This is an automatically translated article.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a technique applied in the treatment of infertility, with a high success rate. An IVF cycle includes preparation, ovulation, follicular monitoring, egg retrieval, insemination, embryo transfer, hormone supplementation, pregnancy testing, and follow-up.Step 1. Preparation
First, at the infertility clinic, the couple will prepare and supplement the medical record, including examining and doing the following tests:
Gynecological examination, PAP test, ultrasound to check the area pot; Basic blood tests: GS-Rh, HIV, HbsAg, BW; Semen map ; Endocrine testing. After the test, if all the results are normal, the patient will be asked to submit a marriage certificate, copy of identity card with the original for comparison. If the documents are correct, the couple will make an appointment to start the treatment.
Start the IVF cycle by taking birth control pills one month before ovarian stimulation. This will ensure that the pill is used at the right time if the patient is having irregular periods.
Recommended video:
How does in vitro fertilization work?
Step 2. Ovarian stimulation
Ovarian stimulation is the 2nd step in the IVF cycle, the implementation depends on the long or short regimen. With a long regimen, doctors start injecting GnRH from day 21 of the previous cycle. With a short regimen, ovarian stimulation is performed during menstruation.
Currently, there are many regimens applied in ovarian stimulation, each regimen is based on a different physiological mechanism, although using the same drug, there are groups of patients who will respond better to this regimen than with other regimens. However, when changing a patient's regimen, it does not mean that the treatment response will change, from poor to good.
Step 3. Monitor the growth of the follicle
Follicle monitoring will be assessed by performing transvaginal ultrasound and hormone blood tests, several times during the IVF cycle. Based on this result, the doctor will adjust the dose of the drug in accordance with the development of the follicle.Step 4. Complete oocyte maturation and hCG . injection
HCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin) is a drug belonging to the endocrine group, which has the effect of stimulating the complete maturation of the ovum. Determining the appropriate date of hCG injection is very important, because on that basis will determine the time of egg retrieval.
HCG có tác dụng kích thích noãn trưởng thành hoàn toàn
Step 5. Vaginal egg retrieval
The woman's eggs will be aspirated from the ovaries with a needle, under the guidance of ultrasound and anesthesia, helping the patient to feel less pain and more comfortable. Tissue damage and infection are very rare.
Egg retrieval is performed approximately 34 - 36 hours after the hCG injection. Anesthesia is given intravenously (to help with pain and anesthesia) to reduce discomfort that occurs during the procedure. Most patients are asleep during egg retrieval. An ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to view the ovaries and the follicles inside the ovaries. A long needle visible on ultrasound is used to aspirate each cyst. The aspirated fluid includes follicular fluid, follicular cells and eggs. The doctor will perform aspiration of the eggs and follicular fluid into a test tube and the embryologist will identify the eggs in the follicular fluid under a microscope.
After a few days of aspiration, a few cases may have vaginal bleeding and abdominal distension. Usually, patients will fully recover in 1-2 days. If after that, the patient shows signs of abdominal distension, abdominal distension, vomiting and nausea, little urine... it is necessary to notify the treating doctor.
The number of eggs aspirated is related to the number of ovaries, the location of the ovaries that can be aspirated, and the number of follicles that develop with ovarian stimulation. On average, each patient will aspirate from 8 to 15 eggs.
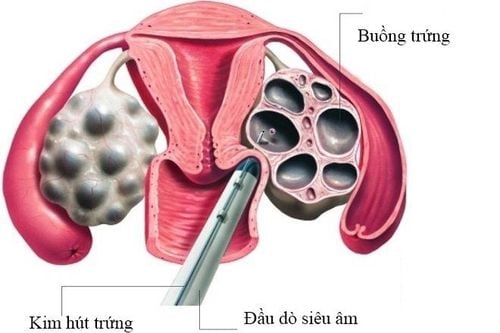
Hình ảnh chọc hút trứng qua đường âm đạo
Step 6. Fertilize eggs and raise embryos
Sperm and egg will be put together to fertilize under a special condition (suitable culture conditions, temperature, humidity and light) to support fertilization. The culture medium is set up to allow fertilization to take place in the best of normal and early embryo development. By growing in laboratory conditions, one can tell which embryos are developing well, which are poor or not developing.
Sperm is obtained by having the man masturbate in the morning on the day of egg retrieval , then the sperm will be separated from the semen . If the patient has difficulty in obtaining sperm, the option of pre-coagulation can be used as a backup sample and sometimes this is the main source of sperm.
After the eggs are successfully aspirated, they will be transferred to the laboratory to be stored in conditions that can maintain growth. Once fertilized, the embryo will be developed in a dish or in a small test tube with the same culture as the fallopian tube and uterus. These embryo discs will be stored in an incubator to ensure the temperature and concentration of gases such as O2, CO2,...
