This is an automatically translated article.
Gonorrhea in the throat and mouth can occur in anyone who has ever had sex. If not detected and treated, gonorrhea will cause very serious health complications. However, if treated, this is a disease that can be cured with the right drugs.
1. What is gonorrhea in the throat?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that affects both men and women. The disease can cause infections of the external genitalia, rectum, and especially the throat and mouth. It is a very common infection in adolescents between the ages of 15-24.
There are many cases of gonorrhea infection without knowing it because the disease often shows few symptoms, especially in women. This is very dangerous, not only because it makes it difficult for patients to detect and treat in time, but also increases the possibility of infecting their sexual partners due to not taking precautions when having sex.
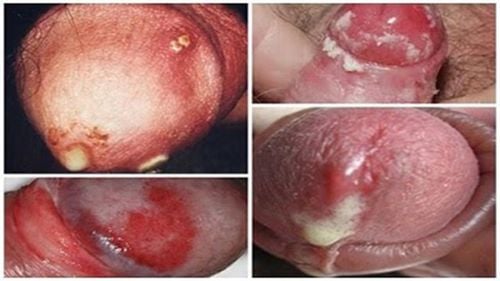
Bệnh lậu không chỉ xuất hiện ở bộ phận sinh dục mà còn ở miệng và họng
2. How is gonorrhea in the throat transmitted?
You can get gonorrhea by having vaginal, anal or oral sex with someone who has gonorrhea. Many people think that having oral sex will not be able to get gonorrhea, but if their partner has gonorrhea in the throat or mouth, the risk of infection is very high.
So the best way to prevent gonorrhea in the throat, mouth as well as sexually transmitted diseases in general is not to have vaginal, post-marital sex and especially oral sex.
In the event of sexual intercourse, the following guidelines should be followed to reduce the risk of catching gonorrhea:
Maintain a long-term monogamous relationship, making sure your “partner” is not gonorrhea infection (negative STD test result). Use condoms correctly during sexual intercourse. Note that washing your genitals, urinating, or douching after sex does NOT prevent STDs.
3. Who is at risk for throat gonorrhea?
The risk of catching gonorrhea is in anyone who has unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex.
If you are sexually active, talk to your doctor about whether it's necessary to get tested for gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted diseases.
In case you are a bisexual, gay man who has a relationship with someone of the same sex - a group with a high risk of gonorrhea infection - you should get tested for gonorrhea once a year. Sexually active women under 25, older women with a new/multiple sex partner/partner with an STD should be tested for gonorrhea annually.

Cả nam và nữ đều là các đối tượng dễ mắc bệnh lậu
4. Symptoms of gonorrhea in the throat
Signs of gonorrhea in each person will manifest differently depending on the infected organ and their sex. Common sites include the rectum, urinary tract, uterus (for women), penis (for men), ... and especially gonorrhea in the throat found in both sexes.
4.1 In women
Most cases of gonorrhea in women cause no symptoms. Even when they do have symptoms, they can easily be mistaken for a vaginal or bladder infection. Women are also at risk for serious infection, even if they don't have symptoms of gonorrhea.
Lesser cases have symptoms, the disease will manifest in parts such as eyes, mouth, throat, anus, urinary tract or uterus.
If gonorrhea infection is in the uterus or urinary tract, women will have the following symptoms:
Vaginal bleeding even if it is not during menstruation. Increased discharge from the vagina. Pain or burning sensation when urinating. If gonorrhea infection is in the rectum, women will experience itching, pain, bleeding, discharge from the rectum or pain when passing stools.
If you have a gonorrhea infection in your throat or mouth, you will notice a sore throat.
4.2 In men
Common sites of gonorrhea infection in men are the eyes, mouth, throat, penis, anus.
In the penis, gonorrhea manifests itself through the following symptoms:
Burning sensation when urinating. White, yellow or green discharge from the penis. Testicles are painful and swollen. In the rectum, men infected with gonorrhea often experience itching, pain, bleeding, discharge from the rectum or pain when passing stools.
In the throat and mouth, like women, men infected with gonorrhea also experience pain in the throat.
5. How is gonorrhea diagnosed?
In most cases, your doctor will determine if you have gonorrhea by testing your urine. In the event that you have anal and/or oral sex, your doctor will use a swab to collect a sample from your rectum and/or throat for testing. In addition, a sample can also be collected from the urethra (in men) or the cervix (in women) for testing in certain cases.
6. Can gonorrhea in the throat be cured?
Gonorrhea in throat, mouth and other sites can be cured with proper treatment. It is important for the patient to remember to take all the medicine prescribed by the doctor. Do not share medicine to treat gonorrhea with anyone. And keep in mind that, although medication works to stop the infection, it cannot reverse the permanent damage the disease causes to the body.
Currently, the treatment of gonorrhea is facing many difficulties, due to the increasing resistance to anti-gonorrhea drugs. If the symptoms of the disease persist for many days after being treated, the patient needs to return to the place of treatment for a checkup.
After taking all medications, the patient should wait another 7 days before having sex again. And keep in mind that even if you're cured, there's still a chance you could get re-infected with gonorrhea if you've had unprotected sex with someone who already has gonorrhea or a new sexual partner.
7. Complications of gonorrhea
If left untreated, gonorrhea whether in the throat or elsewhere can cause serious health problems in both men and women. Gonorrhea remains in the body. People with HIV are more likely to get HIV if they have unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner. Gonorrhea can also spread to the blood and joints, which is a very serious and life-threatening condition.
Women with untreated gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), with the following complications:
Formation of scar tissue that blocks the fallopian tubes. Ectopic pregnancy . Female infertility. Persistent abdominal or pelvic pain. Men infected with gonorrhea but not treated can have testicular pain, in rare cases will lead to male infertility, difficulty conceiving.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cdc.gov