This is an automatically translated article.
Patients with severe dengue often experience significant thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, drainage, sepsis, multiple organ failure and, in the worst case, death.
1. Dengue fever
Dengue fever occurs all year round, the disease often breaks out in the rainy season in areas with poor sanitation, many ponds with stagnant water. To date, there is no specific treatment or vaccine for dengue fever.
Typical dengue fever has the following basic developments:
Fever phase: During the first 3 days, the patient has a high fever, headache, body aches... just like other common viral fevers. Critical phase: From the end of the 3rd to the 7th day, the patient's fever subsides, but more dangerous complications may appear such as: peripheral blood thrombocytopenia and increased vascular permeability causing fluid drainage, hemoconcentration, multiple organ failure, sepsis and possibly death. Recovery phase: From the 7th day onwards, these disorders will gradually resolve on their own. However, the patient will still feel tired for the next 1 to 2 weeks.
2. Death due to dengue fever

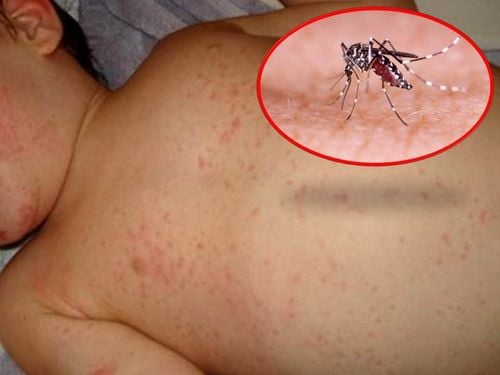
Bệnh nhân sốt xuất huyết có thể bị những đốm chảy máu, xuất huyết trên da
There is always a certain percentage of patients with severe dengue who are at risk of dying from dengue. In addition, cases with severe warning conditions that are not promptly treated, and late arrivals also put the disease at risk of worsening, leading to death.
Severe complications appear mainly in the critical period, that is, from the 3rd to 7th day of the disease. During this period, the patient's fever has subsided, so it is sometimes subjective that the disease has been cured.
Patients who die from severe dengue are often caused by peripheral blood thrombocytopenia, increased vascular permeability, sepsis, and multi-organ failure.
Peripheral thrombocytopenia: thrombocytopenia in dengue means the inability of the blood to clot and the inability to fight infections. Platelet counts usually drop significantly by day 4 of illness. If the patient with severe dengue has low platelet count, there will be bleeding spots, hemorrhages on the skin and other parts of the body, and plasma leakage. Severe dengue can seriously affect the lungs, liver, or heart. Blood pressure can drop to dangerous levels, causing shock, and in some cases death.
Increases vascular permeability causing fluid drainage, blood concentration. While hemorrhagic complications are often easy to recognize, the complication of double drainage is relatively difficult to self-recognize, even when the patient is in shock, he can detect it himself. Therefore, early recognition of the warning signs of this complication, along with periodic examination at the request of the doctor to detect early if the condition becomes worse for timely intervention.
Sepsis and multi-organ failure: is a dangerous complication causing death in many dengue patients. Multiple organ failure is dysfunction of at least 2 organ systems in patients with acute illness for whom homeostasis cannot be maintained without therapeutic intervention. The most common in hemorrhagic fever multi-organ failure is fulminant liver failure, renal failure, hypotension, heart failure... When a patient has complications of multi-organ failure, immediate emergency dialysis is required.
3. Warning signs of severe dengue fever
Trẻ sốt cao liên tục không kiểm soát được bằng các thuốc hạ sốt thông thường có thể là dấu hiệu cảnh báo của sốt xuất huyết nặng
Symptoms of dengue fever are diverse, with rapid progression from mild to severe. Common complications of the disease are shock, bleeding and multi-organ failure, the patient can die if not detected early and treated promptly.
Danger warning signs:
Subcutaneous bleeding: Red dots or spots on the skin, bleeding from the nose, gums, bleeding gums,... Gastrointestinal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, menstruation Heavy or bloody vaginal discharge, black stools. Drowsiness, confusion or convulsions. Blue-violet, hands and feet cold and damp. Shortness of breath. Urinary tract, enlarged liver, swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Persistent high fever that cannot be controlled with conventional antipyretics. Therefore, as soon as dengue fever occurs, the patient should be taken to the hospital to be examined and tested to assess the level of thrombocytopenia in the blood.
In case of being treated as an outpatient, the patient also needs periodic examinations and tests at the request of the doctor, closely monitored. If there are any signs of severe dengue fever above, it is necessary to take the patient to the nearest medical facility for emergency treatment, to avoid serious illness that is life-threatening.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.