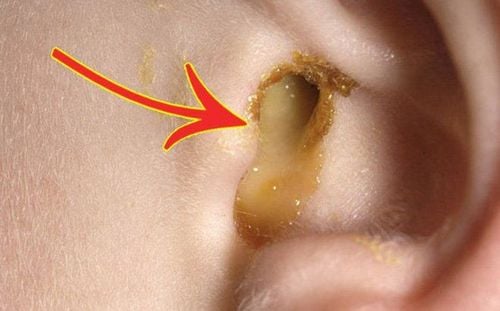
Acute purulent otitis media: is a form of otitis media with 2 stages: pus stasis and purulent rupture, usually caused by inflammation of the nasopharyngeal area, V.A or blocked ear canal. In the period of pus stasis, children will have symptoms of fever, runny nose, cough with digestive disorders and obvious ear pain, making them fussy and stop feeding. After this period, there is a period of purulent rupture, which helps relieve symptoms, improve overall condition, reduce fever, reduce ear pain, and have discharge from the ear at first, yellow after cloudy mucus
Acute necrotizing otitis media: an inflammatory form In the middle ear caused by respiratory infections such as measles, diphtheria, influenza, the middle ear has necrosis of the mucosa, which can destroy the bones and cause dangerous complications. Children often tired, digestive disorders, ear pain with spreading to the first half, hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, which can progress to mastoid otitis and even complete hearing loss.

3. How to treat otitis media?
The treatment of otitis media depends on the stage of the disease, and the treatment will vary. Otitis media will go through stages of congestion, pus stasis and purulent rupture, with each stage we will have the following treatments:
Congestive phase: treatment is mainly medical treatment with antibiotics Systemic with beta lactam is the preferred group in combination with anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and antipyretic, analgesic drugs. Can combine nasopharyngeal treatment if it is the cause. Stage of pus stasis: if otitis media progresses to this stage, the purulent injection will be considered to drain the pus out to reduce pressure in the middle ear cavity. After the incision is still treated at the same time as in the congestive stage. The purulent stage: At this time, the pus has broken through the thin part of the eardrum to escape, the eardrum is perforated, so the treatment with drops Anti-inflammatory ear is very important, avoid using antibiotic ear drops containing aminoside group.
4. Is it dangerous to inject pus at the stage of otitis media with pus?
Incisional injection is often considered when the child has an acute pus-filled condition that requires urgent drainage to limit dangerous complications. The external purulent injection has the effect of reducing the pressure, and also avoids the self-perforated eardrum to drain the pus, causing severe damage to the eardrum and the reduction of symptoms, which makes parents subjectively not take the child to the doctor.
Incision of the tympanic membrane is not dangerous, with early incision and good combination treatment, the disease tends to be cured in a short time of about 2 weeks, the puncture hole caused by the incision is sealed and the child's hearing is guaranteed. .
Otolaryngology - Vinmec International General Hospital is an address specializing in the examination and treatment of otitis media as well as common ENT diseases, head and neck tumors, regional congenital malformations. otolaryngology using common surgical methods such as surgery, microscopic or endoscopic tympanic patch, fistula removal surgery, Bondy surgery, nasopharyngeal aerosolization, nasal septum injection, nasal burning...
Is In the key areas of Vinmec Health System, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including: leading experts, with high professional qualifications (professor, associate professor, doctorate, master), rich experience, have worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. The doctors are all well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment. Dr. Tien has more than 8 years of experience in the field of Internal Medicine - Neonatology, specializing in Emergency Resuscitation, Pediatric Cardiology, Neonatal Resuscitation. The doctor has been trained nationally and internationally such as: National Children's Hospital; the University of Sydney, Australia; Seoul National University, Korea before being a Resident Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital as it is now.
To register for examination and treatment with pediatricians at Vinmec International General Hospital, please click the "Contact Us" button on the website or register online.