This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Trinh Thi Phuong Nga - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalOvarian torsion is a common disease in women of reproductive age. If not detected in time, ovarian torsion can lead to necrosis, infection, toxicity and affect fertility later on. Therefore, timely diagnosis of ovarian torsion is very important in the treatment of the disease and prevention of complications.
1. An overview of ovarian torsion
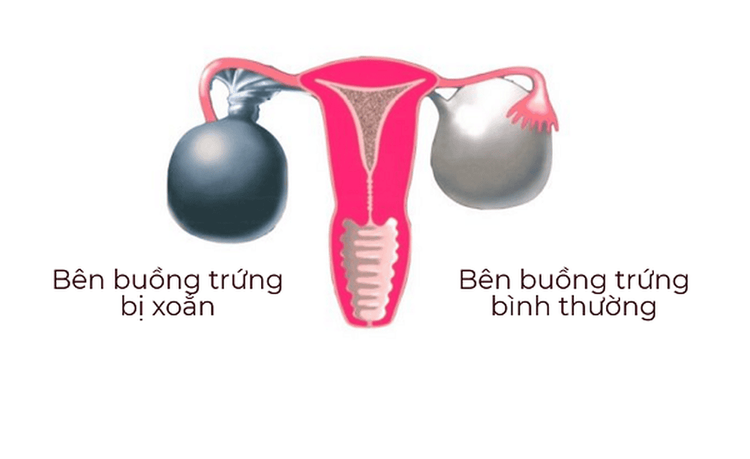
Ovarian torsion is a condition in which the ovary becomes twisted around the ligaments that hold it. This condition can cause a sudden cut off of the blood supply to the ovaries and fallopian tubes, leading to sharp pain in this area.
Ovarian torsion can occur at any age, most commonly in women of reproductive age 20-40 years old. However, the disease can also appear in postmenopausal women, children and even infants. More than 65% of cases of ovarian torsion occur in the fallopian tube, fallopian tube.
The risk factor for ovarian torsion is having an ovarian cyst (simple cyst, dermoid cyst, hemorrhagic cyst). The larger the tumor, the higher the risk of ovarian torsion. In addition, people who have had ovarian stimulation (create ovulation in assisted reproduction), people with a history of surgery in the pelvic region, pelvis, ... are also at high risk of ovarian torsion. In addition, changes in intra-abdominal pressure such as vomiting, coughing, vigorous exercise, etc. can also trigger ovarian torsion.
The disease has unclear clinical symptoms, many different manifestations, depending on the time, extent, location and frequency of torsion. Ovaries that cannot untwist on their own can lead to dangerous complications such as ovarian necrosis, pelvic abscess or peritonitis.
2. Diagnosis of ovarian torsion
In medicine, there are ways to diagnose ovarian torsion:
2.1. Based on clinical symptoms
Occurrence of sudden, severe pain in the pelvis, usually the right pelvis, intermittent or continuous pain. Pain often does not improve even with conventional pain relievers. In case the ovaries untwist on their own, the pain can be relieved. Vomiting and nausea: Occurs in about 47-70% of cases of ovarian torsion and is easily confused with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract such as esophagus, stomach, colon or urinary tract (urinary infection) , ureteral stones ) Symptoms due to compression: Difficulty urinating, constipation, edema of the lower extremities Fever: Usually occurs in the late stage, when there is an infection. Symptoms of ovarian torsion are vague, often varied, and depend on the location, duration, extent and frequency of torsion.
2.2. Based on laboratory tests
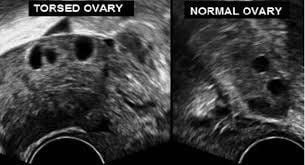
Ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian torsion is a widely used technique because of its fast implementation, low cost, and relative effectiveness. Your doctor may perform a transvaginal ultrasound or an abdominal ultrasound. Ultrasound image will show enlarged ovaries, anterior and upper uterine compression, edematous follicles, thickened mucosa, decreased or absent vascular signal of the ovary
Other techniques include imaging Computed tomography (CT scan) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are imaging modalities that may be used. In addition, the patient is also tested for a complete blood count, which measures the number of white blood cells in the body.
Through the above tests, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis of ovarian torsion. To determine exactly, the doctor needs to do surgery.
Patients with ovarian torsion will be indicated for surgery (preferably before 6 hours) to restore blood flow to the ovaries. In case of prolonged ovarian torsion, late detection, lack of blood flow to the ovary, ovarian necrosis, the doctor will have to surgically remove the ovary.
With ovarian torsion, the risk of rupture, cracking, infection, toxicity and acute blood loss is very high, which can affect fertility and even cause death. Therefore, when symptoms of ovarian torsion appear, it is necessary to see a doctor immediately for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment intervention.
To avoid unnecessary consequences as well as affect reproductive health in the future. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has deployed the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package, which helps women detect early infectious diseases for easy and inexpensive treatment. Besides, the examination package also screened for early detection of gynecological cancer (cervical cancer), a cancer that accounts for a high rate today.
The examination is always done by a team of qualified doctors with many years of experience who have treated many cases of patients with gynecological diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.