This is an automatically translated article.
The most frightening manifestation of blocked fallopian tubes is when this is one of the possible causes of female infertility. Indeed, in most cases, signs of tubal occlusion are not apparent until after reproductive age. However, because there are a number of risk factors that can increase the chance of getting blocked fallopian tubes, it is important to recognize how blocked fallopian tubes can manifest early so that they can be promptly corrected before it causes later effects.
1. What is tubal occlusion?
The fallopian tubes or fallopian tubes are two muscular tubes on either side of the uterus lined with delicate, hairy mucosal structures. The lumen works in both directions; Help the egg travel from the ovary to the uterus and help the sperm travel up from the uterus to meet the egg for fertilization. Because of this, the fallopian tubes play an important role in conception because most of the eggs are fertilized.If any part of the fallopian tube is damaged, such as from surgery or an infection, tubal occlusion can result from being blocked by scar tissue.
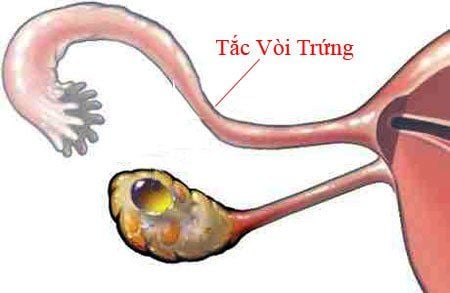
Tắc vòi trứng
2. How does tubal occlusion manifest?
Fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus and play an important role in fertility. Therefore, the signs of blocked fallopian tubes are not often present other than difficulty in conceiving. Doctors usually determine this when they have been trying to conceive for 1 year. If both fallopian tubes are affected, a woman may be infertile.
In other cases, the signs of blocked fallopian tubes can cause pain in the pelvis or abdomen. This pain may occur frequently, such as around the time of a menstrual period such as dysmenorrhea, or intermittent pain.
Sometimes the sign of a blocked fallopian tube is a fertilized egg getting stuck causing an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy may not always cause symptoms and is often detected during an ultrasound. Some women may experience symptoms that suggest an ectopic pregnancy, such as missed periods, abdominal pain, and unusual vaginal bleeding. Any woman who suspects an ectopic pregnancy should seek medical attention immediately.
3. What causes blocked fallopian tubes?
Fallopian tubes can become blocked for a variety of reasons, including:
Have a history of pelvic infections Previous fallopian tube interventions Have a sexually transmitted disease, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia Have endometriosis, a condition that causes the lining of the uterus to grow outside the uterus Have a history of abdominal surgery Collection of fluid in the end of the fallopian tubes All of these conditions can directly affect fallopian tubes, creating scar tissue that can block the fallopian tubes.
4. How to diagnose blocked fallopian tubes?
Signs of blocked fallopian tubes can be difficult to identify. Because the fallopian tubes have intrinsic peristalsis, it's not always easy to tell if this is a sign of a blocked or just closed fallopian tube.
In fact, there are three important tests to diagnose blocked fallopian tubes:
Hysterosalpingogram: The doctor injects a harmless dye into the uterus, which flows into the tubes. fallopian tubes and produce images that can be seen on x-ray films. If fluid doesn't drain into the fallopian tubes, they may have become blocked.
Adnexal ultrasound: This tool is very similar to a hysterosalpingogram but uses sound waves to build an image of the fallopian tubes.
Laparoscopy : The surgeon makes a small cut in the body and installs a very small camera to take pictures of the fallopian tubes from the inside. Among the techniques, laparoscopy is the most accurate means of finding signs of tubal obstruction. However, doctors generally don't recommend this test as an early diagnostic tool because of how invasive it is and the inability to treat the problem.
In addition, the diagnosis of tubal occlusion should be based on history. For example, a woman who may have had a ruptured appendix in the past and now has difficulty conceiving could be a sign of a blocked fallopian tube.

Nội soi ổ bụng giúp chẩn đoán tắc vòi trứng
5. How to treat blocked fallopian tubes?
Only surgical intervention can correct blocked fallopian tubes. However, this depends on the extent of the scar and the location of the blockage.
Surgical procedure that aims to open the fallopian tube using one of the following methods:
Removal of scar tissue Creating a new hole on the outside of the fallopian tube Opening the fallopian tube from the inside Either method, surgery tubal ligation carries the same potential complications as any surgery, including risks such as:
Infection Creating more scar tissue Injury to nearby organs Bleeding into the socket belly A scary risk after tubal occlusion surgery is an ectopic pregnancy, which means a fertilized egg becomes trapped outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube and at the site of the blockage. If the embryo implants here and grows, it will cause tubal rupture and more serious complications. Therefore, after surgery to block the fallopian tubes and find out that she is pregnant, women should go to the doctor right away to check for an ectopic pregnancy.
In short, when feeling late to get pregnant, a woman needs to think about the possibility that this is one of the signs of blocked fallopian tubes. The fertility outlook remains positive if only one fallopian tube is affected or endothelial scarring is minimal. Therefore, if signs of tubal occlusion are suspected, women should seek medical attention to consider surgical treatment of blocked fallopian tubes or to implement assisted reproductive measures.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.