This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Senior Doctor, Dr. Vu Van Tam - Infectious Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalTrichinosis can occur in people of any age. In particular, people who often eat raw or undercooked meat will have a high risk of developing trichiasis. So where do helminths parasitize and what diseases do they cause?
1. What diseases do helminths cause?
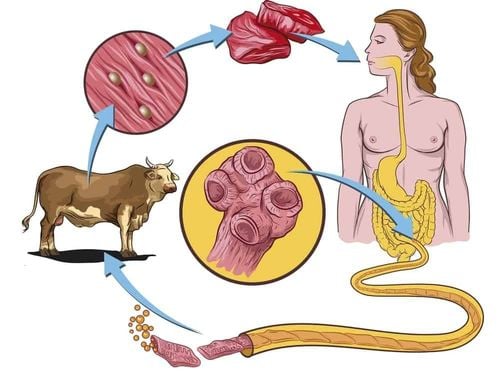
Trichinosis is an infection with a roundworm (of the genus Trichinella), which lives in the intestines of pigs and other animals. When eating meat contaminated with helminth larvae and undercooked, the larvae move into the intestines and continue to develop into adult worms within a few weeks.
Then the helminths spawn new larvae. These larvae crept throughout the tissues of the patient's body, even appearing in the muscles. Common complications of trichiasis include respiratory failure, pneumonia, congestive heart failure, and kidney, heart, and brain damage. This is a parasitic disease that is quite common in rural areas. However, when we know where helminths are parasitic, we can proactively prevent them easily.
2. Causes of roundworm disease
Roundworms cannot be transmitted directly from person to person, but through food. The disease can occur anywhere in the world but is more common in developing countries. Where parasitic worms live depends on the habits and cultures of eating and drinking fresh in each region. In some places, bear meat is the main source of infection. However, currently in Vietnam, infected pork still accounts for the majority.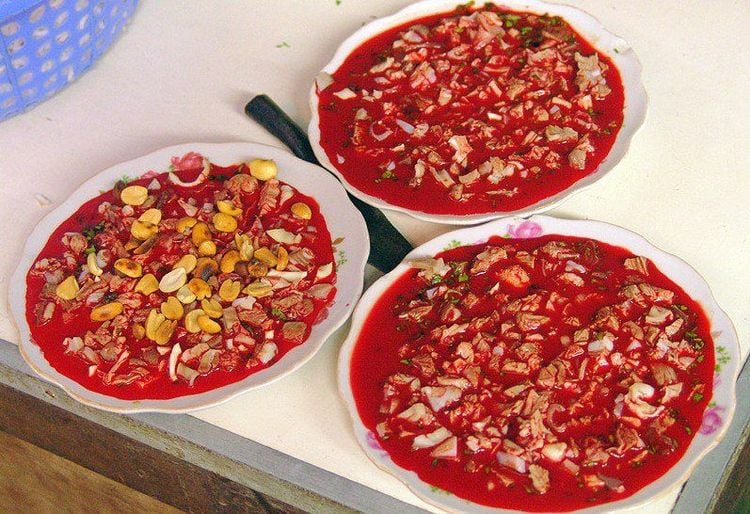
Nhiễm giun xoắn qua tiết canh heo
In places where the slaughter of pigs does not have the inspection and quarantine of the Department of Animal Health, the possibility of disease will be higher. Some areas have the custom of eating raw, eating rare, drinking pig blood soup and undercooked pork products, which will have the risk of parasitic diseases, one of which is roundworm infection.
3. Symptoms of roundworm disease
3.1. Clinical signs
Many people wonder what disease caused by helminths and how to recognize them? Clinical manifestations of helminthiasis have 4 basic symptoms as follows:
Eyelid edema: this is the earliest and most characteristic sign of helminthiasis, sometimes the whole face, spreading to the neck and shoulders and two hands. Local eyelid edema is sometimes accompanied by bleeding under the cornea, retina. Pain and muscle spasticity: occurs when breathing deeply, when coughing, chewing, swallowing, defecating, pain in the face and neck area, pain when moving, even when eating, talking. Myalgia limits the patient's mobility. Mild fever, gradually increasing after 2-3 days: infection with helminth parasites can cause body temperature to rise to 39-40 oC. Cardiovascular and neurological complications: in severe cases, patients may die from heart failure, occurring in the first or second week of illness. Other complications may appear in the 3rd or 4th week, including: myositis, pneumonia, encephalitis, also potentially fatal, depending on the extent and duration of infection with the larvae of roundworm larvae. . Mortality rates range from 6-30%. Other symptoms of trichiasis can include: diarrhea, thirst, profuse sweating, chills, fatigue, and exhaustion.
3.2. Symptoms help identify
Patients infected with helminths when performing complement agglutination, immunofluorescence or ELISA test results are positive, blood counts show abnormally elevated eosinophils.