A few hours after egg retrieval, sperm will be introduced into the environment. fertilizing an egg (IVF), or inserting a sperm to fertilize a mature egg directly, is called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Next, eggs continue to be cultured in an incubator. The technician will periodically survey these culture dishes to assess embryo development.
Days after IVF or ICSI , embryos will be evaluated for developmental status. On the first day, a normal developing embryo is characterized by a single cell with two nuclei, this is called a zygote. Two days later, the embryo begins to divide into four cells. On the third day, the embryo contains 8 cells. If culture is stable until day five, the embryo will grow exponentially to the blastocyst stage, which contains a mass of 80 cells or more, an internal fluid cavity.
Because some eggs and embryos develop abnormally, not all eggs will fertilize and all embryos will develop normally. The ability of the embryo to form a fetus is related to the normal development of the embryo. However, this is uncertain as not all observed embryos will develop with normal genomes and not all slower-growing embryos will have abnormal genomes. On the other hand, the morphology observed under the microscope is the most important and common guide for selecting good embryos for transfer into the uterus, a process called embryo transfer.
Although all steps work well, there may still be some situations in the laboratory that lead to a non-pregnancy.
Tinh trùng sẽ được tách khỏi tinh dịch trong phòng thí nghiệm dưới một điều kiện đặc biệt
Step 7. Embryo transfer
Within 2 - 3 days after egg retrieval, well-developed embryos will be selected for transfer. The number of embryos transferred affects the pregnancy rate and the rate of multiple pregnancies. However, maternal age and new embryo morphology are the two most influential factors on pregnancy outcome. The remaining non-transferred embryos, if qualified, will be frozen and can be transferred to the next IVF cycle.
Embryos are usually transferred on the 3rd or 5th day after egg retrieval. The doctor inserts a flexible tube through the cervix into the uterus and places the embryo inside the uterus. During this procedure, anesthesia is usually not needed and the patient is likely to be discharged from the hospital within a few hours of bed rest.
Step 8. Supplementing with Hormones
The ability of the embryo to successfully implant in the uterus depends on adequate hormonal support. Progesterone is routinely used for this reason.
Progesterone supplementation can be taken orally, intravenously or vaginally and in some cases requires a combination of ways. Start adding medication on the day of the aspiration. Normally, cells in the follicle will produce progesterone after egg retrieval. However, during aspiration, these cells may be removed along with the egg. Therefore, supplementing with progesterone is essential, helping the endometrium to prepare well to receive the implanted embryo.
The drug is taken daily until a pregnancy test is performed. If the pregnancy test is done, the woman will have to continue taking progesterone for a few more weeks.
Recommended video:
How long does it take for the embryos to implant after embryo transfer?
Step 9. Pregnancy test
It is necessary to take a pregnancy test whether the vaginal bleeding is heavy or light. This test helps to confirm pregnancy and is performed 10-14 days after embryo transfer. The test can be repeated after 2 days for confirmation if the result is positive. If the test is negative, the doctor will stop the progesterone pill and guide you on next steps.Step 10. Early pregnancy monitoring
If pregnancy test results, close monitoring of pregnancy is necessary to determine the risk of complications such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy or multiple pregnancy for appropriate and timely treatment. . Taking hormonal drugs containing progesterone supports the corpus luteum of pregnancy.
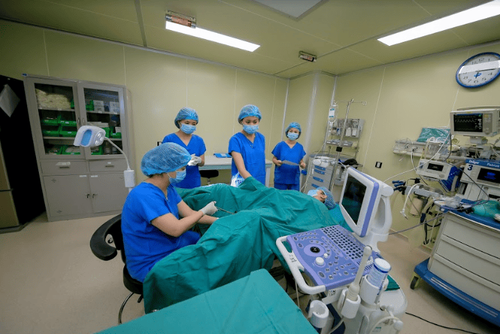
Công đoạn chuyển phôi thai được thực hiện tại Trung tâm Hỗ trợ sinh sản - Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec
When you are not pregnant but have a frozen embryo, your doctor can continue to use the stored embryo to transfer to the woman's uterus in the next IVF cycles without having to repeat the steps of egg stimulation or poaching eggs.
During the IVF cycle, husband and wife should prepare psychologically, physically, arrange work and prepare costs... to ensure that the fertilization process is complete and not influenced by subjective factors.
At Vinmec International Hospital system, currently applying in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique in the treatment of infertility. Vinmec brings together a team of fertility specialists who are leading experts in the field of obstetrics and gynecology locally and internationally, trained at leading centers in the world such as in the US, Singapore, and Japan. , Australia,... With a high level of expertise and extensive experience, the team of experts at Vinmec is capable of comprehensively implementing the most advanced assisted reproductive techniques in the world.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.