This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Le Thi My - Director of Thyroid Pathology Center - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalHypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland cannot produce enough hormones for the body to function properly. This disease can affect any age, including children and infants. In children, hypothyroidism may appear soon after birth or may develop later in childhood.
1. Causes of hypothyroidism in children
The leading cause of hypothyroidism in children is family history. Children whose parents, grandparents, or siblings have had hypothyroidism have a higher risk of developing it than other children. This risk is also present if there is a family history of certain immune problems that affect the thyroid gland.
Of which Hashimoto's thyroiditis (also called autoimmune thyroiditis) is the most common cause of acquired hypothyroidism in children and adolescents (and adults), it usually presents in the years early life. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakes thyroid cells for foreign agents and attacks them and leads to thyroiditis.
Over time, inflammation damages the thyroid gland, leading to a gradual decrease in thyroid hormone levels. Once thyroid hormone levels drop below normal (called hypothyroidism), the pituitary gland responds by making more thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to try to make the thyroid gland work harder and increased thyroid hormone levels. The cause of Hashimoto's thyroiditis is unknown, but it has been found to be hereditary.
Other possible causes of hypothyroidism in children include:
Eating too much or too little iodine causes the thyroid to function abnormally When born with an underactive or no thyroid gland (congenital hypothyroidism) The mother has thyroid disease but does not treat it completely during pregnancy Thyroiditis: Temporary inflammation of the thyroid gland caused by a viral infection. Thyroidectomy: To treat thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, or goiters Radiotherapy: Causes destruction or damage to the thyroid gland, including radioactive iodine to treat goiter protrusion, or radiation therapy to the neck area to treat Hodgkin's disease, lymphoma, or other cancer. Use of drugs such as lithium , amiodarone and oxcarbazepine can interfere with thyroid function Pituitary damage: The pituitary gland in the brain regulates the amount of hormones the thyroid gland makes. When the pituitary gland is damaged, it may not make enough TSH to ensure normal thyroid function.
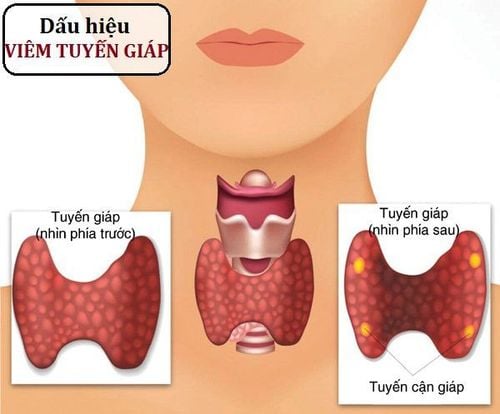
2. Symptoms of hypothyroidism in children
Hypothyroidism can occur at any age, but the symptoms can also be quite different from age to age and from individual to individual.
Newborns
For infants, symptoms manifest in the first few weeks or months after birth. Symptoms during this stage that are easily overlooked by parents or doctors include:
Jaundice , yellow eyes Constipation Refuses to breastfeed Cold skin Less crying Strong breathing Stronger sleep/reduced activity Soft fontanel in size larger on the crown of the head Large tongue, protruding navel Toddlers and primary school children
Thyroid diseases during this period may manifest outwardly in signs and symptoms such as:
Shorter than average height Shorter than average limb length Permanent teeth grow slowly Delayed puberty Mental retardation Slower-than-normal heart rate Fragile hair Puffy face Some other symptoms: Fatigue, constipation, dry skin Teenage
At this age, girls have a greater incidence of hypothyroidism than boys and often autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Children with a family history of autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease or type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing thyroid problems than other children. Children with genetic disorders such as Down syndrome are also at increased risk for thyroid problems.
Symptoms in adolescents are similar to those in adults but can be vague and difficult to recognize. Some clinical symptoms:
Weight gain Slow growth Lower than average height Delayed puberty Heavy bleeding during menstrual cycle Increased testicle size in boys Dry skin, brittle hair and nails Constipation Swollen face enlarged, enlarged thyroid gland Muscle pain and stiffness Adolescents with thyroid disease may experience behavioral changes such as:
Fatigue, forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating Mood and behavioral problems Difficulty Difficulty studying at school Depressed, depressed

3. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism in children
The doctor will determine the best way to diagnose a child's disease depending on age and other factors. In general, physical examination as well as specific laboratory tests that can help confirm the diagnosis include:
Physical examination to evaluate the general condition, detection of signs and physical signs, Physical examination of the neck. your child's tests may include blood tests to evaluate thyroid function (measurement of TSH or FT4 hormone levels) Imaging tests such as thyroid ultrasound , thyroid scans.
4. Treatment of hypothyroidism in children
Children with excessive hypothyroidism (elevated TSH and low T4 levels) are treated with hormone replacement. The goal is to bring T4 and TSH to normal levels and restore normal body functions. There are many treatment options for hypothyroidism, typically daily hormone therapy in the form of the drug levothyroxine (Synthroid). The dose is prescribed by your doctor and depends on many factors such as the age of the child.
The ideal time to take levothyroxine is on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before eating. However, the most important thing is to take levothyroxine regularly, at a time that is easy to remember, and to avoid forgetting it. If you forget your medication, take it as soon as you remember.
Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with modern equipment system (GE S8 ultrasound machine, SPECT scanner system, international standard laboratory system...) and a team of experts multi-specialty including neonatology - pediatrics - endocrinology - imaging and oncology. All complicated medical cases will be consulted by experienced doctors to help the children be examined, diagnosed and treated according to the most optimal regimen.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.