This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Nhat - Infectious Disease Specialist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalDengue hemorrhagic fever is an infectious disease caused by the dengue virus. Dengue hemorrhagic fever is characterized by fever, hemorrhage and plasma leakage, which can lead to thrombocytopenia, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
1. Dengue fever concept
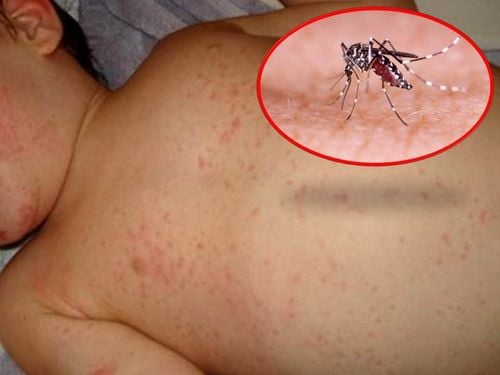
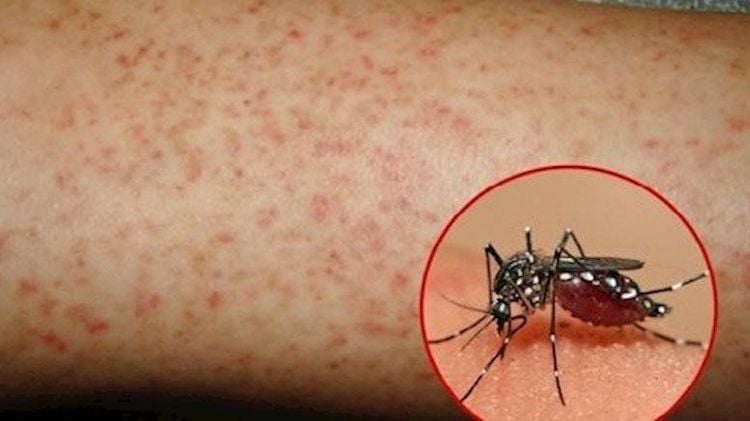
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is an acute infectious disease caused by the dengue virus. The disease is transmitted by blood by the vector Aedes aegypti mosquito. The main clinical manifestations are acute fever, accompanied by bleeding in the skin or mucous membranes and thrombocytopenia in the blood. Among them, thrombocytopenia is the most dangerous complication. Platelets are the smallest of all blood cells. When viewed under a microscope, platelets are dark purple spots that are only 20% the diameter of red blood cells. Platelets are approximately 2μm in diameter (ranging from 1.2 to 2.3 μm) with a maximum diameter of up to 3 μm.
A platelet count that is too low can cause many dangerous complications.
2. Progression of dengue fever
Dengue fever has a rapid progression from mild to severe. The disease usually has a sudden onset and goes through three phases: the febrile phase, the critical phase, and the convalescent phase.Fever phase:
Patient has a sudden, continuous high fever. Headache, loss of appetite, nausea. Congestive skin.
Muscle pain, joint pain, eye pain. Positive ligature test. Usually there are petechiae under the skin, bleeding gums or nosebleeds. The critical phase, usually on the 3rd-7th day of the disease:
Clinical: The patient may still have fever or have decreased fever and have the following symptoms:
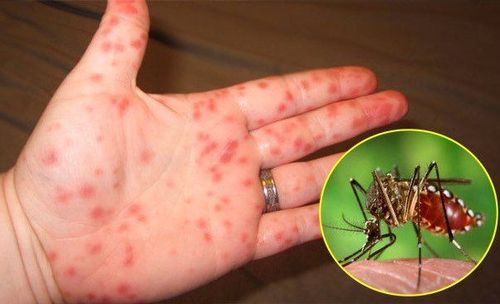
Plasma leakage due to increased vascular permeability (usually prolonged 24-48 hours) pleural effusion, interstitial tissue, peritoneum, eyelid swelling, hepatomegaly, possibly pain. In the case of a lot of plasma leakage, it will lead to shock with manifestations of fatigue, restlessness or lethargy, cold extremities, cold and moist skin, small rapid pulse, stuck blood pressure (maximum and minimum blood pressure difference ≤ ≤ ). 25 mmHg), low blood pressure or unmeasured blood pressure, urinating less. Hemorrhage: Subcutaneous hemorrhage: Scattered or punctate petechiae usually on the front of the legs and on the insides of the arms, abdomen, thighs, ribs, or bruises. Bleeding in the mucous membranes: Leads to bleeding from the nose and gums; bloody urine. Menstruation lasts or occurs earlier than the period. Bleeding in internal organs such as gastrointestinal tract, lungs, brain is a severe manifestation. In severe cases, organ failure may appear such as: severe hepatitis, encephalitis, myocarditis. These severe manifestations may occur in some patients with no obvious signs of plasma leakage or without shock. Recovery phase:
Clinical: After 24 - 48 hours of the dangerous phase, there is a gradual reabsorption of fluid from the interstitial tissue into the vascular lumen. This phase lasts from 48 to 72 hours. When the patient is fever-free, general condition improves, appetite, hemodynamic stability and urinary frequency are increased, bradycardia and ECG changes may occur. During this period, excessive perfusion can lead to pulmonary edema or heart failure.
3. The danger of leukopenia in dengue fever
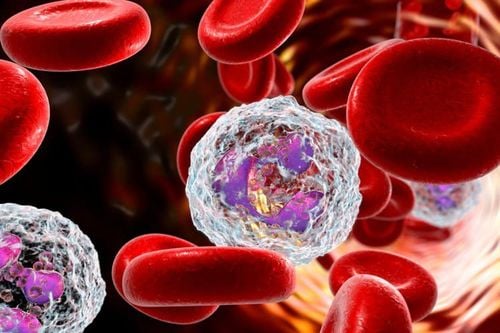
The normal number of platelets in the blood is usually about 150,000 to 400,000 platelets/μl of blood (1 μl = 1 mm3), with an average of 200,000 platelets/μl of blood. Each liter of blood contains about 150-400 billion platelets. When dengue fever, Hematocrit increases compared to the initial value of the patient or compared with the average value of the population at the same age, the platelet count falls below 100,000/mm3 (<100 G/L) causing a dangerous conditions such as: bone marrow suppression or replacement, chemotherapeutic agents, splenic enlargement, disseminated intravascular coagulation, platelet antibodies, posttransfusion purpura, immune thrombocytopenia In order to prevent the spread of dengue fever, patients can take measures to limit the transmission of the disease by sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets, especially in fever duration.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.