Eosinophilia occurs from the first days of helminth infection, peaks in the 3rd week after infection and lasts for 2-4 months even after recovering from the disease. In mild form, the amount of eosinophils increases about 15 - 30%; Severe body can be up to 50-60%.
In the early stages after the disease, if you notice, you can see adult helminths in the stool. When reaching the full-blown stage, biopsies of the motor muscles will find larval cysts.
When infected with helminth or detecting symptoms of helminth infection, patients need to be examined accurately and treated promptly at medical facilities. When we know where helminths are parasitic, we can be more proactive in detecting and diagnosing the disease.
4. Where do helminths parasitize?
The problem of parasitic helminths depends on different geographical areas. However, in developing countries like Vietnam, the reservoirs for roundworms are mainly pigs, in addition to other species such as rats, dogs, cats and wild animals such as foxes, wild boars,...
Process The infection of helminths is as follows: first, people eat undercooked meat contaminated with cocoons containing roundworm larvae. Once in the stomach, the larvae will escape the cocoon and move to the small intestine within 1-2 hours. In the small intestine, helminth larvae will continue to develop into adults after 24 hours and then invade and parasitize the mucosa of the small intestine. After about 4-5 days, female worms begin to lay new larvae.
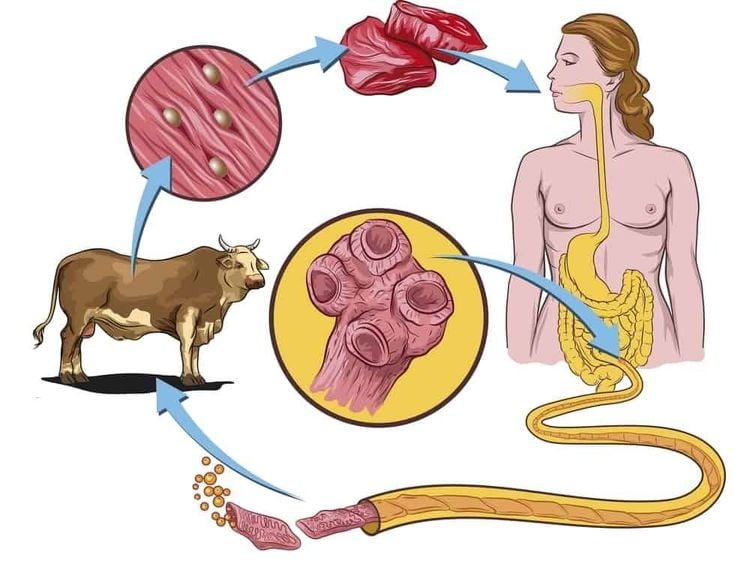
Quá trình lây nhiễm và ký sinh của giun xoắn.
On average, a female helminth can lay up to 1000 larvae in about 4-6 weeks. Larvae penetrate into the circulatory system, reach the heart, parasitize and create cocoons in skeletal muscle organizations, diaphragm, ... after about 10-15 days of development, these larvae-containing cocoons begin to infect. After about half a year, this cocoon will be gradually calcified. On the other hand, parasitic cysts in muscle tissue can survive for several years, even up to 20 - 30 years and still have the ability to infect.
As for the incubation period: Typical symptoms of roundworm usually appear within 5 - 15 days after ingesting infected meat. The incubation period is long or short, depending on the amount of helminth larvae that the patient eats is more or less, sometimes it takes up to 45 days to notice the signs of helminth infection.
When existing in the environment outside the body, helminth larvae in the cocoon have very high resistance. In animal meat, the life span can be up to 2 - 5 months. However, when coming out of the cocoon, the larvae will die after only a few seconds at a temperature of about 45 - 70 oC. At a cold temperature of -20 oC, larvae die after about 20 days.
5. How to prevent helminth disease
Once we know where the parasitic worms are and how this parasite is transmitted, we can easily proactively prevent the disease:
Propagandize and educate people to raise awareness in the culture of eating food. Drink: Clean food carefully, eat cooked, drink boiled, especially in residential areas where people have the habit of eating raw, rare, and using blood soup. When eating meat contaminated with helminths is suspected: diagnostic testing should be performed immediately. Environmental treatment and implementation of food safety and hygiene: do not use dirty pork of unknown origin; confiscate, isolate and destroy meat or meat products that have been contaminated with helminth parasites. Local epidemic prevention: strengthen inspection and tighten handling of animal slaughterhouses, especially in suburban, remote and remote areas. Epidemiological situation report: urgent notification to higher levels to arrange epidemic prevention team to go to the place where there are cases of disease to investigate epidemiology, organize treatment, communicate and educate local people about the role of disease prevention and control. against helminthiasis in the community. Prevention is always the most effective measure to prevent the consequences that occur due to parasitic infections. Therefore, the whole people should equip themselves with sufficient knowledge about where helminths are parasitic and what diseases do helminths cause to best protect their health and those around them.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.