This is an automatically translated article.
Routine hearing tests offered to infants and young children can help detect any problems early in their development. Although serious hearing problems in childhood are rare, early testing can ensure early detection and treatment of hearing conditions in children.1. The Importance of Hearing Tests for Children
Hearing tests can be performed soon after birth to help diagnose significant hearing loss in children as well as detect any hearing problems that are getting worse.Routine baby hearing screening can help detect an undiagnosed hearing problem for months or even years in a child. Therefore, you should have your child tested for hearing as soon as possible because late detection conditions can affect a child's language, speech, social and academic skills development.
2. When should a child have a hearing test?
Your baby's hearing can be tested against the following milestones:Within the first 2 weeks after birth: This is called a newborn hearing test, usually done before you leave the hospital after birth child. Children 9 months - 2.5 years: During the evaluation of the health and development of children in this age group, you should take your child for a hearing test to check for any hearing problems that may be interfering with your child's health. to child development. Children 4 - 5 years old: Most children will have their hearing tested when they start school. These tests can be done at a school or at an ENT clinic. In addition, parents can also test their baby's hearing at any time you feel concerned. It's best to talk to your GP if you're concerned about your child's hearing.

Kiểm tra thính giác trẻ sơ sinh được thực hiện trong vòng 2 tuần đầu sau khi sinh
3. Hearing tests for children
Here are some common hearing tests for babies, children, and young children, including:3.1.Vision-reinforced audiometry (VRA) VRA is commonly used to test hearing for children. Children from 6 months to 2 and a half years old. During visual reinforcement audiometry, children are taught to associate sounds with visual rewards, such as bright computer screens or toys.
When children are able to associate sounds with visual rewards, the volume and pitch of the sounds will change to identify the quietest sounds they can hear.
3.2.Play hearing test Young children from 1.5 to 5 years old can have their hearing tested while playing. During the test, sounds will be played through headphones or speakers, then children will be asked to do a simple task when they hear the sounds, such as placing a ball in a crate to complete a puzzle. Riddle.
Similar to the VRA method, the volume and pitch of the emitted sound will be varied so that the quietest sound a child can hear can be determined.
3.3. Pure acoustic audiometry Older children can have pure acoustic audiometry to test hearing before children start school. It is similar to a hearing test for adults.
During pure acoustic audiometry, the instrument produces sounds at different volumes and frequencies. The sound is played through the headset and the doctor will ask the child to respond by pressing a button when they hear it. By varying the level of sound, the doctor can find the quietest sounds a baby can hear.
3.4.Skeletal sound conduction test Besides using headphones or speakers, most of the above tests can also be done using a small vibrating device placed behind the ear. This device transmits sound directly to the ear through the bones in the head, helping to determine which part of the ear is not working properly if the child is having hearing problems.
3.5.Measurement of the eardrum The tympanic membrane is a hearing test that assesses the flexibility of the eardrum.
For good hearing, a child's eardrum needs to be flexible to allow sound to pass through it. If the eardrum is too stiff due to fluid behind it (glue ear), it can cause sound to bounce back instead of traveling through the eardrum.
During the examination of the eardrum, the doctor will place a soft rubber tube at the entrance to the child's ear. Air is gently blown down the tube and sound is played through a small speaker inside the tube, then the sound meter is bounced back from the ear.
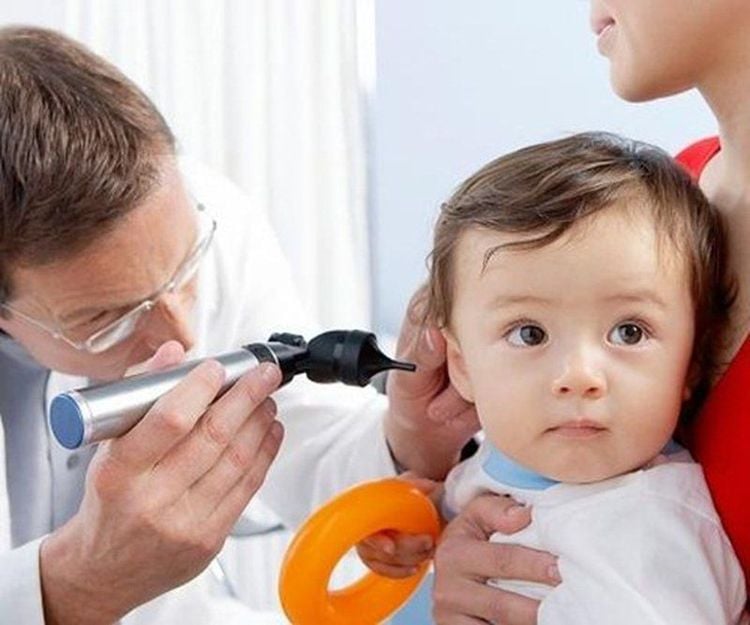
Kiểm tra thính giác giúp phát hiện sớm bất kỳ vấn đề nào về khả năng nghe của trẻ
4.What causes hearing problems in children
In fact, there are many causes of hearing problems in children, including temporary hearing loss due to colds. In addition, a number of other causes of hearing loss in children can also be detected during routine hearing tests, including:Glue: A large accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, often occurs commonly in young children. Infections: Developing in the womb or at birth, such as cytomegalovirus and rubella, causing progressive hearing loss in children Genetic conditions: Such as otosclerosis, which causes The auditory nerve is not working as efficiently as it should. Damage to the cochlea or auditory nerve: This can happen from a serious head injury, head surgery, or exposure to loud noises. Asphyxia at birth: The baby is deprived of oxygen at birth. Certain medical conditions: Such as encephalitis or meningitis.
5. Spot the signs of hearing problems in your child
Although children can have their hearing checked periodically as they get older, parents should still be on the lookout for signs of a hearing abnormality in their child, including:Poor concentration or lack of attention Speaks loudly and listens to the TV at high volume Does not respond when a child's name is called by others Mispronounced words Difficulty identifying and recognizing where sounds are coming You should talk to your doctor doctor if you are concerned about your child's hearing ability. Baby hearing tests can be done at any age.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website (vinmec.com) for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: medlineplus.gov, nhs.uk