This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi My Linh has 12 years of experience in diagnosing and treating pediatric diseases.Birth defects syndrome is always a threat to children, Turner syndrome is one of them. Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of Turner syndrome is something parents should be concerned about.
1. What is the definition of Turner syndrome?
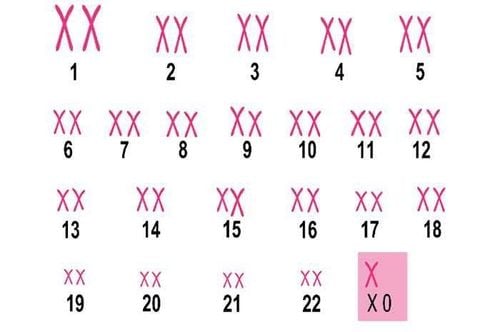
At birth, a child inherits 23 single chromosomes (chromosomes) from the father and 23 single chromosomes from the mother, forming 23 pairs of chromosomes. Chromosomes play an important role in heredity, recording genetic structure at the cellular level.Turner syndrome (TS) is a disease caused by partial or complete loss of the sex chromosome (chromosome) in females. Loss of one sex chromosome can be in all 45,X cells – monosomy, or only in one cell line in the body – mosaic.
The cause of this syndrome is the result of aberrant segregation of the sex chromosomes during meiosis or during protozoan division to form monosomy or mosaic.
Structural mutations of chromosomes are disorders caused by chromatid breakage of chromosomes when chromosomes have not been duplicated in the interphase of the cell cycle. Structural disorders of the X chromosome can be caused by deletions, inversions, isochromosomes, translocations, and ring-shaped chromosome formation to create different structural disorders of TS.
2. Diagnosis and clinical symptoms of the disease
2.1. Diagnostic criteria
The patient presented with clinical features described as short stature, hypogonadism, excess neck skin, short hair growth, and forearm curvature.Patient has karyotype:
45,XO Mosaic: 45,XO/46,XX, 45,XO/46,XX/47,XXX,... Structural disorder: iXp, iXq, delXp, delXXq, rX, ... The study carried out prenatal diagnosis for Turner syndrome by testing maternal blood, fetal ultrasound, fetal karyotype from amniotic fluid, placenta previa. But when there is doubt about prenatal diagnosis of Turner syndrome, karyotype should be done to confirm the diagnosis after birth.
2.2. Clinical symptoms
Short: usually 2 standard deviations lower than age. Hypogonadism: up to 12-13 years of age without secondary sexual characteristics such as developed mammary glands, pubic hair, menstruation. Excess skin on the neck / gills: Excess skin on the back of the neck, making the neck appear larger. Low hair growth: The lower hairline is lower than normal. Forearm curvature: In a normal adult female, the arm and forearm angle is about 12 degrees. While in TS patients this angle is usually 15-30 degrees. Eye wrinkles: skin folds at the corners of the eyes. In addition to the clinical symptoms, the patient may have other symptoms such as:Nail hypoplasia: Nails are short and raised. Shield-shaped chest: The chest is wide compared to the length of the ribcage, the distance between the nipples is relatively far apart. Low humerus IV/V: When drawing a line from the beginning of the III metatarsal and the V humerus, the IV humerus is below this line. Edema of the feet/hands: Edema of the feet/hands is thought to be due to a lymphatic disorder in TS. Myopia / astigmatism: When the child has been examined by an eye specialist and is diagnosed with myopia / astigmatism. Skin pigmentation: Dark pigmentation spots.
2.3. Test
FSH, LH and estradiol levels are measured for patients on admission, and measured every 6-12 months after female hormone therapy. Thyroid function is indicated for Turner patients by measuring TSH and T4 or FT4. To detect malformations of the cardiovascular system and urinary kidney, echocardiography and urological ultrasound are indicated for the patient. Assessment of hearing ability. DQ or IQ. Bone density (if over 18 years old). For patients with karyotype with mar (chromosomal segment unknown), PCR technique is applied to determine whether the patient has TDF gene or not.
3. Methods of treatment
3.1. CHOICE Treatment
GH is indicated for patients with dwarfism when the bone age is <13 years old and the height is low - 2SD compared to the female age (Biological value of Vietnamese people - Ministry of Health 2003 or WHO 2007). Treatment should start as early as 7-8 years old, even 2 years old.The dose of GH is 0.05mg/kg/day, injected subcutaneously in the evening daily. Height needs to be monitored every 3-6 months, adjust the dose for appropriate growth. If a higher dose of GH is given, it should be checked and IGF-I should not be higher than normal.
Stop GH treatment until normal height is achieved, bone age is over 14 years old, or height increase is less than 2 cm/year.
3.2. Female hormone treatment
Turner's patient aged 12-15 years with delayed sexual development is indicated for female hormone therapy.The dose of estrogen is started as follows: ethinyl estradiol brand name Mikrofollin/Vinafolin 0.05 mg, dose 1⁄4 tablets/day. The estrogen dose was increased gradually every 3-6 months up to a dose of ethinyl estradiol 2mg/day. Dosage needs to be adjusted based on secondary sexual development, bone age, and uterine growth to complete puberty in 2-4 years.
Progesterone, brand name is Orgametril or Duphaston 5mg/1 tablet, the dose of 1 tablet/day is added when the child starts having menstruation. To induce a sham cycle, estrogen is given from day 1 to day 23 of the menstrual cycle. Progesterone is given from day 10 to day 23 of the menstrual period.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.